MVPN over BIERv6 Dual-Root 1+1 Protection
Solution Overview
In an MVPN over BIERv6 scenario, if a node or link fails, multicast services can be restored only after BGP peer convergence is complete. However, such convergence takes a long time and therefore cannot meet the high reliability requirements of multicast services. To speed up convergence, you can use BFD for BGP. You can also deploy the dual-root 1+1 protection solution, which further improves the performance of multicast service convergence.
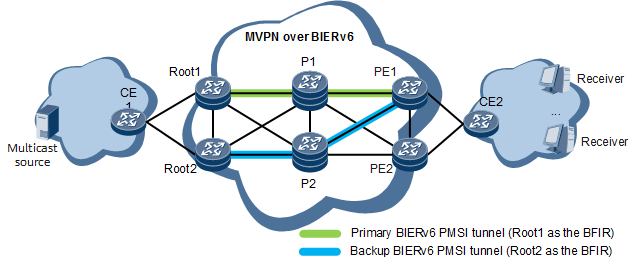
The networking shown in Figure 1 is used as an example to describe how the MVPN over BIERv6 dual-root 1+1 protection solution is deployed.
- Two sender PEs (Root1 and Root2) are deployed. Root1 and Root2 each set up a PMSI tunnel with themselves as the BFIRs. PE1 is a leaf node on the two tunnels.
- VPN fast reroute (FRR) is configured on PE1 so that PE1 has two routes to the same multicast source. In this example, PE1 selects the route advertised by Root1 as the primary route, and the one advertised by Root2 as the backup route.
Flow detection-based C-multicast FRR is configured on PE1. When the links function correctly, both the primary and backup tunnels forward the same multicast traffic. In this case, PE1 accepts the traffic received through the primary tunnel (Root1 is the BFIR) and discards the traffic received through the backup tunnel (Root2 is the BFIR).
Switchover upon a Failure
After MVPN over BIERv6 dual-root 1+1 protection is deployed:
- For the multicast traffic PE1 receives from the multicast source through the primary tunnel, PE1 forwards it to the corresponding VPN. PE1 discards the multicast traffic it receives through the backup tunnel.
- If PE1 detects an interruption of traffic received through the primary tunnel, it immediately checks whether the traffic received through the backup tunnel is normal. If the traffic received through the backup tunnel is normal, PE1 performs a primary/backup tunnel switchover and forwards the traffic received through the original backup tunnel to the corresponding VPN.
To ensure that failures do not lead to prolonged interruption of multicast services, you are advised to plan separate paths for the primary and backup tunnels.