TFTP
Message Types
A TFTP packet header contains
a two-byte operation code, with values defined as follows:
- Read request (RRQ): indicates a read request.
- Write request (WRQ): indicates a write request.
- Data (DATA): indicates data packets.
- Acknowledgment (ACK): indicates a positive reply packet.
- Error (ERROR): indicates error packets.
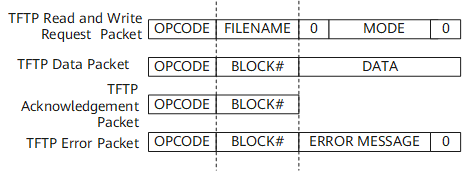
Figure 1 shows a TFTP packet header.
A TFTP packet consists of the following fields:
- OPCODE: operation code or command line
Operation Code
Command
Description
1
Read Request
Request to read a file
2
Write Request
Request to write to a file
3
File Data
Transfer of file data
4
Data Acknowledge
Acknowledgement of file data
5
Error
Error message
- FILENAME: name of the file to be transferred
- MODE: data mode, which is transmitted as a protocol
- BLOCK #: Block numbers in a data packet begin with 1 and increase by one for each new block of data.
- DATA: This field ranges from 0 to 512 bytes.
ERROR MESSAGE: The server cannot read or write a request. The code "0" indicates a stop flag.
An error message consists of the following items:- Error code: 2 bytes. The following table describes the error codes
supported by TFTP.
Error Code
Description
0
Not defined
1
File not found
2
Access violation
3
Disk full
4
Illegal TFTP operation
5
Unknown port
6
File already exists
7
No such user exists
- Error information: indicated by a two-byte ASCII code.
- Error code: 2 bytes. The following table describes the error codes
supported by TFTP.
Transfer Modes
TFTP supports
the following transfer modes:
- Binary mode: used for program file transfers
- ASCII mode: used for text file transfers
 HUAWEI NetEngine 8000 F Series can function only as a TFTP client and transmit files in binary mode.
HUAWEI NetEngine 8000 F Series can function only as a TFTP client and transmit files in binary mode.