Example for Configuring Hub and Spoke (Using BGP4+ Between the PE and CE)
Networking Requirements
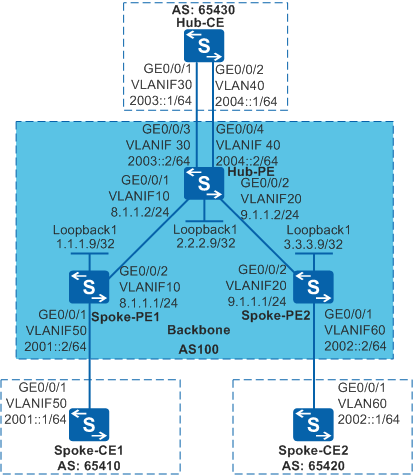
The headquarters and branch of a bank use isolated IPv6 networks that are far from each other. The bank wants to realize secure communication between its headquarters and branches through MPLS VPN. VPN traffic from branches passes the headquarters so that the headquarters can monitor the traffic. The Hub and Spoke networking can meet the bank's needs. As shown in Figure 1, the Spoke-CEs connect to branches, and the Hub-CE connects to the headquarters. All traffic transmitted between Spoke-CEs is forwarded by the Hub-CE.

In this scenario, to avoid loops, ensure that all connected interfaces have STP disabled and connected interfaces are removed from VLAN 1. If STP is enabled and VLANIF interfaces of switches are used to construct a Layer 3 ring network, an interface on the network will be blocked. As a result, Layer 3 services on the network cannot run normally.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure an IGP protocol on the backbone network to enable the Hub-PE and Spoke-PEs to communicate with each other.
Configure basic MPLS capabilities and MPLS LDP on the backbone network to establish MPLS LSPs.
Create two IPv6 VPN instances, namely, vpn_in and vpn_out, on the Hub-PE. The VPN target received by vpn_in is the same as the VPN target advertised by the Spoke-PEs. The VPN target advertised by vpn_out is different from the VPN target received by vpn_in, but is the same as the VPN target received by the Spoke-PEs.
Create an IPv6 VPN instance on each Spoke-PE. The VPN target received by the IPv6 VPN instance is the same as the VPN target advertised by vpn_out, and the VPN target advertised by the IPv6 VPN instance is the same as the VPN target received by vpn_in.
Configure BGP4+ on the CEs and PEs to enable them to exchange VPN routing information.
Configure the Hub-PE to accept the routes with two repeated AS numbers.

Ensure that STP is disabled on the Hub-PE and Hub-CE.
Procedure
- Configure an IGP protocol on the backbone network to enable
the Hub-PE and Spoke-PEs to communicate with each other.
In this example, OSPF and Spoke-PE1 are used as examples.
# Configure Spoke-PE1.
<HUAWEI> system-view [HUAWEI] sysname Spoke-PE1 [Spoke-PE1] ospf 1 [Spoke-PE1-ospf-1] area 0 [Spoke-PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 8.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [Spoke-PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 1.1.1.9 0.0.0.0 [Spoke-PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [Spoke-PE1-ospf-1] quit
The configuration on the Hub-PE and Spoke-PE2 is similar to the configuration on Spoke-PE1 and is not mentioned here.
After the configuration is complete, an OSPF neighbor relationship is established between the PEs. Run the display ospf peer command, and you can see that the neighbor status is Full. Run the display ip routing-table command on the PEs. The command output shows that the PEs have learned the route to the loopback interface of each other.
- Configure basic MPLS capabilities and MPLS LDP on the backbone
network to establish LDP LSPs.
# Configure the Hub-PE.
[Hub-PE] mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.9 [Hub-PE] mpls [Hub-PE-mpls] quit [Hub-PE] mpls ldp [Hub-PE-mpls-ldp] quit [Hub-PE] interface vlanif 10 [Hub-PE-Vlanif10] mpls [Hub-PE-Vlanif10] mpls ldp [Hub-PE-Vlanif10] quit [Hub-PE] interface vlanif 20 [Hub-PE-Vlanif20] mpls [Hub-PE-Vlanif20] mpls ldp [Hub-PE-Vlanif20] quit
# The configuration on Spoke-PEs is similar to the configuration on the Hub-PE and is not mentioned here.
After the configuration is complete, LDP peer relationships are established between the Hub-PE and Spoke-PEs. Run the display mpls ldp session command on each device, and you can see that the status is Operational.
