Basic Concepts
An MPLS-TP network consists of the section, LSP, and PW layers in bottom-up order. A lower layer is a server layer, and an upper layer is a client layer. For example, the section layer is the LSP layer's server layer, and the LSP layer is the section layer's client layer.
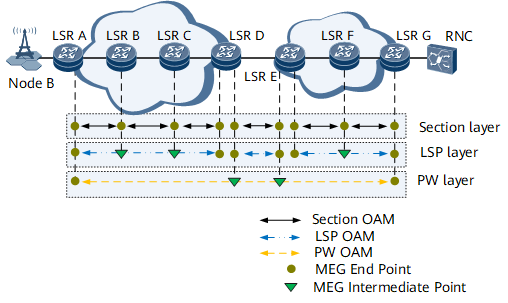
On the MPLS-TP network shown in Figure 1, MPLS-TP OAM detects and locates faults in the section, LSP, and PW layers. Table 1 describes MPLS-TP OAM components.
Name |
Description |
Example |
|---|---|---|
Maintenance entity (ME) |
All MPLS-TP OAM functions are performed on MEs. Each ME consists of two maintenance entity group end points (MEPs) and maintenance entity group intermediate points (MIPs) on the link between the two MEPs. |
|
Maintenance entity group (MEG) |
A MEG is comprised of one or more MEs that are created for a transport link. MEGs for various services contain different MEs:
|
NOTE:
If two tunnels in opposite directions between LSR A and LSR D are established, a single MEG consisting of two MEs is established. |
MEG end point (MEP) |
A MEP is the source or sink node in a MEG. |
|
MEG intermediate point (MIP) |
Intermediate nodes between two MEPs on both ends of a MEG. MIPs only respond to OAM packets sent by MEPs and do not take the initiative in OAM packet exchanges. |
|
Usage Scenario
- Static bidirectional co-routed CR-LSPs
- Static VLL-PWs and VPLS-PWs