Interaction Process for Intelligent Video O&M
Basic Process
Intelligent video O&M aims to provide the user and application experience awareness capability for networks. CampusInsight or eSight an intelligent O&M system, is adopted to intelligently associate changes to user and application experience with those to network status, thereby implementing visualization, association, diagnosis, rectification, and prediction of network faults. Intelligent video O&M saves manpower, reduces OPEX and fault self-healing time, and improves user experience.
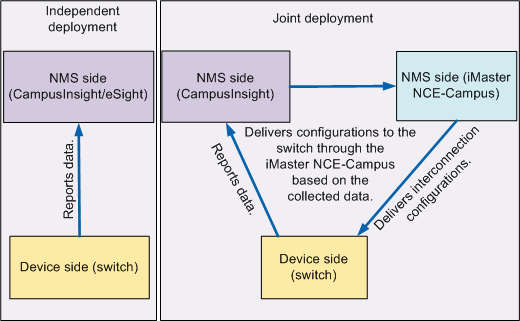
The intelligent video O&M system supports data collection and reporting as well as data analysis and display. The system uses Telemetry technology to collect KPI information about network devices to obtain user experience indicators in seconds. User logs and alarms are reported through Syslog and Telemetry. CampusInsight or eSight as an intelligent analysis platform, identifies faults by using big data analytics technology and machine learning algorithms, and displays services visually. For details about data collection using Telemetry technology, see Figure 1. The data collection process involves devices and an NMS.
- The devices refer to switches. They receive data collection instructions from the NMS, sample data sources specified by the NMS, and send sampling data to the collector in the NMS.
- The NMS is composed of a collector, an analyzer, and the iMaster NCE-Campus.
- Collector (CampusInsight or eSight): receives and stores monitoring data sent by devices.
- Analyzer (CampusInsight or eSight): analyzes the monitoring data saved on the collector.
- iMaster NCE-Campus: configures and manages network devices, and sends data required by the collector. The controller is not required when CampusInsight or eSight is deployed in standalone mode.
Telemetry technology has the following advantages over traditional data collection technologies (such as SNMP and CLI):
- Data is collected in push mode instead of the pull mode. After data collection is configured, devices report data at the specified interval. This push mode improves data analysis timeliness, and avoids the impacts of the pull mode on the collector and network traffic.
- Data is organized based on the YANG model, coded using the Google Protocol Buffer (GPB) protocol, and transmitted using the Http2 protocol. This standard data model simplifies data analysis and monitoring, and allows multi-vendor devices to be managed compatibly and easily.
Reporting Device-Level KPI Statistics
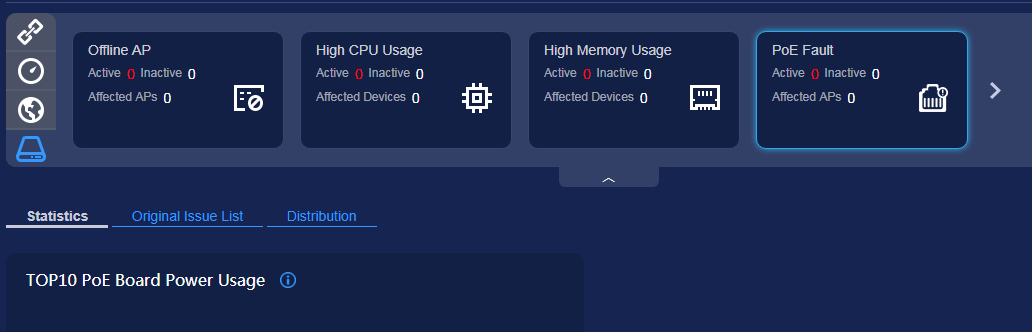
Switches report device-level KPI statistics (such as port traffic statistics, packet loss rate, CPU usage, and PoE information) to an NMS through HTTP/2+Protobuf interfaces. The NMS analyzes and summarizes the information reported by the switches, and then displays the running status of the switches. According to the PoE information reported by switches, CampusInsight displays the PoE power supply information and issue list, as shown in Figure 2. This figure is only an example. For all O&M items supported by CampusInsight, see the CampusInsight V100R002C00 Product Documentation. For the KPI statistics that can be reported by switches to the NMS, see KPI Information That Switches Can Send to an NMS.