- Configure IPv6 VPN instances on PEs and bind the interfaces
connected to CEs to the VPN instances.

The VPN targets of the two IPv6 VPN instances on the Hub-PE are the VPN targets advertised by the two Spoke-PEs, and the advertised VPN target is different from the received VPN target.
Configure IPv6 VPN instances on Spoke-PEs. The import VPN target on the Spoke-PEs is the VPN target advertised by the Hub-PE.
# Configure Spoke-PE1.
[Spoke-PE1] ip vpn-instance vpna [Spoke-PE1-vpn-instance-vpna] ipv6-family [Spoke-PE1-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv6] route-distinguisher 100:1 [Spoke-PE1-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv6] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity [Spoke-PE1-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv6] vpn-target 200:1 import-extcommunity [Spoke-PE1-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv6] quit [Spoke-PE1-vpn-instance-vpna] quit [Spoke-PE1] interface vlanif 50 [Spoke-PE1-Vlanif50] ipv6 enable [Spoke-PE1-Vlanif50] ip binding vpn-instance vpna [Spoke-PE1-Vlanif50] ipv6 address 2001::2 64 [Spoke-PE1-Vlanif50] quit
#Configure Spoke-PE2.
[Spoke-PE2] ip vpn-instance vpna [Spoke-PE2-vpn-instance-vpna] ipv6-family [Spoke-PE2-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv6] route-distinguisher 100:3 [Spoke-PE2-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv6] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity [Spoke-PE2-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv6] vpn-target 200:1 import-extcommunity [Spoke-PE2-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv6] quit [Spoke-PE2-vpn-instance-vpna] quit [Spoke-PE2] interface vlanif 60 [Spoke-PE2-Vlanif60] ipv6 enable [Spoke-PE2-Vlanif60] ip binding vpn-instance vpna [Spoke-PE2-Vlanif60] ipv6 address 2002::2 64 [Spoke-PE2-Vlanif60] quit
# Configure the Hub-PE.
[Hub-PE] ip vpn-instance vpn_in [Hub-PE-vpn-instance-vpn_in] ipv6-family [Hub-PE-vpn-instance-vpn_in-af-ipv6] route-distinguisher 100:21 [Hub-PE-vpn-instance-vpn_in-af-ipv6] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity [Hub-PE-vpn-instance-vpn_in-af-ipv6] quit [Hub-PE-vpn-instance-vpn_in] quit [Hub-PE] ip vpn-instance vpn_out [Hub-PE-vpn-instance-vpn_out] ipv6-family [Hub-PE-vpn-instance-vpn_out-af-ipv6] route-distinguisher 100:22 [Hub-PE-vpn-instance-vpn_out-af-ipv6] vpn-target 200:1 export-extcommunity [Hub-PE-vpn-instance-vpn_out-af-ipv6] quit [Hub-PE-vpn-instance-vpn_out] quit [Hub-PE] interface vlanif 30 [Hub-PE-Vlanif30] ipv6 enable [Hub-PE-Vlanif30] ip binding vpn-instance vpn_in [Hub-PE-Vlanif30] ipv6 address 2003::2 64 [Hub-PE-Vlanif30] quit [Hub-PE] interface vlanif 40 [Hub-PE-Vlanif40] ipv6 enable [Hub-PE-Vlanif40] ip binding vpn-instance vpn_out [Hub-PE-Vlanif40] ipv6 address 2004::2 64 [Hub-PE-Vlanif40] quit
# Assign IPv6 addresses to the interfaces on the CEs according to Figure 1. The configuration procedure is not mentioned here.
After the configuration is complete, run the display ip vpn-instance verbose command on the PEs to check the configuration of IPv6 VPN instances. Each PE can ping its connected CE.
- Establish EBGP peer relationships between PEs and CEs and
import VPN routes into BGP.

To accept the routes advertised by Hub-CE, configure the Hub-PE to allow AS number to be repeated once.
