PKI System
The PKI system is a universal secure infrastructure. It ensures information security by using the public key theory and technology. The PKI system, as an integration of software and hardware system and security policy, provides a set of security mechanisms. The PKI system provides a secure network environment where users can conveniently use encryption and digital signature technologies in various application scenarios, ensuring confidentiality, integrity, and validity of the data.
The PKI largely uses digital certificates for establishing mutual authentication and thereby securing communications. A certificate is used to authenticate the peers that attempt to set up an IPsec tunnel, and provides a centralized key management mechanism for IPsec. Certificates are issued by the third party CA, a certificate authorization center.
Certificates include root certificates and entity certificates:
- A root certificate is also called a CA certificate. It proves that the corresponding local certificate is issued by a legitimate CA.
- An entity certificate is also called a local certificate. It identifies a device in a CA domain, indicating that the device is authorized.
A certificate includes a certificate serial number, holder name, issuer name, valid period, public key, and digital signature of the issuer.
Component |
Function |
|---|---|
Terminal entity |
Applicant and user of a certificate. The terminal entity can be an individual, an organization, a device (router/switch), or a process running in a PC. |
Certificate registration authority (RA) |
It receives users' certificate applications, authenticates users. In applications, the RA can work either independently or with the CA. |
Certificate Authority (CA) |
A third-party organization that issues and manages digital certificates. A CA is in charge of issuing certificates, specifying the validity periods of certificates, and issuing the CRL to revoke certificates when necessary. |
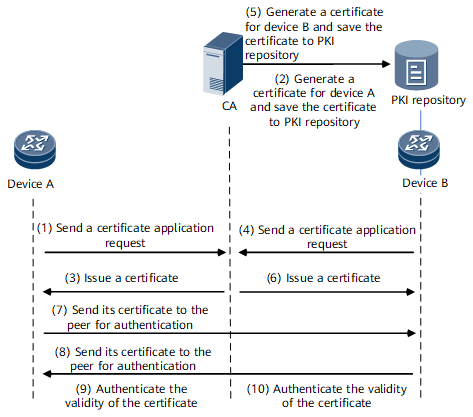
Figure 1 shows the interaction among the components.
- For example, device A sends a certificate request to the CA. The request contains the entity information (describing end features) that the CA adopts to generate an entity certificate for device A.
The CA authenticates the received device information, generates the certificate for device A, and saves the certificate to the PKI repository.

Two types of certificates are available, namely, the root certificate (CA certificate) and entity certificate (local certificate). The root certificate represents the identity of the CA, whereas the entity certificate represents the identity of the device. In a CA domain, each certificate has a unique serial number for authenticating the validity or revocation state of the certificate.
- The CA issues the root certificate and entity certificate simultaneously to device A.
- Device A uses the root certificate to authenticate the validity of the entity certificate, that is, to verify that the entity certificate is issued by a legal CA, but not an attacker.
- Device B follows the same procedure as device A.
- If a device wants to use the certificate to prove its identity, for example, before the establishment of the IPsec VPN through IKE, the device can send its certificate to the peer.