| DecoySensor |
- Detects scanning of IP addresses and TCP ports.
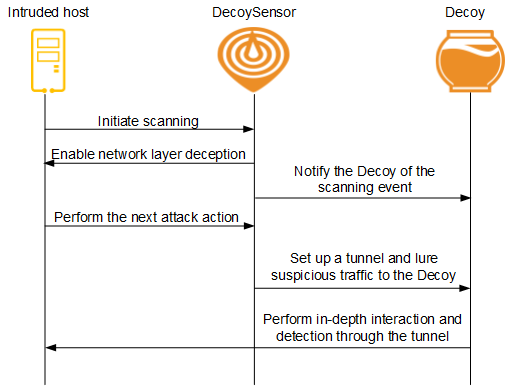
- In non-strict mode, if a DecoySensor detects that the scanning frequency initiated by an IP address exceeds the specified threshold and the scanned destination IP address is not online or the TCP port is not open, the DecoySensor starts network
layer deception and proactively responds to the scanning request of the hacker. In this way, the hacker incorrectly considers that the scanned destination IP address is online or the TCP port is open, and continues to the next phase of the attack.
- In strict mode, a DecoySensor immediately performs network layer deception once detecting that the scanned destination IP address is not online or the TCP port is not open, without checking the scanning frequency.
Supports the detected network segments.
After such a network segment is configured, the DecoySensor detects scanning behavior only in this network segment.
Supports the bait network segments.
You can add some idle IP addresses to the blacklist. Once hackers scan these IP addresses or their TCP ports, they will be lured to a Decoy.
Supports the deception whitelist function.
- You can add the IP addresses of devices that proactively detect the network (such as the NMS) to the source IP address whitelist to prevent them from being incorrectly considered to be attackers by DecoySensors.
- You can add the IP addresses of devices that do not respond to ARP requests and port connection requests (such as traditional printers) to the destination IP address whitelist to prevent normal traffic sent to these devices from being lured.
Supports deception for packets with unknown domain names.
When the rate of DNS request packets that a DecoySensor receives from the same source address exceeds the threshold, the DecoySensor determines that a
scanning behavior is being performed and records a log.
If the DecoySensor receives response packets indicating that the domain name does not exist from the DNS server, the DecoySensor automatically constructs DNS response packets. The source
IP address in the DNS response packets is an IP address on the bait network segment and is on the same network segment as the source address of DNS request packets. The subsequent packets sent from the hacker will be diverted to the Decoy.
Supports ACI-based deception.
ACI is an isolation scheme for controlling intranet communication through DNS access. After this function is enabled, the source or destination address in the detected network segment must be accessed through the domain name. If
the IP address is directly accessed or the IP address that does not exist is accessed, traffic is deceived to the Decoy.
The DecoySensor parses DNS reply packets and establishes mappings between the source addresses of DNS request packets
and the IP addresses corresponding to the domain names in DNS reply packets (that is, the ACI table). Subsequent TCP SYN packets and ICMP ping packets will match the ACI table. Traffic that fails to match the table is deceived to the Decoy for in-depth
interactive detection.
An ACI suffix needs to be set. The default value is "aci". An ACI suffix is equivalent
to a key for intranet access. For example, when the IP address of a server on the detected network segment is 192.168.1.1, the domain name 192.168.1.1.aci must be used to access the server. If a user attempts to access the server through 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.1.1.aaa, the user traffic is lured to the Decoy for in-depth interaction detection.
|
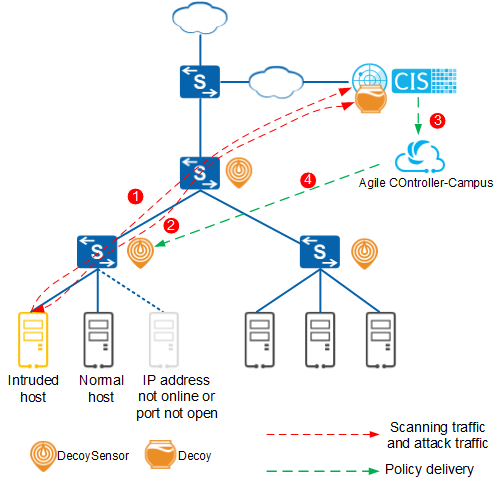
A DecoySensor can run on a switch, hardware firewall, or software firewall. For details about the firewall models that can act as DecoySensors, see the firewall product documentation.
The DecoySensor deployment requirements vary according
to the scanning behavior:
IP address scanning: The DecoySensor must have at least one VLANIF interface, for which the primary IP address must be on the network segment to be detected.
TCP port scanning: The scanning packets and reply packets must pass through the DecoySensor.
|
| Decoy |
- Provides the HTTP, SSH, Server Message Block (SMB), and Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) services for in-depth interaction with hackers, analyzes behavior of the hackers, and identifies attack tools.
- Sends the interaction logs and the scanning logs provided by DecoySensors to the Cybersecurity Intelligence System (CIS) for further analysis.
- Provides bait file download.
- Simulates web pages in a subnet to provide a more interactive experience.
|
You can deploy the Decoy as software on a CIS flow probe. In this scenario, the Decoy is a component of the CIS server. |