Stack Upgrade
A stack supports three upgrade methods: intelligent upgrade, traditional upgrade, and smooth upgrade.
Intelligent Upgrade
When a stack is set up or new member switches join a stack, the standby and slave switches or new member switches check whether their software versions are the same as that of the master switch. If not, they download the system software from the master switch, restart with the new system software, and rejoin the stack.
Traditional Upgrade
You can specify the startup system software on the master switch and restart the entire stack to upgrade the software of member switches. This upgrade method causes lengthy service interruptions, and is therefore not suitable for scenarios sensitive to the service interruption time.
Smooth Upgrade
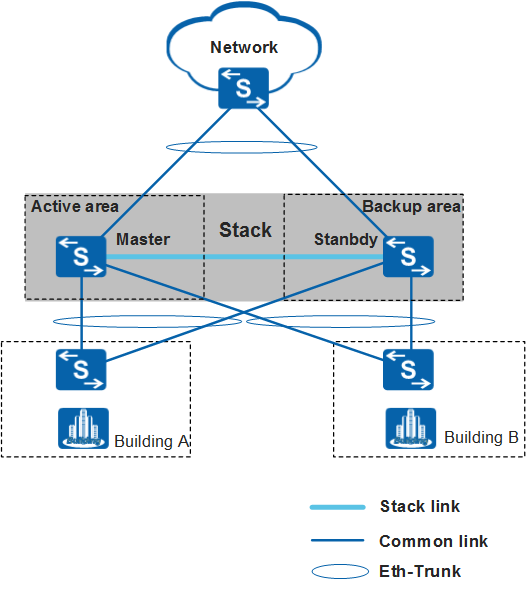
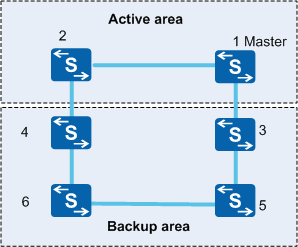
A smooth upgrade can be performed in a stack that has uplinks and downlinks working in redundancy mode. In Figure 1, the stack is divided into an active area (with the master switch) and a backup area. Member switches in the two areas are upgraded in turn. When one area is being upgraded, traffic is transmitted through the other area, minimizing the impact on services. Use this upgrade method in scenarios that are sensitive to the service interruption time.
In a network with uplinks and downlinks working in redundancy mode, both upstream traffic and downstream traffic are forwarded through the active and backup areas. When member switches in the backup area are being upgraded, traffic is forwarded through the active area. Likewise, when member switches in the active area are being upgraded, traffic is forwarded through the backup area.

To implement smooth upgrade for a stack, the stack must have uplinks and downlinks working in redundancy mode. To ensure a successful upgrade, you are advised to add at least one link on each member switch to an inter-device Eth-Trunk.
Uplinks and downlinks work in redundancy mode.
The system software for the next startup supports the smooth upgrade function.
Stack members are running the same system software, with the same software package name, version, and path.
Stack members have the same system software specified for next startup, with the same software package name, version, and path.
- The active and backup areas cannot have the same member switch, and both areas must have at least one member switch.
- The backup area cannot contain the master switch.
- Member switches in each area must be directly connected.
- Member switches in the active and backup areas constitute the entire stack.
Smooth Upgrade Process
- The master switch issues the smooth upgrade command to the entire stack. Member switches in the backup area restart with the new system software.
- Member switches in the backup area set up an independent stack running the new system software and notify member switches in the active area. The master switch in the backup area starts to control the stack, and traffic is transmitted through the backup area. The active area then starts the upgrade.
- Member switches in the active area restart with the new system software and join the stack set up in the backup area. The master switch in the backup area displays the upgrade result depending on the stack setup result.

If errors or exceptions occur during a smooth upgrade, or the upgrade times out (the timeout interval is 70 minutes), member switches automatically roll back to the original system version and set up a stack again.