ICMPv6
Internet Control Message Protocol for Internet Protocol version 6 (ICMPv6) is an integral part of IPv6 and used on IPv6 networks. It provides similar functions to those of ICMPv4 on IPv4 networks.
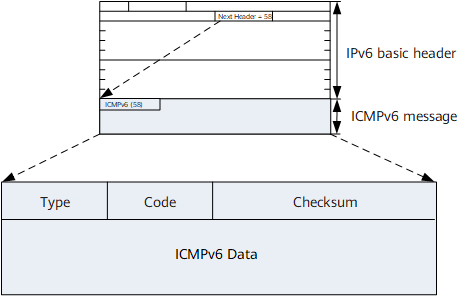
ICMPv6 Message Format
The ICMPv6 type number (Next Header field value in an IPv6 packet) is 58. Figure 1 shows the ICMPv6 message format.
The following describes each of the fields in an ICMPv6 message:
Type: indicates a message type. Values 0 to 127 indicate the error message type, and values 128 to 255 indicate the informational message type.
Code: indicates a specific message type.
Checksum: indicates the ICMPv6 message checksum.
ICMPv6 Message Classification
ICMP messages are classified as error or informational messages. ICMP reports errors and information relating to IP packet forwarding to the source node to facilitate fault diagnosis and information management. In ICMPv4, these messages include Destination Unreachable, Packet Too Big, Time Exceeded, Echo Request, and Echo Reply. ICMPv6 extends ICMPv4 and provides additional mechanisms, such as neighbor discovery (ND), stateless address configuration (including duplicate address detection), path maximum transmission unit (PMTU) discovery, and multicast listener discovery (MLD).
Category |
Type |
Name |
Code |
Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
ICMPv6 error messages |
1 |
Destination Unreachable |
0: no route to destination |
When an IPv6 node forwards IPv6 packets and finds that the destination address of the packets is unreachable, it sends an ICMPv6 Destination Unreachable message to the source node of the packets. The code carried in the message identifies the cause of the error. |
1: communication with destination administratively prohibited |
||||
2: not assigned |
||||
3: address unreachable |
||||
4: port unreachable |
||||
2 |
Packet Too Big |
0 |
When an IPv6 node forwards IPv6 packets and finds that the size of the packets exceeds the outbound interface's path MTU (PMTU), it sends an ICMPv6 Packet Too Big message to the source node of the packets. The message carries the outbound interface's PMTU. PMTU discovery is implemented based on Packet Too Big messages. |
|
3 |
Time Exceeded |
0: hop limit exceeded in transit |
During IPv6 packet transmission, when a router receives a packet with the hop limit 0 or reduces the hop limit to 0, it sends an ICMPv6 Time Exceeded message to the source node of the packets. During the processing of a packet to be fragmented and reassembled, an ICMPv6 Time Exceeded message is also generated when the reassembly time is longer than the specified period. |
|
1: fragment reassembly time exceeded |
||||
4 |
Parameter Problem |
0: erroneous header field encountered |
When a destination node receives an IPv6 packet, it checks the validity of the packet. If the node detects any of the following errors, it sends an ICMPv6 Parameter Problem message to the source node of the packet:
|
|
1: unrecognized Next Header type encountered |
||||
2: unrecognized IPv6 option encountered |
||||
ICMPv6 informational messages |
128 |
Echo Request |
0 |
During interworking detection between two nodes, after a node receives an Echo Request message, it sends an Echo Reply message to the source node. Packets are subsequently transmitted between the two nodes. |
129 |
Echo Reply |
0 |
||
130 |
Multicast Listener Query |
0 |
These messages are used by user hosts and directly connected multicast devices to establish and maintain multicast group memberships. |
|
131 |
Multicast Listener Report |
0 |
||
132 |
Multicast Listener Done |
0 |
||
133 |
Router Solicitation |
0 |
Compared with ARP in IPv4, ND provides functions such as route discovery and redirection in addition to address resolution.
|
|
134 |
Router Advertisement |
0 |
||
135 |
Neighbor Solicitation |
0 |
||
136 |
Neighbor Advertisement |
0 |
||
137 |
Redirect |
0 |
||
143 |
Multicast Listener Report v2 |
0 |
MLD is responsible for IPv6 multicast member management. MLDv2 can be directly applied to the SSM model to maintain and manage group memberships and exchange information with upper-layer multicast routing protocols. |
|
... |
... |
... |
... |