Packet Loss Measurement
- Near-end packet loss value: the number of dropped packets expected to arrive at the local MEP.
- Far-end packet loss value: the number of dropped packets the local MEP has sent.
- TxFCl: records the number of packets sent to the RMEP.
- RxFCl: records the number of packets received by the local MEP.
Packet loss measurement can be performed in either single- or dual-ended mode. Table 1 describes the single- and dual-ended packet loss measurement.
Function |
Description |
Usage Scenario |
|---|---|---|
Dual-ended packet loss measurement |
Collects packet loss statistics to assess the quality of the link between two MEPs that have connectivity fault management (CFM) continuity check (CC) enabled. |
Dual-ended packet loss measurement provides more accurate results than the single-ended method. The interval between dual-ended packet loss measurements varies with the interval between CCM transmissions. The CCM transmission interval is shorter than the interval between LMM transmissions. Therefore, the dual-ended method allows for a shorter measurement interval than the single-ended method. |
Single-ended packet loss measurement |
Collects packet loss statistics to assess the quality of the link between two MEPs. This method is independent of CC. |
Sending CCMs imposes a heavier burden on the network than sending LMMs and LMRs. To minimize the burden, single-ended packet loss measurement can be used. |
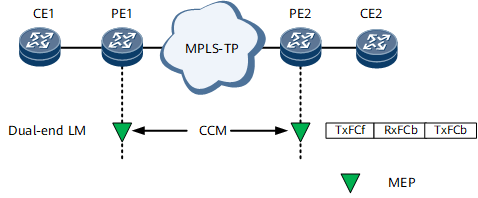
Dual-ended Packet Loss Measurement
- TxFCf: the local TxFCl value recorded when the local MEP sent a CCM.
- RxFCb: the local RxFCl value recorded when the local MEP received a CCM.
- TxFCb: the TxFCf value carried in a received CCM. This TxFCb value is the local TxFCl when the local MEP receives a CCM.
After receiving CCMs carrying packet count information, both MEPs use the following formulas to measure near- and far-end packet loss values:
Near-end packet loss value = |TxFCf[tc] - TxFCb[tp]| - |RxFCl[tc] - RxFCl[tp]|
Far-end packet loss value = |TxFCb[tc] - TxFCb[tp]| - |RxFCb[tc] - RxFCb[tp]|
- TxFCf[tc], RxFCb[tc], and TxFCb[tc] are the TxFCf, RxFCb, and TxFCb values, respectively, which are carried in the most recently received CCM. RxFCl[tc] is the local RxFCl value recorded when the local MEP received the CCM.
- TxFCf[tp], RxFCb[tp], and TxFCb[tp] are the TxFCf, RxFCb, and TxFCb values, respectively, which are carried in the previously received CCM. RxFCl[tp] is the local RxFCl value recorded when the local MEP received the previous CCM.
- tc is the time a current CCM was received.
- tp is the time the previous CCM was received.
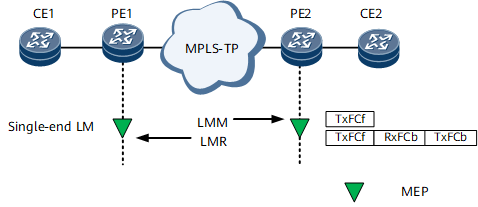
Single-ended Packet Loss Measurement
- TxFCl: the local TxFCl value recorded when the LMM was sent.
- TxFCf: equal to the TxFCf value carried in the LMM.
- RxFCf: the local RxFCl value recorded when the LMM was received.
- TxFCb: the local TxFCl value recorded when the LMR was sent.
Figure 2 illustrates proactive single-end packet loss measurement.
After receiving an LMR, the local MEP uses the following formulas to calculate near- and far-end packet loss values:
Near-end packet loss value = |TxFCb[tc] - TxFCb[tp]| - |RxFCl[tc] - RxFCl[tp]|
Far-end packet loss value = |TxFCf[tc] - TxFCf[tp]| - |RxFCf[tc] - RxFCf[tp]|
- TxFCf[tc], RxFCf[tc], and TxFCb[tc] are the TxFCf, RxFCf, and TxFCb values, respectively, which are carried in the most recently received LMR. RxFCl[tc] is the local RxFCl value recorded when the most recent LMR arrives at the local MEP.
- TxFCf[tp], RxFCf[tp], and TxFCb[tp] are the TxFCf, RxFCf, and TxFCb values, respectively, which are carried in the previously received LMR. RxFCl[tp] is the local RxFCl value recorded when the previous LMR arrived at the local MEP.
- tc is the time a current LMR was received.
- tp is the time the previous LMR was received.