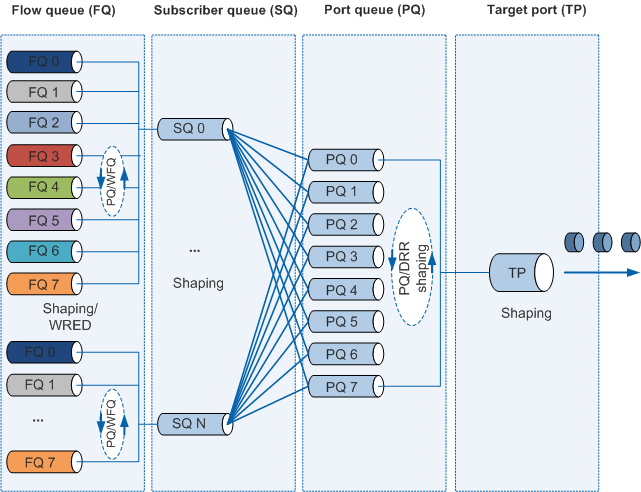
Understanding HQoS
HQoS implements hierarchical scheduling based on queues. The switch supports the flow queue (FQ) and subscriber queue (SQ). The HQoS hierarchy is a tree structure, with flow queues as the leaf nodes and subscriber queues as root nodes. Packets on an interface are first sent to leaf nodes, scheduled, and sent out of the root node. In addition, packets can be further scheduled. For example, the packets can be scheduled in port queues. The device supports the mapping between flow queues and port queues to schedule the same service from different users, as shown in Figure 1.
Flow Queue
Based on the DiffServ model, an HQoS-enabled switch places packets into flow queues based on mapped internal priorities to differentiate services. Each user has eight flow queues corresponding to eight service priorities: BE, AF1, AF2, AF3, AF4, EF, CS6, and CS7. Priority Queuing (PQ) or Weighted Fair Queueing (WFQ) scheduling can be configured for flow queues. A flow queue supports Weighted Random Early Detection (WRED) and traffic shaping, ensuring the bandwidth and preferential scheduling for high-priority services.
Subscriber Queue
Subscriber queues are used to differentiate users.
Users can be VLANs or VPNs and are differentiated using access control lists (ACLs). Each user has a subscriber queue, which is the aggregation of eight flow queues. Traffic shaping can be configured to limit the total bandwidth of each user.
Port Queue
Similar to flow queues, the eight port queues correspond to eight service types. PQ or WDRR scheduling can be configured for the eight port queues. Each queue supports WRED and traffic shaping. For details, see Configuring Congestion Management (Interface Mode), Configuring Congestion Avoidance (WRED Drop Profile Mode), and Configuring Traffic Shaping. The device supports the mapping between flow queues (BE, AF1, AF2, AF3, AF4, EF, CS6, and CS7) and port queues. The mapping allows the device to flexibly send service traffic in a flow queue to a port queue.
Target Port
Target ports are physical interfaces through which outgoing data is sent. Traffic shaping can be performed for each target port after scheduling of flow queues, subscriber queues, and port queues is performed. For details, see Configuring Outbound Interface-based Rate Limiting.