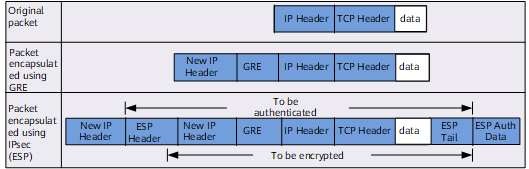
GRE over IPsec
IPsec adds an IP header, in which the source address is the address of the IPsec gateway interface to which an IPsec policy is applied and the destination address is the address of the IPsec peer interface to which an IPsec policy is applied, when encapsulating an IP packet.
The data flow protected by IPsec is from the GRE startpoint to the GRE endpoint. In the IP header added by GRE during encapsulation, the source address is the source address of the GRE tunnel, and the destination address is the destination address of the GRE tunnel.
Various applications are based on GRE over IPsec, for example, Border Gateway Protocol (BGP), Label Distribution Protocol (LDP), Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), Intermediate System to Intermediate System (IS-IS), and IPv6. Based on the same principle, these applications encapsulate packets as IP packets using GRE and then transmit the packets over IPsec tunnels.
IPsec over GRE is also an application scheme of IPsec and GRE combination. IPsec over GRE encapsulates packets using IPsec and then GRE. However, this encapsulation mode does not fully play advantages of IPsec and GRE and does not support multicast, broadcast, and non-IP packets. Therefore, it is not recommended.