RADIUS Server Selection Mechanism
- RADIUS server primary/secondary algorithm (default)
- RADIUS server load balancing algorithm
In addition, the algorithm for selecting a RADIUS server can be set to the single user-based or packet-based algorithm. If the algorithm for selecting a RADIUS server is set to the single user-based algorithm, authentication server information is saved in the authentication phase, and the device preferentially sends an accounting request to the accounting server in the accounting phase when the authentication server is also the accounting server. If the algorithm for selecting a RADIUS server is set to the packet-based algorithm, authentication server information is not saved in the authentication phase, and the accounting server is reselected in the accounting phase, which may result in that authentication and accounting for a user is not performed on the same server.
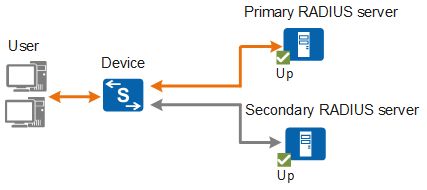
RADIUS Server Primary/Secondary Algorithm
The primary and secondary roles are determined by the weights configured for the RADIUS authentication servers or RADIUS accounting servers. The server with the largest weight is the primary server. If the weight values are the same, the earliest configured server is the primary server. As shown in Figure 1, the device preferentially sends an authentication or accounting packet to the primary server among all servers in Up status. If the primary server does not respond, the device then sends the packet to the secondary server.
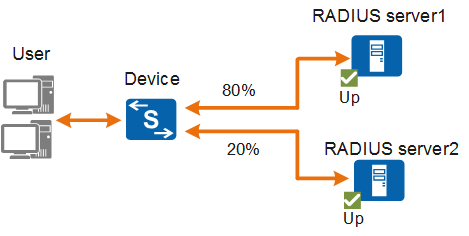
RADIUS Server Load Balancing Algorithm
If this algorithm is used and a device sends an authentication or accounting packet to a server, the device selects a server based on the weights configured for the RADIUS authentication servers or RADIUS accounting servers. As shown in Figure 2, RADIUS server1 is in Up status and its weight is 80, and RADIUS server2 is also in Up status and its weight is 20. The possibility for the device to send the packet to RADIUS server1 is 80% [80/(80 + 20)], and that for RADIUS server2 is 20% [20/(80 + 20)].
Regardless of which algorithm is used, if all the servers in Up status do not respond to a packet sent by a device, the device retransmits the packet to a server among the servers whose status is originally marked as Down (to which the device has not sent any authentication or accounting packets) based on the server weight. If the device does not receive any response in the current authentication mode, the backup authentication mode is used, for example, local authentication mode. The backup authentication mode needs to be already configured in the authentication scheme. Otherwise, the authentication process ends.