OSPF Virtual Link
Background
All non-backbone areas must be connected to the backbone area during OSPF deployment to ensure that all areas are reachable.
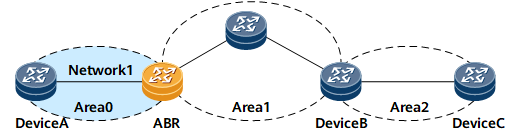
In Figure 1, area 2 is not connected to area 0 (backbone area), and Device B is not an ABR. Therefore, Device B does not generate routing information about network 1 in area 0, and Device C does not have a route to network 1.
Some non-backbone areas may not be connected to the backbone area. You can configure an OSPF virtual link to resolve this issue.
Related Concepts
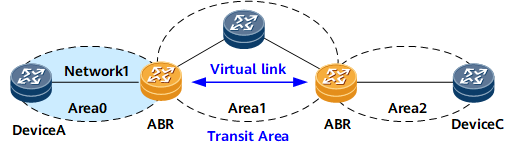
A virtual link refers to a logical channel established between two ABRs over a non-backbone area.
- A virtual link must be configured at both ends of the link.
- The non-backbone area involved is called a transit area.
A virtual link is similar to a point-to-point (P2P) connection established between two ABRs. You can configure interface parameters, such as the interval at which Hello packets are sent, at both ends of the virtual link as you do on physical interfaces.
Principles
In Figure 2, two ABRs use a virtual link to directly transmit OSPF packets. The device between the two ABRs only forwards packets. Because the destination of OSPF packets is not the device, the device transparently transmits the OSPF packets as common IP packets.