IS-IS for BIER
BIER Flooding
IS-IS for BIER encapsulates BIER path computation information in the packet header, and uses IS-IS LSPs to flood the information.
IS-IS defines the BIER Info Sub-TLV to support the flooding of BIER information.
BIER Info Sub-TLV
The BIER Info Sub-TLV carries BIER sub-domain information, and its format is as follows.
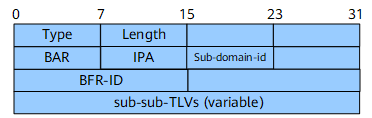
Field |
Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Type |
8 bits |
The value is 32. |
Length |
8 bits |
Specifies the packet length. |
BAR |
8 bits |
Specifies the BIER algorithm. |
IPA |
8 bits |
Specifies the IGP algorithm. |
Sub-domain-id |
8 bits |
Specifies a unique BIER sub-domain ID. |
BFR-ID |
16 bits |
Specifies a bit forwarding router (BFR) ID in a sub-domain. |
sub-sub-TLVs (variable) |
32 bits |
Carries BIER MPLS encapsulation information. |
The sub-sub-TLVs field in the BIER Info Sub-TLV carries the BIER MPLS encapsulation information and appears multiple times in one BIER Info Sub-TLV.
The format of sub-sub-TLVs is as follows:
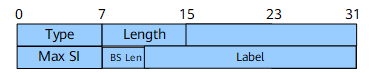
Field |
Length |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Type |
8 bits |
Its value is 1, which indicates BIER MPLS encapsulation information. |
Length |
8 bits |
Indicates that the packet length is 1 byte. |
Max SI |
8 bits |
Specifies the length of the BitString in a BIER sub-domain. Each SI maps a label in the label range. The first label corresponds to SI 0, the second label corresponds to SI 1, and the rest can be deduced by analogy. If the label associated with the Maximum Set Identifier exceeds the 20-bit range, the sub-sub-TLVs field is ignored. |
BS Len |
4 bits |
Specifies the length of the local BitString. |
Label |
20 bits |
Indicates the first label value of the label block that consists of Max SI + 1 consecutive labels. |
Bit Allocation Fundamentals
Each edge node in a BIER sub-domain is represented by an independent bit position, and transit nodes do not need bit positions. All edge nodes' bits form a BitString. The position of each bit in the BitString is called a BFR-ID.
BIER uses IS-IS LSPs to flood the mapping between bit positions (BFR-IDs) of edge nodes and prefixes. Devices learn the complete BIER neighbor table through flooding. The neighbor table has the following characteristics:
- In the neighbor table, each directly connected neighbor has one entry.
- Each entry contains information about the edge nodes that are reachable to a neighbor.