SNMP Support for AAA Users
Background
AAA is an authentication, authorization, and accounting technique. AAA local users can be configured to log in to a device through FTP, Telnet, or SSH. However, SNMPv3 supports only SNMP users, which can be an inconvenience in unified network device management.
To resolve this issue, configure SNMP to support AAA users. AAA users can then access the NMS, and MIB node operation authorization can be performed based on tasks. The NMS does not distinguish AAA users and SNMP users.
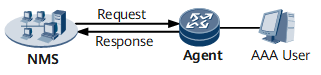
Figure 1 shows the process of an AAA user logging in to the NMS through SNMP.
Principles
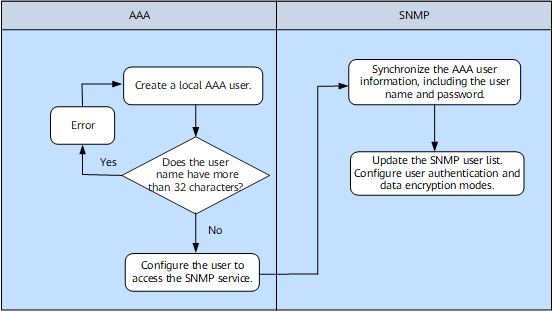
Figure 2 shows the principles of SNMP's support for AAA users.
Create a local AAA user.
If the AAA user needs to log in through SNMP, the user name must have fewer than 32 characters.
Configure the AAA user to log in through SNMP.
SNMP synchronizes the AAA user data and updates the SNMP user list. Configure a mode to authenticate the AAA user and a mode to encrypt the AAA user's data.
The AAA user's authentication and encryption modes are SNMP. An authentication password is not used.
After the preceding operations are performed, the AAA user can log in to the NMS in the same way as an SNMP user.

To improve system security, it is recommended that you configure different authentication and encryption passwords for an SNMP local user.
Task-based MIB Node Operation Authorization
AAA allows you to perform the following operations:
- Configure users, user groups, tasks, and task groups.
- Add a user to a user group and associate a user group with a task group.
- Configure multiple tasks in a task group.
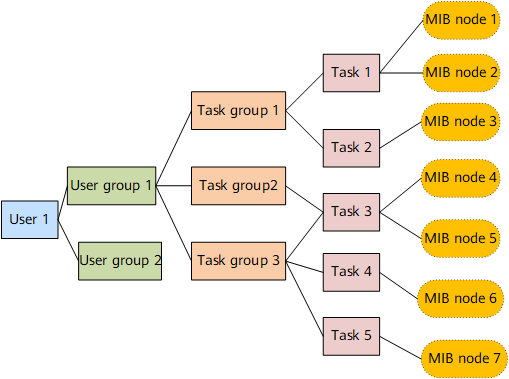
You can configure the read, write, and execute permissions for a specific task to control MIB node operations that an AAA user is allowed to perform. As shown in Figure 3:
- MIB nodes 1 and 2 are added to task 1.
- Task group 1 is associated with user group 1.
- User 1 is added to user group 1
If the read permission is assigned in task 1, user 1 is allowed to read MIB nodes 1 and 2.