Application of MPLS OAM in VPLS Networking
Service Overview
The operation and maintenance of virtual leased line (VLL) and virtual private LAN service (VPLS) services require an operation, administration and maintenance (OAM) mechanism. MultiProtocol Label Switching Transport Profile MPLS OAM provides a mechanism to rapidly detect and locate faults, which facilitates network operation and maintenance and reduces the network maintenance costs.
Networking Description
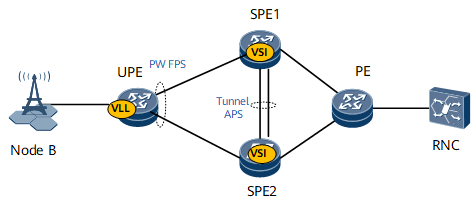
As shown in Figure 1, a user-end provider edge (UPE) on the access network is dual-homed to SPE1 and SPE2 on the aggregation network. A VLL supporting access links of various types is deployed on the access network. A VPLS is deployed on the aggregation network to form a point-to-multipoint leased line network. Additionally, Fast Protection Switching (FPS) is configured on the UPE; MPLS tunnel automatic protection switching (APS) is configured on SPE1 and SPE2 to protect the links between the virtual switching instances (VSIs) created on the two superstratum provider edges (SPEs).
Feature Deployment
To deploy MPLS OAM to monitor link connectivity of VLL and VPLS pseudo wires (PWs), configure maintenance entity groups (MEGs) and maintenance entities (MEs) on the UPE, SPE1, and SPE2 and then enable one or more of the continuity check (CC), loss measurement (LM), and delay measurement (DM) functions. The UPE monitors link connectivity and performance of the primary and secondary PWs.
- When SPE1 detects a link fault on the primary PW, SPE1 sends a Remote Defect Indication (BDI) packet to the UPE, instructing the UPE to switch traffic from the primary PW to the secondary PW. Meanwhile, the UPE sends a MAC Withdraw packet, in which the value of the PE-ID field is SPE1's ID, to SPE2. After receiving the MAC Withdraw packet, SPE2 transparently forwards the packet to the NPE and the NPE deletes the MAC address it has learned from SPE1. After that, the NPE learns a new MAC address from the secondary PW.
- After the primary PW recovers, the UPE switches traffic from the secondary PW back to the primary PW. Meanwhile, the UPE sends a MAC Withdraw packet, in which the value of the PE-ID field is SPE2's ID, to SPE1. After receiving the MAC Withdraw packet, SPE1 transparently forwards the packet to the NPE and the NPE deletes the MAC address it has learned from SPE2. After that, the NPE learns a new MAC address from the new primary PW.