Protection Switching
The protection switching mechanism of clock synchronization ensures that, if a clock source traced by a switch is missing, another clock source automatically takes over. The new clock source may trace clock signals from the same reference clock as the old clock source or may be a clock source with a lower SSM quality level. When the original clock source is restored, the switch determines whether to re-select a clock source based on the configuration.
Protection Switching in Automatic Clock Source Selection Mode
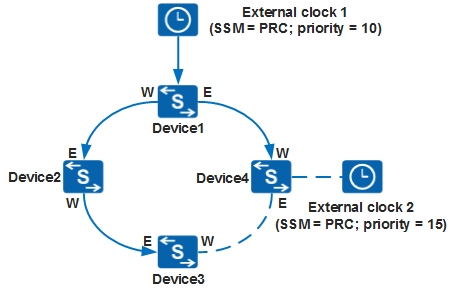
- As shown in Figure 1, when
the network functions normally, the switch determines to trace external
clock 1 and its clock tracing path using the automatic clock source
selection algorithm based on SSM quality levels and priorities of
clock sources.
 In this chapter, the networking figures use W to represent the westbound interface and E to represent the eastbound interface. W and E indicate the interfaces connecting devices and distinguish the input and output directions of clock signals.
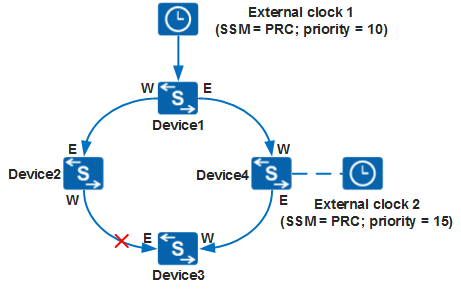
In this chapter, the networking figures use W to represent the westbound interface and E to represent the eastbound interface. W and E indicate the interfaces connecting devices and distinguish the input and output directions of clock signals. - As shown in Figure 2, if a link fails, the switch determines that the clock source to trace remains unchanged based on the automatic clock source selection algorithm and updates only the clock tracing path.
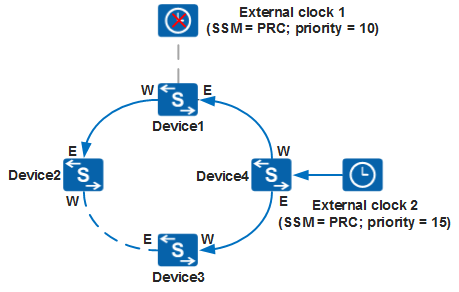
- As shown in Figure 3, if the clock source is faulty, the switch determines to trace external clock 2 based on the automatic clock source selection algorithm and updates the clock tracing path.
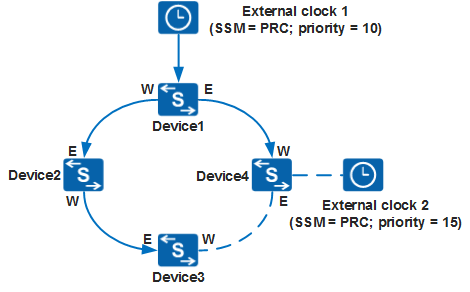
- As shown in Figure 4, if the link or clock source fault is rectified, the switch re-traces external clock 1 based on the automatic clock source selection algorithm and updates the clock tracing path.
Protection Switching in Manual Clock Source Selection Mode
- If the manually specified clock source is normal, the switch traces this clock source.
- If the manually specified clock source is faulty, the switch works in automatic clock source selection mode, traces a new clock source based on the automatic clock source selection algorithm, and updates the clock tracing path.
- If the fault affecting the manually specified clock source is rectified, the switch determines whether to trace the recovered clock source based on the automatic clock source selection algorithm.
Protection Switching in Forcible Clock Source Selection Mode
- If the forcibly specified clock source is normal, the switch traces this clock source.
- If the forcibly specified clock source is faulty, the switch enters the clock holding state.
- If the fault affecting the forcibly specified clock source is rectified, the switch re-traces the forcibly specified clock source.