Configuring an Interface to Forward Directed Broadcast Packets
Context
Directed broadcast packets are sent to a specified network. In the destination IP address of a directed broadcast packet, the network number is that of the specified network and the host number is all 1s.
Hackers use directed broadcast packets to attack networks, which threatens the network security. Therefore, directed broadcast packets are isolated by Layer 3 switches in normal cases. However, in some scenarios, the device needs to receive or forward these directed broadcast packets. For example, when Wake on LAN (WOL) is configured on a PC, the interface can be set to forward directed broadcast packets. (WOL enables a PC in dormancy or shutdown state to wake up from dormancy state to running state or turn from shutdown state to power-on state through the instruction from the peer of the network.)
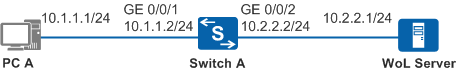
As shown in Figure 1, on Switch A, GE0/0/1 is on the same network segment with PC A; GE0/0/2 is on another network segment with the WOL server. The WOL server uses directed broadcast packets to wake up PC A. In normal cases, the directed broadcast packets are isolated by Switch A. After the ip forward-broadcast command is run on Switch A's GE0/0/1 to enable the interface to forward the directed broadcast packets, PC A can receive the directed broadcast packets from the WOL server.

By default, the device identifies directed broadcast packets as malformed packets, and intercepts and discards them because the attack defense function of malformed packets is enabled on the device. In this case, the interface on the device cannot forward the directed broadcast packets.
To solve this problem, use either of the following methods:
Run the anti-attack abnormal disable command to disable the attack defense function of malformed packets. However, after this command is configured, other malformed packets will not be intercepted and discarded, which brings certain security risks. Use this command with caution.
Run the anti-attack disable command to disable all attack defense functions. However, after this command is configured, not only malformed packets but also fragmented, tcp-syn, udp-flood, and icmp-flood attack packets will not be intercepted and discarded, which brings certain security risks. Use this command with caution.
The device can also be enabled to receive and forward a certain type of directed broadcast packets based on ACLs. For example, if the basic ACL is used, run the acl (system view) and rule (basic ACL view) commands to define the directed broadcast packets to be received and forwarded as permit, and then run the ip forward-broadcast command to bind this ACL.
Procedure
- Configure the basic or advanced ACL. For details, see Configuring an ACL or Deleting an ACL in "ACL Configuration" in the S2720, S5700, and S6700 V200R019C10 Configuration Guide - Security.
- Run system-view
The system view is displayed.
- Run interface interface-type interface-number
The interface view is displayed.
- (Optional) On an Ethernet interface, run undo portswitch
The interface is switched to Layer 3 mode.
By default, an Ethernet interface works in Layer 2 mode.

Only the S5720-EI, S5720-HI, S5730-HI, S5731-H, S5731-S, S5731S-H, S5731S-S, S5732-H, S6720-EI, S6720-HI, S6720S-EI, S6730-H, S6730S-H, S6730-S, and S6730S-S support switching between Layer 2 and Layer 3 modes.
- Run ip forward-broadcast [ acl acl-number ]
The interface is configured to forward directed broadcast packets.
By default, an interface does not forward directed broadcast packets.
Only broadcast packets that match the permit action defined in the ACL are forwarded. Broadcast packets that match the deny action defined in the ACL or do not match any ACL rules are not forwarded.