Reporting Audio and Video Information
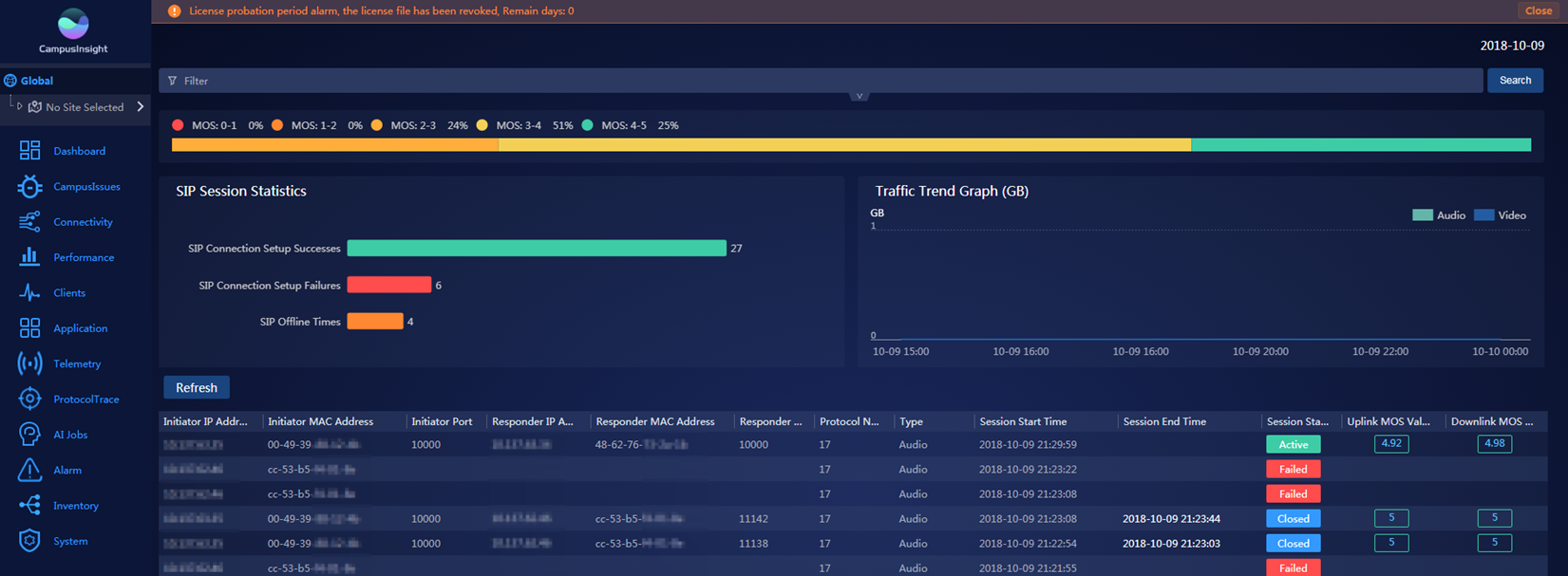
If audio and video devices are connected through a switch to a network with audio and video traffic, the switch can monitor the setup and termination of sessions for media streams transmitted over SIP. Switches can also obtain audio quality parameters through Enhanced Media Delivery Index (eMDI) instances and detect dynamic indicators of media streams, thereby implementing real-time monitoring of session packets on network nodes and fast demarcation of faulty network segments. Then, switches can calculate the mean opinion scores (MOSs) of media streams based on the data packet loss rate monitored through the eMDI instance and the size of the largest packet lost in the specified period. Finally, the switches report the KPIs and MOSs of media streams monitored by eMDI to the NMS using Telemetry technology. For example, CampusInsight displays statistics about SIP session setup failures and successes and the number of abnormal offline sessions, as well as traffic trends and the session list, as shown in Figure 3.
