Overview of MPLS-TP OAM
Definition
Multiprotocol Label Switching Protocol Transport Profile (MPLS-TP) is a transport technique that integrates MPLS packet switching with traditional transport network features. MPLS-TP networks are poised to replace traditional transport networks in the future. MPLS-TP Operation, Administration, and Maintenance (MPLS-TP OAM) works on the MPLS-TP client layer. It can effectively detect, identify, and locate faults in the client layer and quickly switch traffic when links or nodes become defective. OAM is an important part of any plan to reduce network maintenance expenditures.
Purpose
Both networks and services are part of an ongoing process of transformation and integration. New services like triple play services, Next Generation Network (NGN) services, carrier Ethernet services, and Fiber-to-the-x (FTTx) services are constantly emerging from this process. Such services demand more investment and have higher OAM costs. They require state of the art QoS, full service access, and high levels of expansibility, reliability, and manageability of transport networks. Traditional transport network technologies such as Multi-Service Transfer Platform (MSTP), Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH), or Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) cannot meet these requirements because they lack a control plane. Unlike traditional technologies, MPLS-TP does meet these requirements because it can be used on next-generation transport networks that can process data packets, as well as on traditional transport networks.
- Fault management
- Performance monitoring
- Triggering protection switching
Benefits
- MPLS-TP OAM can rapidly detect link faults or monitor the connectivity of links, which helps measure network performance and minimizes OPEX.
- If a link fault occurs, MPLS-TP OAM rapidly switches traffic to the standby link to restore services, which shortens the defect duration and improves network reliability.
MPLS-TP OAM Components
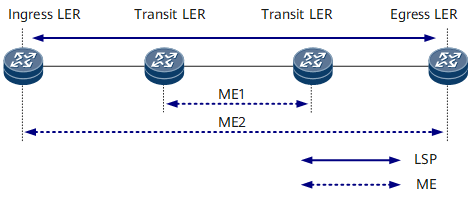
MPLS-TP OAM functions are implemented by maintenance entities (MEs). An ME consists of a pair of maintenance entity group end points (MEPs) located at two ends of a link and a group of maintenance entity group intermediate points (MIPs) between them.
-
An ME maintains a relationship between two MEPs. On a bidirectional label switched path (LSP) that has two MEs, MPLS-TP OAM detection can be performed on the MEs without affecting each other. One ME can be nested within another ME but cannot overlap with another ME.
ME1 and ME2 in Figure 1 are used as an example:- ME1 consists of two MEPs only.
- ME2 consists of two MEPs and two MIPs.
-
A maintenance entity group (MEG) comprises one or more MEs that are created for a transport link. If the transport link is a point-to-point bidirectional path, such as a bidirectional co-routed LSP or pseudo wire (PW), a MEG comprises only one ME.
-
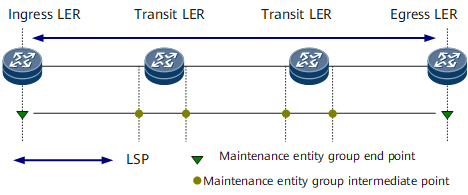
A MEP is the source or sink node in a MEG. Figure 2 shows ME node deployment.
For a bidirectional LSP, only the ingress label edge router (LER) and egress LER can function as MEPs, as shown in Figure 2.
For a PW, only user-end provider edges (UPEs) can function as MEPs.
Fault Management
Performance Monitoring
Function |
Description |
|---|---|
Loss measurement (LM) |
Collects statistics about lost frames. LM includes the following functions:
|
Delay measurement (DM) |
Collects statistics about delays and delay variations (jitter). DM includes the following functions:
|