Configuring a VPN Instance on a PE Device
Context
To enable local VPNs to access each other, VPN instances must be configured on the PE device, and the VPN target attributes must be configured for the VPN instances.
Perform the following steps on each PE device.
Procedure
- Run system-view
The system view is displayed.
- Run ip vpn-instance vpn-instance-name
A VPN instance is created, and its view is displayed.

A VPN instance name is case sensitive. For example, "vpn1" and "VPN1" are different VPN instances.
- (Optional) Run description description-information
The description is configured for the VPN instance.
- (Optional) Run service-id service-id
A service ID is created for the VPN instance.
A service ID is unique on a device. It distinguishes a VPN service from other VPN services on the network.
- Run ipv4-family
The IPv4 address family is enabled for the VPN instance, and the VPN instance IPv4 address family view is displayed.
VPN instances support both the IPv4 and IPv6 address families. Configurations in a VPN instance can be performed only after an address family is enabled for the VPN instance based on the advertised route and forwarding data type.
- Run route-distinguisher route-distinguisher
An RD is configured for the VPN instance IPv4 address family.
A VPN instance IPv4 address family takes effect only after being configured with an RD. The RDs of different VPN instances on a PE must be different.

An RD can be modified or deleted only after the VPN instance is deleted or the VPN instance IPv4 address family is disabled.
- If you configure an RD for the VPN instance IPv4 address family in the created VPN instance view, the VPN instance IPv4 address family is enabled and the VPN instance IPv4 address family is displayed.
- Run vpn-target vpn-target &<1-8> [ both | export-extcommunity | import-extcommunity ]
A VPN target is configured for the VPN instance IPv4 address family.
A VPN target is a BGP extended community attribute. It is used to control the receiving and advertisement of VPN routing information. A maximum of eight VPN targets can be configured using a vpn-target command.
For each VPN instance configured for mutual access between local VPNs, the VPN target export-extcommunity of the peer end must be set to the VPN target import-extcommunity of the local end.
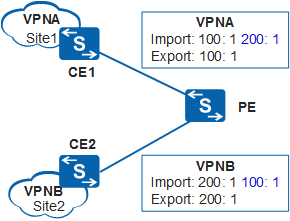
On the network shown as follows, the import target and export target of VPNA are 100:1, whereas the import target and export target of VPNB are 200:1. To ensure mutual access between VPNA and VPNB, add 200:1 as the import target of VPNA, and add 100:1 as the import target of VPNB.
- (Optional) Configure a routing policy for the VPN instance.
In addition to using VPN targets to control VPN route advertisement and reception, you can configure a routing policy for the VPN instance to better control VPN routes.
- An import routing policy filters routes before they are imported into the VPN instance IPv4 address family.
- An export routing policy filters routes before they are advertised to other PE devices.

Before applying a routing policy to a VPN instance, create the routing policy. For details about how to configure a routing policy, see Routing Policy Configuration in the S2720, S5700, and S6700 V200R019C10 Configuration Guide - IP Unicast Routing.
Run the following command as required:- To configure an import routing policy for the VPN instance IPv4 address family, run import route-policy policy-name.
- To configure an export routing policy for the VPN instance IPv4 address family, run export route-policy policy-name.
Follow-up Procedure
After VPN instances are configured, VPN routes need to be imported to BGP. For the detailed configuration, see Configuring Route Exchange Between PE and CE Devices.