Reporting Log and Alarm Information
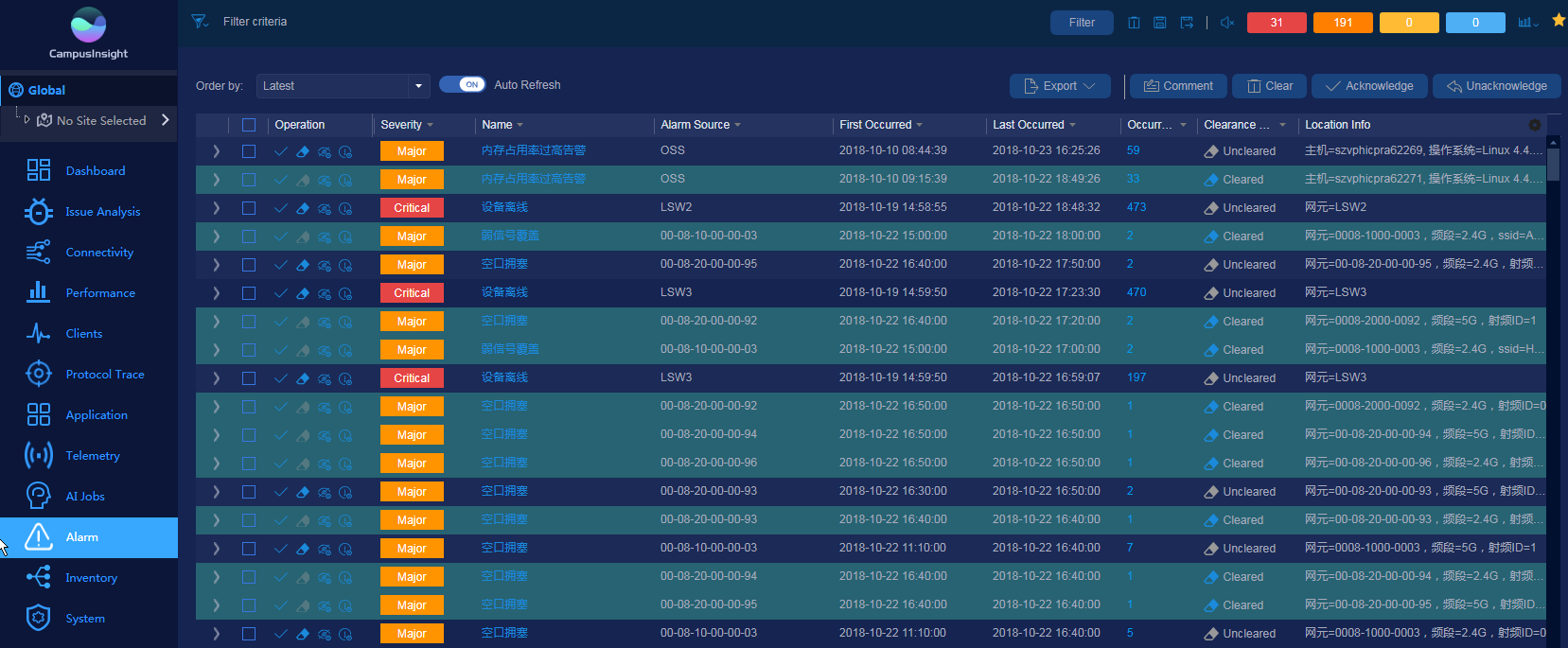
When a log or an alarm is generated on a switch, the switch reports the log or alarm to the NMS through Syslog or SNMP. As shown in Figure 4, CampusInsight displays the severity, name, and occurrence time of the log or alarm, helping network administrators locate and rectify faults. For the log and alarm information that can be reported by switches to the NMS, see Logs and Alarms that Can Be Reported by Switches to an NMS.