Inter-Device Link Aggregation and Local Preferential Forwarding
Inter-Device Link Aggregation
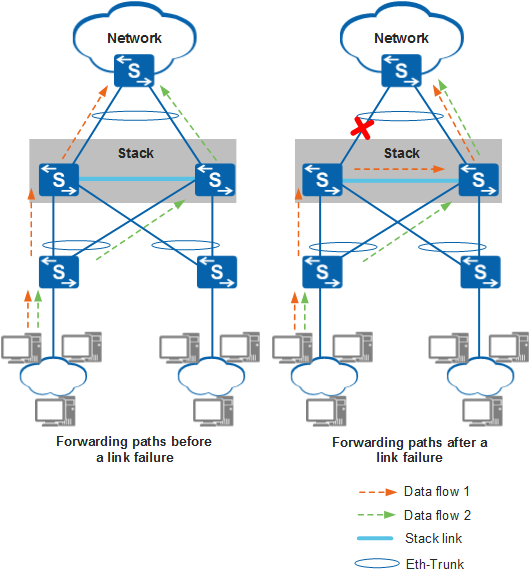
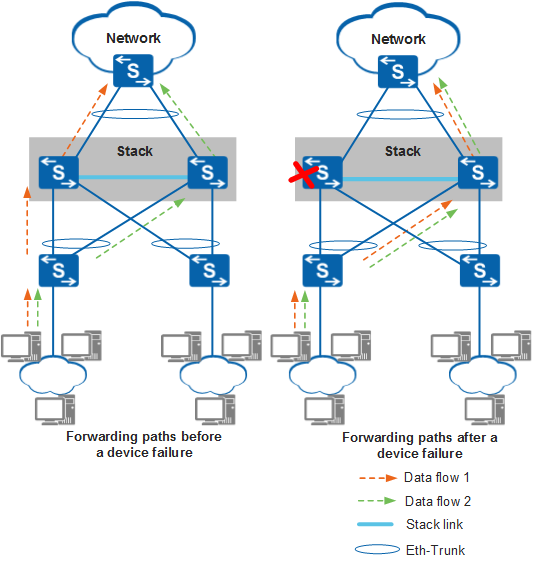
A stack supports inter-device link aggregation through Eth-Trunks. Physical Ethernet interfaces on different member switches can bundle into an Eth-Trunk, which connects the stack to an upstream or downstream device. If a member link of the Eth-Trunk or a member switch fails, traffic on this link or switch can be distributed to other member links through the stack cables connecting member switches. Inter-device link aggregation implements link and device backup and ensures reliable data traffic transmission.
In Figure 1, traffic sent to the core device on a network is evenly distributed to member links of an Eth-Trunk set up between stack member switches. If a member link fails, traffic on this link is distributed to the other link through the stack cables. This link backup mechanism improves network reliability.
In Figure 2, traffic sent to the core device on a network is evenly distributed to member links of an Eth-Trunk set up between stack member switches. If a member switch fails, traffic toward this switch is distributed to the other switch. This device backup mechanism improves network reliability.
Local Preferential Forwarding
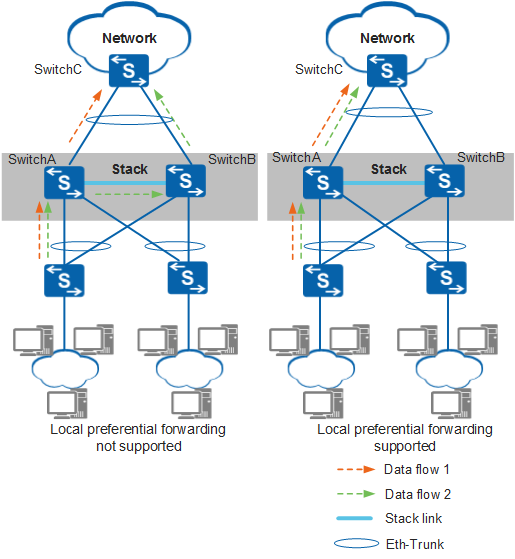
Inter-device link aggregation implements reliable data traffic transmission and backup between stack member switches. Because stack cables provide limited bandwidth, inter-device forwarding increases the load on stack cables and reduces forwarding efficiency. To improve the forwarding efficiency and reduce traffic on stack cables, a switch provides the local preferential forwarding function. The function allows traffic reaching the local switch to be preferentially forwarded through a local interface. If the local device has no outbound interface or all outbound interfaces fail, traffic is forwarded through an interface on the other member switch.
In Figure 3, SwitchA and SwitchB form a stack, and their uplink and downlink interfaces bundle into Eth-Trunks. If local preferential forwarding is not configured, traffic reaching SwitchA is load balanced between the Eth-Trunk member links. Some traffic is forwarded from SwitchA to SwitchB through the stack cables and is sent out from a physical interface on SwitchB. If local preferential forwarding is configured, traffic reaching SwitchA is forwarded through a local physical interface and does not pass through the stack cables. By default, the local preferential forwarding function is enabled on the device.