SNMP Test
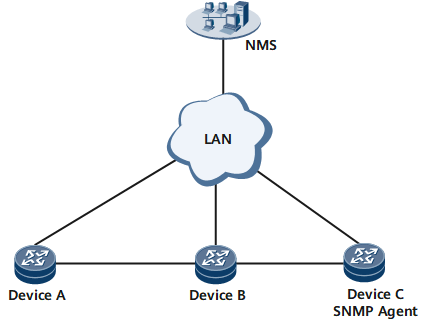
The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is used for network management on TCP/IP networks. SNMP uses a central computer that functions as a network management station (NMS). This central computer runs network management software to manage network elements (NEs). On the network shown in Figure 1, the NMS manages Devices A, B, and C.
NQA SNMP tests use UDP packets to measure the communication speed and SNMP connectivity between a host and an SNMP agent. If a faulty NE is detected when the network management software is deployed on the NMS, an NQA SNMP test instance can be configured on another NE to detect an NE failure or a communication failure between the NMS and the NE. Figure 1 demonstrates the SNMP test process.
- Device A sends an SNMP request packet to the SNMP agent Device C to request the system time. Because Device A does not know which SNMP version Device C runs, it sends an SNMPv1 request packet, SNMPv2c request packet, and SNMPv3 request packet to Device C.
- Once the SNMP request packets are received, Device C queries the system time, constructs SNMP response packets, and sends the SNMP response packets to Device A. If SNMPv1, SNMPv2c, and SNMPv3 are all enabled on Device C, Device C constructs all three SNMP response packet versions.
- After receiving the first SNMP response packet, Device A calculates the duration between the time Device A sent the SNMP request packet and the time Device A received the SNMP response packet. The time taken reflects the SNMP connectivity and SNMP performance on the network.