Migration from an HVPLS Network to a PBB-EVPN
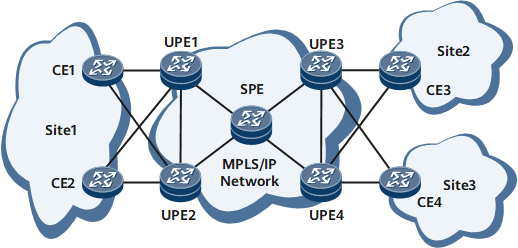
On the network shown in Figure 1, VPLS is deployed to allow services of the same private network to access VSIs over different PEs. To avoid establishment of full-mesh PWs, SPEs are deployed on the network to form an HVPLS.
Configure a B-EVPN instance on the SPE and specify a unique B-MAC address for the B-EVPN instance.
Change the existing VSI on the SPE to be an MP2MP I-VSI and bind the I-VSI to the B-EVPN instance previously configured. The I-tag for the I-VSI must be the same as the I-tag for the B-EVPN instance. Otherwise, services cannot be forwarded.
Specify each UPE as an EVPN BGP peer for the SPE.
Configure a B-EVPN instance on each UPE and specify the SPE as an EVPN BGP peer for each UPE. Then, UPEs will learn B-MAC addresses from their EVPN BGP peers and the SPE will learn the B-MAC addresses of the entire network.
Change the existing VSI on each UPE to be an I-EVPN instance, bind the I-EVPN instance to the previously configured B-EVPN instance, and bind the AC interface on each UPE to the I-EVPN instance on that UPE. After all configurations are complete, the network becomes a PBB-EVPN.