Interface-based Hard Pipe Bandwidth Reservation
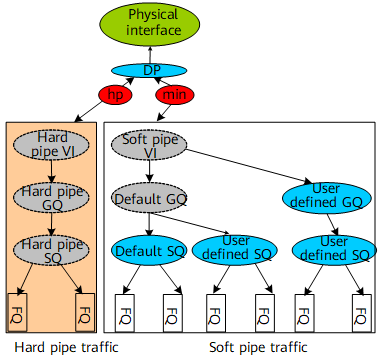
During network planning, traffic is classified as hard pipe traffic and soft pipe traffic based on interfaces. Hard pipe traffic must have low delay and no packet loss and not be affected by soft pipe traffic. Therefore, fixed bandwidth must be allocated to hard pipe traffic on interfaces. This bandwidth is exclusive to hard pipe traffic.
On devices, hard pipe and soft pipe services on interfaces are assigned forwarding paths with different priorities. When both hard and soft pipes have traffic, the hard pipe traffic is preferentially forwarded, guaranteeing low delay. The maximum bandwidth is also configured for the forwarding paths to ensure that the sum of hard and soft pipe bandwidth does not exceed the interface bandwidth. Subsequently, the hard and soft pipe services do not affect each other.
End-to-end hard pipe service deployment can be implemented only through the NMS. The NMS delivers hard pipe VLL/PWE3 or TE LSP configurations based on the bearer capabilities of the hard pipe. The device establishes VLL/PWE3 PWs and TE LSPs based on the delivered data and transmits VLL/PWE3 or TE services through the hard pipe.
The NMS supports alarm thresholds for services exceeding the hard pipe's processing capabilities, ensuring that services transmitted over the hard pipe do not exceed the hard pipe's processing capabilities.