BFD Echo
BFD echo is a rapid fault detection mechanism in which the local system sends BFD echo packets and the remote system loops back the packets. BFD echo is classified into passive BFD echo and one-arm BFD echo modes. These two BFD echo modes have the same detection mechanism but different application scenarios.
Passive BFD Echo
The NetEngine 8000 F supports passive BFD echo for interworking with other vendors' devices.
Passive BFD echo applies only to single-hop IP link scenarios and works with asynchronous BFD. When a BFD session works in asynchronous echo mode, the two endpoints of the BFD session perform both slow detection in asynchronous mode and quick detection in echo mode.
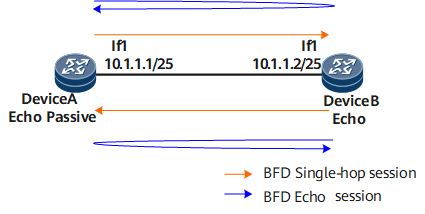
As shown in Figure 1, Device A is directly connected to Device B, and asynchronous BFD sessions are established between the two devices. After active BFD echo is enabled on Device B and passive BFD echo is enabled on Device A, the two devices work in asynchronous echo mode and send single-hop and echo packets to each other.
If Device A has a higher BFD performance than Device B, for example, the minimum intervals between receiving BFD packets supported by Device A and Device B are 3 ms and 100 ms respectively, then BFD sessions in asynchronous mode will adopt the larger interval (100 ms). If BFD echo is enabled, Device A can use echo packets to implement faster link failure detection. If BFD echo is disabled, Device A and Device B can still use asynchronous BFD packets to detect link failures. However, the minimum interval between receiving BFD packets is the larger interval value (100 ms in this example).
The process of establishing a passive BFD echo session as shown in Figure 1 is as follows:
- Device B functions as a BFD session initiator and sends an asynchronous BFD packet to Device A. The Required Min Echo RX Interval field carried in the packet is a nonzero value, which specifies that Device A must support BFD echo.
- After receiving the packet, Device A finds that the value of the Required Min Echo RX Interval field carried in the packet is a nonzero value. If Device A has passive BFD echo enabled, it checks whether any ACL that restricts passive BFD echo is referenced. If an ACL is referenced, only BFD sessions that match specific ACL rules can enter the asynchronous echo mode. If no ACL is referenced, BFD sessions immediately enter the asynchronous echo mode.
- Device B periodically sends BFD echo packets, and Device A sends BFD echo packets (the source and destination IP addresses are the local IP address, and the destination physical address is Device B's physical address) at the interval specified by the Required Min RX Interval field. Both Device A and Device B start a receive timer, with a receive interval that is the same as the interval at which they each send BFD echo packets.
- After Device A and Device B receive BFD echo packets from each other, they immediately loop back the packets at the forwarding layer. Device A and Device B also send asynchronous BFD packets to each other at an interval that is much less than that for sending echo packets.
One-Arm BFD Echo
One-arm BFD echo applies only to single-hop IP link scenarios. Generally, one-arm BFD echo is used when two devices are directly connected and only one of them supports BFD. Therefore, one-arm BFD echo does not require both ends to negotiate echo capabilities. A one-arm BFD echo session can be established on a device that supports BFD. After receiving a one-arm BFD echo session packet, devices that do not support BFD immediately loop back the packet, implementing quick link failure detection.
The local device that has one-arm BFD echo enabled sends a special BFD packet (both the source and destination IP addresses in the IP header are the local IP address, and the MD and YD in the BFD payload are the same). After receiving the packet, the remote device immediately loops the packet back to the local device to determine link reachability. One-arm BFD echo can be used on low-end devices that do not support BFD.
Similarities and Differences Between Passive BFD Echo and One-Arm BFD Echo
To ensure that passive BFD echo or one-arm BFD echo can take effect, disable strict URPF on devices that send BFD echo packets.
Strict URPF prevents attacks that use spoofed source IP addresses. If strict URPF is enabled on a device, the device obtains the source IP address and inbound interface of a packet and searches the forwarding table for an entry with the destination IP address set to the source IP address of the packet. The device then checks whether the outbound interface for the entry matches the inbound interface. If they do not match, the device considers the source IP address invalid and discards the packet. After a device enabled with strict URPF receives a BFD echo packet that is looped back, it checks the source IP address of the packet. As the source IP address of the echo packet is a local IP address of the device, the packet is sent to the platform without being forwarded at the lower layer. As a result, the device considers the packet invalid and discards it.
BFD Session |
Supported IP Type |
Session Type |
Descriptor |
Negotiation Prerequisite |
IP Header |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Common static single-hop session |
IPv4 and IPv6 |
Static single-hop session |
MD and YD must be configured. |
A matching session must be established on the peer. |
The source and destination IP addresses are different. |
Passive BFD echo session |
IPv4 and IPv6 |
Dynamic single-hop session |
No MD or YD needs to be configured. |
A matching session must be established and echo must be enabled on the peer. |
Both the source and destination IP addresses are a local IP address of the device. |
One-arm BFD echo session |
IPv4 IPv4 and IPv6 |
Static single-hop session |
Only MD needs to be configured (MD and YD are the same). |
A matching session does not need to be established on the peer. |
|