Application of BGP Flow Specification on a Network with Multiple Ingresses
This section describes the application of BGP Flow Specification on a Network with Multiple Ingresses.
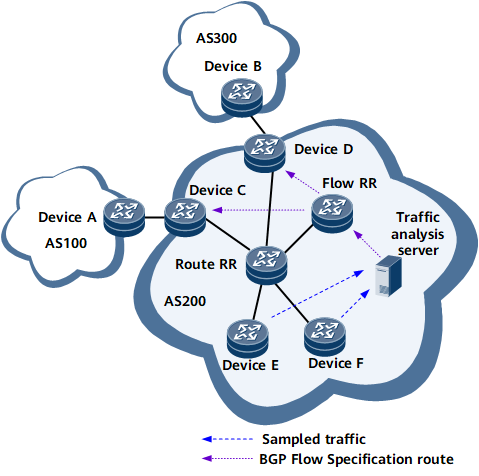
In the example in Figure 1, attack traffic may flow to AS200 through Device C and Device D, posing a threat to AS200.
In this situation, BGP Flow Specification must be deployed (the following description uses dynamic BGP Flow Specification as an example). A BGP Flow route reflector (Flow RR) must also be deployed to reduce the number of BGP Flow Specification peer relationships maintained on the traffic analysis server and to save CPU resources.
A Flow RR reflects, or propagates, the BGP Flow Specification route. The traffic analysis server establishes a BGP Flow Specification peer relationship only with the Flow RR, and the Flow RR establishes a BGP Flow Specification peer relationship with Device C and Device D. The Flow RR considers the traffic analysis server, Device C, and Device D to be its clients.
If the server detects abnormal traffic, it generates a BGP Flow Specification route and sends the route to the Flow RR. The Flow RR then reflects the route to Device C and Device D to filter out or control attack traffic.

Because one BGP RR supports a great many of peers, using Flow Specification together with a BGP Flow RR provides extensibility.
A Flow RR can be a device that has been configured as an ordinary RR or another device.