Configuring the Generation of Snooping MAC Entries Based on the Binding Table
Background
Snooping MAC entries are a type of secure MAC entries. They are dynamically generated based on binding entries. After a device is configured to generate snooping MAC entries based on the binding table, the device does not dynamically learn MAC addresses, and only the hosts in the binding table can communicate with the device. This function improves communication security.
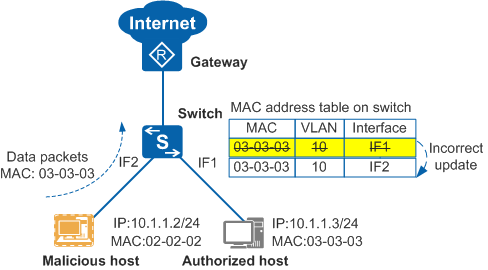
IPSG based on a binding table prevents hosts with unauthorized MAC addresses from accessing the network, but cannot solve MAC address flapping caused by incorrect MAC address table updates. In Figure 1, when a malicious host sends data (for example, bogus ARP packets) to the switch by using an authorized host's MAC address, the switch incorrectly updates the MAC address table. As a result, the malicious host can intercept the packets destined for the authorized host.
To address the preceding issue, you can configure the device not to dynamically learn MAC entries and to generate snooping MAC entries based on the binding table.
Function Description |
Command |
|---|---|
Enable 802.1X authentication on an interface. |
dot1x enable |
Enable MAC address authentication on an interface. |
mac-authen |
Enable MAC address learning. |
mac-address learning disable |
Set the maximum number of MAC addresses to be learned. |
mac-limit |
Enable VLAN mapping. |
port vlan-mapping vlan map-vlan port vlan-mapping vlan inner-vlan |
Configure port security. |
port-security enable |
Pre-configuration Tasks

When configuring a static binding entry, you must specify at least the MAC address, VLAN ID, and interface number. The VLAN ID must already exist on the device. The device can then generate snooping MAC entries based on the static binding table.