CMPv2
- Manages components in a public key infrastructure (PKI).
- Implements online interaction between components in a PKI.
- Defines CMP packets related to certificate generation and management, such as certificate application, certificate revocation, key update, key recovery, and cross-authentication packets.

In a PKI, the device functions as an end entity. This section describes the end entity operations defined by CMPv2.
CMPv2 manages digital certificates for end entities, including initial request (IR), certificate request (CR), key update request (KUR), and polling.
IR
IR is performed when an end entity applies for the first certificate from a certificate authority (CA).
The end entity can apply for a certificate manually in outband mode or online by using CMP. The former method takes a long time, and the certificate is difficult to update. Therefore, the device applies for a certificate online by using CMP.
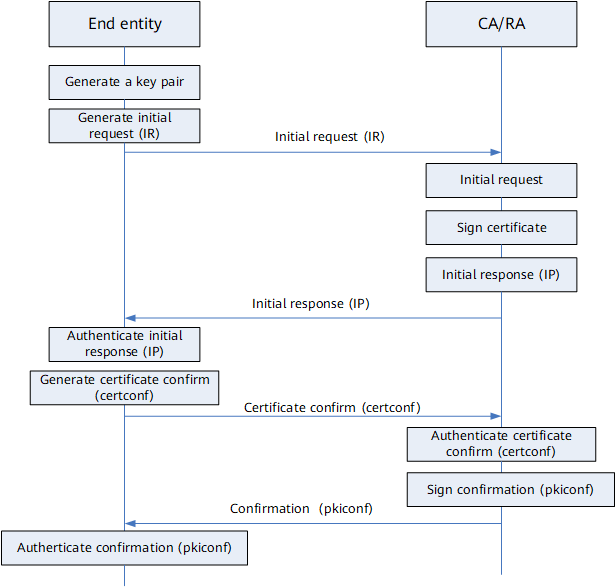
Figure 1 shows how an end entity applies for the first certificate online by using CMP.
An end entity applies for the first certificate from a CA as follows:
- The end entity generates a key pair.
- The end entity sends an IR packet to the CA to request the first certificate.
- After receiving the IR packet, the CA authenticates the packet. If the authentication succeeds, the CA generates a certificate and sends a reply packet to the end entity.
- After receiving the reply packet, the end entity authenticates the packet. If the authentication succeeds, the end entity sends a certificate confirmation packet to the CA.
- After receiving the certificate confirmation packet, the CA authenticates the packet. If the authentication succeeds, the CA sends a PKI confirmation packet to the end entity.
- After receiving the PKI confirmation packet, the end entity authenticates the packet. If the authentication succeeds, IR is completed.
During the preceding process, all packets transmitted between the end entity and the CA must be authenticated using either the end-entity-generated key pair or the supplier-provided certificate.

The device supports only authentication using the supplier-provided certificate.
The supplier-provided certificate refers to a digital certificate that uniquely identifies an end entity. This digital certificate is issued by the supplier's CA. After a customer buys the end entity, the customer does not use the supplier-provided certificate any longer. Instead, the customer applies for a new digital certificate from a trusted CA by sending an IR request defined by CMPv2.
KUR
For security consideration, a key pair needs to be changed periodically. Each certificate has a validity period. When a certificate expires, it is revoked, and you must apply for a new one. The KUR function can update key pairs and certificates.
The key update request (KUR) interaction process is the same as the initial authentication process.
Polling
After receiving a request packet (an IR, CR, or KUR packet) from an end entity, a CA sends a reply packet with the PKI status set to Waiting if it cannot respond to the request packet immediately. Then, the end entity sends polling requests to check whether a certificate is generated.