Application of MPLS-TP OAM in the IP RAN Layer 2 to Edge Scenario
MPLS-TP OAM is deployed on PEs to maintain and operate MPLS networks. Working at the MPLS client and server layers, MPLS-TP OAM can effectively detect, identify, and locate client layer faults and quickly switch traffic if links or nodes become faulty, reducing network maintenance cost.
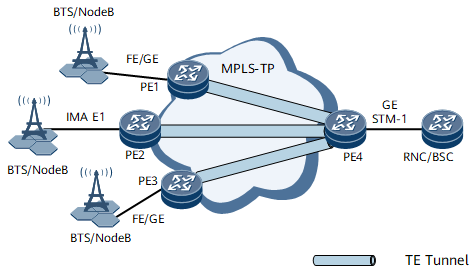
In Figure 1, in Layer 2 to edge scenario on an IP RAN, mature PWE3 techniques are used to carry services. The process of transmitting services between a BST/NodeB and a RNC/BSC is as follows:
- The BTS, NodeB, BSC, and RNC can be directly connected to an MPLS-TP network.
- A TE tunnel between PE1 and PE4 is established. PWs are established over the TE tunnel to transmit various services.
- MPLS-TP OAM is enabled on PE1 and PE4 OAM parameters are configured on PE1 and PE4 on both ends of a PW. These PEs are enabled to send and receive OAM detection packets, which allows OAM to monitor the PW between PE1 and PE4. OAM can obtain basic PW information. If OAM detects a default, PE4 sends a RDI packet to PE1 over a reverse tunnel. PEs notify the user-side BTS, NodeB, RNC, and BSC of fault information so that the user-side devices can use the information to maintain networks.