BIER Application to MVPN Services
Service Overview
In MVPN services, BIER can replace the traditional P2MP tunnel or public network PIM technology and provide public network tunnels (P-Tunnels) to carry MVPN traffic.
Networking Description
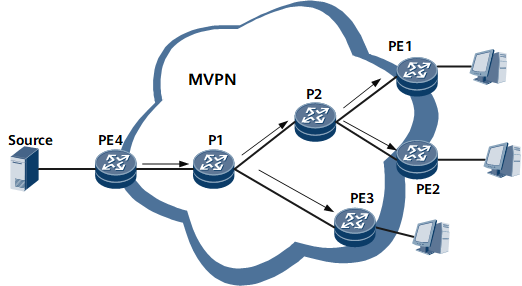
PE1, PE2, PE3, and PE4 are edge nodes of the service provider's backbone network. PE4 is connected to the multicast source, and PE1, PE2, and PE3 are connected to multicast users. An MVPN is configured for the PEs, as shown in Figure 1
Feature Deployment
- Control plane:
IGP BIER is configured on the service provider's backbone network, and the unicast VPN runs properly.
MVPN is configured on the service provider's backbone network, and BGP is used by PEs in the same MVPN to exchange BGP A-D and BGP C-multicast routes.
- PIM is configured on the MVPN to establish VPN MDTs.
- Data plane:
- After receiving a multicast packet from the private network side, the sender PE (PE4) encapsulates the packet with a BIER header carrying the BitString that represents a destination node set and sends the encapsulated packet to P1.
After receiving the packet with the BIER header, receiver PEs (PE1, PE2, and PE3) find their own bit positions in the BitString of the packet, remove the BIER header from the packet, search their VPN routing tables for routing entries, and forward the packet accordingly.
After receiving the packet with the BIER header, intermediate nodes (P1 and P2) replicate the packet, edit the BitString of the packet copy according to the F-BM in the BIER forwarding table, and forward the packet copy according to the BIER forwarding table.