# Configure Spoke-CE1.
<HUAWEI> system-view [HUAWEI] sysname Spoke-CE1 [Spoke-CE1] bgp 65410 [Spoke-CE1-bgp] router-id 10.10.10.10 [Spoke-CE1-bgp] peer 2001::2 as-number 100 [Spoke-CE1-bgp] ipv6-family unicast [Spoke-CE1-bgp-af-ipv6] peer 2001::2 enable [Spoke-CE1-bgp-af-ipv6] import-route direct [Spoke-CE1-bgp-af-ipv6] quit [Spoke-CE1-bgp] quit
# Configure Spoke-PE1.
[Spoke-PE1] bgp 100 [Spoke-PE1-bgp] ipv6-family vpn-instance vpna [Spoke-PE1-bgp6-vpna] peer 2001::1 as-number 65410 [Spoke-PE1-bgp6-vpna] import-route direct [Spoke-PE1-bgp6-vpna] quit [Spoke-PE1-bgp] quit
# Configure Spoke-CE2.
<HUAWEI> system-view [HUAWEI] sysname Spoke-CE2 [Spoke-CE2] bgp 65420 [Spoke-CE2-bgp] router-id 20.20.20.20 [Spoke-CE2-bgp] peer 2002::2 as-number 100 [Spoke-CE2-bgp] ipv6-family unicast [Spoke-CE2-bgp-af-ipv6] peer 2002::2 enable [Spoke-CE2-bgp-af-ipv6] import-route direct [Spoke-CE2-bgp-af-ipv6] quit [Spoke-CE2-bgp] quit
#Configure Spoke-PE2.
[Spoke-PE2] bgp 100 [Spoke-PE2-bgp] ipv6-family vpn-instance vpna [Spoke-PE2-bgp6-vpna] peer 2002::1 as-number 65420 [Spoke-PE2-bgp6-vpna] import-route direct [Spoke-PE2-bgp6-vpna] quit [Spoke-PE2-bgp] quit
# Configure the Hub-CE.
<HUAWEI> system-view [HUAWEI] sysname Hub-CE [Hub-CE] bgp 65430 [Hub-CE-bgp] router-id 30.30.30.30 [Hub-CE-bgp] peer 2003::2 as-number 100 [Hub-CE-bgp] peer 2004::2 as-number 100 [Hub-CE-bgp] ipv6-family unicast [Hub-CE-bgp-af-ipv6] peer 2003::2 enable [Hub-CE-bgp-af-ipv6] peer 2004::2 enable [Hub-CE-bgp-af-ipv6] import-route direct [Hub-CE-bgp-af-ipv6] quit [Hub-CE-bgp] quit
# Configure the Hub-PE.
[Hub-PE] bgp 100 [Hub-PE-bgp] ipv6-family vpn-instance vpn_in [Hub-PE-bgp6-vpn_in] peer 2003::1 as-number 65430 [Hub-PE-bgp6-vpn_in] import-route direct [Hub-PE-bgp6-vpn_in] quit [Hub-PE-bgp] ipv6-family vpn-instance vpn_out [Hub-PE-bgp6-vpn_out] peer 2004::1 as-number 65430 [Hub-PE-bgp6-vpn_out] peer 2004::1 allow-as-loop 1 [Hub-PE-bgp6-vpn_out] import-route direct [Hub-PE-bgp6-vpn_out] quit [Hub-PE-bgp] quit
After the configuration is complete, run the display bgp vpnv6 all peer command on the PEs. The command output shows that the BGP peer relationships have been established between the PEs and CEs and are in Established state. Each PE can ping its connected CE.

If multiple interfaces on a PE are bound to the same VPN, you must specify the source IPv6 address when you run the ping ipv6 vpn-instance command to ping the CE connected to the peer PE. That is, specify -a source-ipv6-address in the ping ipv6 vpn-instance vpn-instance-name -a source-ipv6-address dest-ipv6-address command. Otherwise, the ping operation may fail.
- Establish MP-IBGP peer relationships between PEs.
Establish MP-IBGP peer relationships between the Spoke-PEs and the Hub-PE, but do not establish an MP-IBGP peer relationship between the Spoke-PEs.

The Spoke-PEs do not need to allow the repeated AS number, because the switch does not check the AS_Path attribute in the routing information advertised by the IBGP peers.
# Configure Spoke-PE1.
[Spoke-PE1] bgp 100 [Spoke-PE1-bgp] peer 2.2.2.9 as-number 100 [Spoke-PE1-bgp] peer 2.2.2.9 connect-interface loopback 1 [Spoke-PE1-bgp] ipv6-family vpnv6 [Spoke-PE1-bgp-af-vpnv6] peer 2.2.2.9 enable [Spoke-PE1-bgp-af-vpnv6] quit [Spoke-PE1-bgp] quit
#Configure Spoke-PE2.
