Configuring a User-Defined ACL
Prerequisites
If you need to configure a time-based ACL, create a time range and associate the time range with the ACL rules. For details, see (Optional) Creating a Time Range in Which an ACL Takes Effect.
Context
A user-defined ACL defines rules based on packet headers, offsets, character string masks, and user-defined character strings. With such a user-defined ACL configured, the system performs an AND operation on the packet bytes from a certain position behind the packet header and the character string mask, compares the extracted character string against the user-defined character string, and then filters IPv4 and IPv6 packets.
User-defined ACLs are more accurate and flexible than basic ACLs, advanced ACLs, and Layer 2 ACLs, as well as providing more functions. For example, a user-defined ACL can be configured to filter ARP packets based on source IP addresses and ARP packet types.
Procedure
- Run system-view
The system view is displayed.
- Configure a user-defined ACL. You can create a numbered or named ACL.
Run the acl [ number ] acl-number [ match-order { auto | config } ] command to create a numbered user-defined ACL (5000-5999) and enter the user-defined ACL view.
Run the acl name acl-name { user | acl-number } [ match-order { auto | config } ] command to create a named user-defined ACL and enter the user-defined ACL view.
By default, no ACL exists on the device.
If the parameter match-order is not specified when you create an ACL, the default matching order config is used. For details about the ACL matching order, see ACL Matching.
The default step of a created ACL is 5. If the default step cannot meet your ACL configuration requirements, you can change the step value. For details about the step, see ACL Increment; for configuration of the step, see Adjusting the Increment of ACL Rules.
- (Optional) Run description text
A description is configured for the ACL.
By default, an ACL has no description.
The ACL description helps you understand and remember the functions or purpose of an ACL.
- Run rule [ rule-id ] { deny | permit } [ [ l2-head | ipv4-head | ipv6-head | l4-head ] { rule-string rule-mask offset } &<1-8> | time-range time-name ] *
Rules are configured in the user-defined ACL.

The S2720-EI, S5720I-SI, S5720-LI, S5735-L, S5735S-L, S5735S-L-M, S5720S-LI, S5720S-SI, S5720-SI, S5735-S, S5735S-S, S5735-S-I, S5730S-EI, S5730-SI, S6720-LI, S6720S-LI, S6720S-SI, and S6720-SI do not support &<1-8> and ipv6-head.
In this example, only one permit or deny rule is configured. In actual configuration, you can configure multiple rules and decide the matching order of the rules according to service requirements.
Configuring a user-defined ACL rule provides a rule configuration example.
- (Optional) Run rule rule-id description description
A description is configured for the ACL rules.
By default, an ACL rule has no description.
The ACL rule description helps you understand and remember the functions or purpose of an ACL rule.
You can configure descriptions for only the existing rules on the device. That is, you cannot configure a description for a rule before creating it.
Follow-up Procedure
After an ACL is configured, it must be applied to a service module so that the ACL rules can be delivered and take effect. For supported service modules and configurations, see Applying an ACL.
Configuration Examples
Configuring a user-defined ACL ruleConfiguring packet filtering rules based on Layer 2 headers, offsets, character string masks, and user-defined character strings
To reject ARP packets from the specified host, configure a rule in a user-defined ACL. For example, to reject ARP packets from the host at 192.168.0.2, configure the following rule in ACL 5001.
In the following rule:- 0x00000806 indicates the ARP protocol.
- 0x0000ffff is the character string mask.
- 10 indicates the protocol type field offset in the ARP packets (without VLAN ID).
- c0a80002 is the hexadecimal format of 192.168.0.2.
- 26 and 30 respectively indicate the offsets of the higher 2 bytes and lower 2 bytes in the source IP addresses in ARP packets (without VLAN ID). The source IP address in an ARP packet begins at the 28th byte in the Layer 2 header and occupies 4 bytes. The Layer 2 header offset defined in a user-defined ACL must be 4n + 2 (n is an integer). Therefore, the source IP address is divided into two segments for matching. The lower 2 bytes among the four bytes behind offset 26 (4 x 6 + 2) and the higher 2 bytes among the 4 bytes behind offset 30 (4 x 7 + 2) are matched separately.
Figure 1 Source IP address field offset in the Layer 2 header of an ARP packet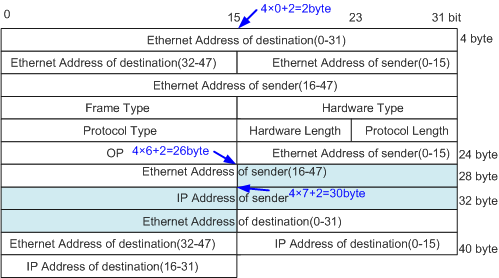
<HUAWEI> system-view [HUAWEI] acl 5001 [HUAWEI-acl-user-5001] rule deny l2-head 0x00000806 0x0000ffff 10 0x0000c0a8 0x0000ffff 26 0x00020000 0xffff0000 30
To reject all TCP packets, configure a rule in user-defined ACL deny-tcp.
In the following rule:- 0x00060000 indicates the TCP protocol.
- 8 indicates the protocol type offset in the IP packets. (The protocol type field in an IP packet begins at the 10th byte in the IPv4 header and occupies 1 byte. The IPv4 header offset defined in a user-defined ACL must be 4n (n is an integer). Therefore, the second higher byte among the 4 bytes behind offset 8 in the IPv4 header is matched.)
<HUAWEI> system-view [HUAWEI] acl name deny-tcp user [HUAWEI-acl-user-deny-tcp] rule 5 deny ipv4-head 0x00060000 0x00ff0000 8
Figure 2 TCP protocol field offset in the IPv4 header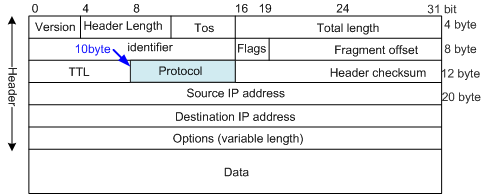

When specifying an ACL rule to match offset bytes in the Layer 2 header on the S5730-SI, S5730S-EI, S6720-56C-PWH-SI-AC, or S6720-56C-PWH-SI, add a tag first if the ACL rule will be applied on a GE electrical interface through which packets having no tag pass.
Configuring a time-based ACL rule
For details, see Configuring a time-based ACL rule in Configuring a Basic ACL.