BGP VPN Route Leaking
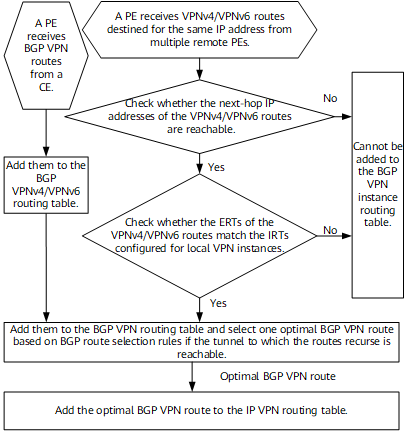
Remote route leaking: After a PE receives a BGP VPNv4/VPNv6 route from a remote PE, the local PE matches the export target (ERT) of the route against the import targets (IRTs) configured for local VPN instances. If the ERT matches the IRT of a local VPN instance, the PE converts the BGP VPNv4/VPNv6 route to a BGP VPN route and adds the BGP VPN route to the routing table of this local VPN instance.
Local route leaking: A PE matches the ERT of a BGP VPN route in a local VPN instance against the IRTs configured for other local VPN instances. If the ERT matches the IRT of a local VPN instance, the PE adds the BGP VPN route to the routing table of this local VPN instance. Locally leaked routes include locally imported routes or routes learned from VPN peers.
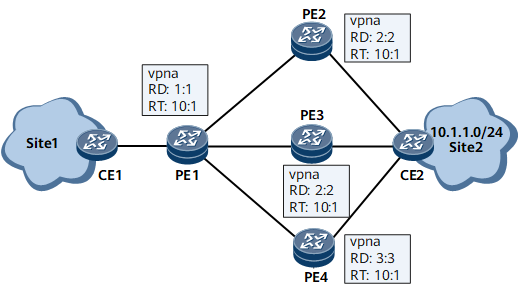
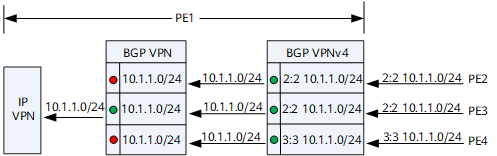
After receiving the BGP VPNv4 routes from PE2, PE3, and PE4, PE1 adds them to the BGP VPNv4 routing table.
PE1 converts the BGP VPNv4 routes to BGP VPN routes by removing their RDs, adds the BGP VPN routes to the routing table of the VPN instance, selects an optimal route from the BGP VPN routes based on BGP route selection rules, and adds the optimal BGP VPN route to the IP VPN instance routing table.