[Spoke-PE2] bgp 100 [Spoke-PE2-bgp] peer 2.2.2.9 as-number 100 [Spoke-PE2-bgp] peer 2.2.2.9 connect-interface loopback 1 [Spoke-PE2-bgp] ipv6-family vpnv6 [Spoke-PE2-bgp-af-vpnv6] peer 2.2.2.9 enable [Spoke-PE2-bgp-af-vpnv6] quit [Spoke-PE2-bgp] quit
# Configure the Hub-PE.
[Hub-PE] bgp 100 [Hub-PE-bgp] peer 1.1.1.9 as-number 100 [Hub-PE-bgp] peer 1.1.1.9 connect-interface loopback 1 [Hub-PE-bgp] peer 3.3.3.9 as-number 100 [Hub-PE-bgp] peer 3.3.3.9 connect-interface loopback 1 [Hub-PE-bgp] ipv6-family vpnv6 [Hub-PE-bgp-af-vpnv6] peer 1.1.1.9 enable [Hub-PE-bgp-af-vpnv6] peer 3.3.3.9 enable [Hub-PE-bgp-af-vpnv6] quit [Hub-PE-bgp] quit
After the configuration is complete, run the display bgp peer or display bgp vpnv6 all peer command on the PEs. The command output shows that BGP peer relationships between the PEs are in Established state.
- Verify the configuration.
After the configuration is complete, the Spoke-CEs can ping each other. Run the tracert command on the Spoke-CEs, and you can see that the traffic between the Spoke-CEs is forwarded through the Hub-CE.
The information displayed on Spoke-CE1 is used as an example.
[Spoke-CE1] ping ipv6 2002::1 PING 2002::1 : 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break Reply from 2002::1 bytes=56 Sequence=1 hop limit=59 time = 187 ms Reply from 2002::1 bytes=56 Sequence=2 hop limit=59 time = 187 ms Reply from 2002::1 bytes=56 Sequence=3 hop limit=59 time = 187 ms Reply from 2002::1 bytes=56 Sequence=4 hop limit=59 time = 187 ms Reply from 2002::1 bytes=56 Sequence=5 hop limit=59 time = 187 ms --- 2002::1 ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 187/187/187 ms[Spoke-CE1] tracert ipv6 2002::1 traceroute to 2002::1 30 hops max,60 bytes packet 1 2001::2 31 ms 31 ms 32 ms 2 2004::2 93 ms 94 ms 110 ms 3 2004::1 93 ms 94 ms 94 ms 4 2003::2 94 ms 93 ms 94 ms 5 2002::2 156 ms 157 ms 156 ms 6 2002::1 187 ms 188 ms 187 ms
Run the display bgp ipv6 routing-table command on a Spoke-CE, and you can see the repeated AS numbers in AS paths of the BGP routes to the remote Spoke-CE.
The information displayed on Spoke-CE1 is used as an example.
[Spoke-CE1] display bgp ipv6 routing-table BGP Local router ID is 10.10.10.10 Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - damped, h - history, i - internal, s - suppressed, S - Stale Origin : i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete Total Number of Routes: 8 *> Network : ::1 PrefixLen : 128 NextHop : :: LocPrf : MED : 0 PrefVal : 0 Label : Path/Ogn : ? *> Network : 2001:: PrefixLen : 64 NextHop : :: LocPrf : MED : 0 PrefVal : 0 Label : Path/Ogn : ? * NextHop : 2001::2 LocPrf : MED : 0 PrefVal : 0 Label : Path/Ogn : 100 ? *> Network : 2001::1 PrefixLen : 128 NextHop : :: LocPrf : MED : 0 PrefVal : 0 Label : Path/Ogn : ? *> Network : 2002:: PrefixLen : 64 NextHop : 2001::2 LocPrf : MED : PrefVal : 0 Label : Path/Ogn : 100 65430 100 ? *> Network : 2003:: PrefixLen : 64 NextHop : 2001::2 LocPrf : MED : PrefVal : 0 Label : Path/Ogn : 100 65430 ? *> Network : 2004:: PrefixLen : 64 NextHop : 2001::2 LocPrf : MED : PrefVal : 0 Label : Path/Ogn : 100 ? *> Network : FE80:: PrefixLen : 10 NextHop : :: LocPrf : MED : 0 PrefVal : 0 Label : Path/Ogn : ?
