Overview of Layer 2 Multicast
Definition
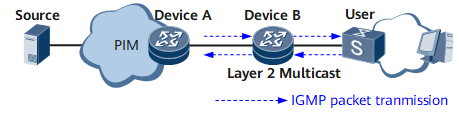
Layer 2 multicast implements on-demand multicast data transmission on the data link layer. Figure 1 shows a typical Layer 2 multicast application where Device B functions as a Layer 2 device. After Layer 2 multicast is deployed on Device B, it listens to Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) packets exchanged between Device A (a Layer 3 device) and hosts and creates a Layer 2 multicast forwarding table. Then, Device B forwards multicast data only to users who have explicitly requested the data, instead of broadcasting the data.
Purpose
Layer 2 multicast is designed to reduce network bandwidth consumption. For example, without Layer 2 multicast, Device B cannot know which interfaces are connected to multicast receivers. Therefore, after receiving a multicast packet from Device A, Device B broadcasts the packet in the packet's broadcast domain. As a result, all hosts in the broadcast domain (including those who do not request the packet) will receive the packet, which wastes network bandwidth and compromises network security.
With Layer 2 multicast, DeviceB can create a Layer 2 multicast forwarding table and record the mapping between multicast group addresses and interfaces in the table. After receiving a multicast packet, Device B searches the forwarding table for downstream interfaces that map to the packet's group address, and forwards the packet only to these interfaces, which reduces bandwidth consumption. A multicast group address can be a multicast IP address or a mapped multicast MAC address.
Functions
Major Layer 2 multicast functions include:
IGMP snooping
Static Layer 2 multicast
Layer 2 SSM mapping
IGMP snooping proxy
Multicast VLAN
Layer 2 multicast entry limit
Layer 2 Multicast Instance
Multicast Listener Discovery Snooping
Benefits
- Reduced network bandwidth consumption
- Lower performance requirements on Layer 3 devices
- Improved multicast data security
- Improved user service quality