Configuration Files
Spoke-CE1 configuration file
# sysname Spoke-CE1 # ipv6 # vlan batch 50 # interface Vlanif50 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001::1/64 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 50 # bgp 65410 router-id 10.10.10.10 peer 2001::2 as-number 100 # ipv6-family unicast undo synchronization import-route direct peer 2001::2 enable # return
Spoke-PE1 configuration file
# sysname Spoke-PE1 # ipv6 # vlan batch 10 50 # ip vpn-instance vpna ipv6-family route-distinguisher 100:1 vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 200:1 import-extcommunity # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.9 mpls # mpls ldp # interface Vlanif10 ip address 8.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface Vlanif50 ip binding vpn-instance vpna ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001::2/64 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 50 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 10 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 1.1.1.9 255.255.255.255 # bgp 100 peer 2.2.2.9 as-number 100 peer 2.2.2.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 2.2.2.9 enable # ipv6-family vpnv6 policy vpn-target peer 2.2.2.9 enable # ipv6-family vpn-instance vpna import-route direct peer 2001::1 as-number 65410 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 8.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 1.1.1.9 0.0.0.0 # return
Spoke-PE2 configuration file
# sysname Spoke-PE2 # ipv6 # vlan batch 20 60 # ip vpn-instance vpna ipv6-family route-distinguisher 100:3 vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 200:1 import-extcommunity # mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.9 mpls # mpls ldp # interface Vlanif20 ip address 9.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface Vlanif60 ip binding vpn-instance vpna ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2002::2/64 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 60 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 20 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 3.3.3.9 255.255.255.255 # bgp 100 peer 2.2.2.9 as-number 100 peer 2.2.2.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 2.2.2.9 enable # ipv6-family vpnv6 policy vpn-target peer 2.2.2.9 enable # ipv6-family vpn-instance vpna import-route direct peer 2002::1 as-number 65420 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 3.3.3.9 0.0.0.0 network 9.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # return
Spoke-CE2 configuration file
# sysname Spoke-CE2 # ipv6 # vlan batch 60 # interface Vlanif60 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2002::1/64 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 60 # bgp 65420 router-id 20.20.20.20 peer 2002::2 as-number 100 # ipv6-family unicast undo synchronization import-route direct peer 2002::2 enable # return
Hub-CE configuration file
# sysname Hub-CE # ipv6 # vlan batch 30 40 # interface Vlanif30 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2003::1/64 # interface Vlanif40 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2004::1/64 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 30 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 40 # bgp 65430 router-id 30.30.30.30 peer 2003::2 as-number 100 peer 2004::2 as-number 100 # ipv6-family unicast undo synchronization import-route direct peer 2003::2 enable peer 2004::2 enable # return
Hub-PE configuration file
# sysname Hub-PE # ipv6 # vlan batch 10 20 30 40 # ip vpn-instance vpn_in ipv6-family route-distinguisher 100:21 vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity # ip vpn-instance vpn_out ipv6-family route-distinguisher 100:22 vpn-target 200:1 export-extcommunity # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.9 mpls # mpls ldp # interface Vlanif10 ip address 8.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface Vlanif20 ip address 9.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface Vlanif30 ip binding vpn-instance vpn_in ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2003::2/64 # interface Vlanif40 ip binding vpn-instance vpn_out ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2004::2/64 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 10 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 20 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/3 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 30 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/4 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 40 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 2.2.2.9 255.255.255.255 # bgp 100 peer 1.1.1.9 as-number 100 peer 1.1.1.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 peer 3.3.3.9 as-number 100 peer 3.3.3.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 1.1.1.9 enable peer 3.3.3.9 enable # ipv6-family vpnv6 policy vpn-target peer 1.1.1.9 enable peer 3.3.3.9 enable # ipv6-family vpn-instance vpn_in import-route direct peer 2003::1 as-number 65430 # ipv6-family vpn-instance vpn_out import-route direct peer 2004::1 as-number 65430 peer 2004::1 allow-as-loop # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 2.2.2.9 0.0.0.0 network 8.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 9.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # return