Why Do I Need to Disable MAC Address Learning When Configuring Layer 2 Remote Port Mirroring?
First, it is important to understand how mirrored packets are forwarded to the monitoring device after Layer 2 remote port mirroring is configured.
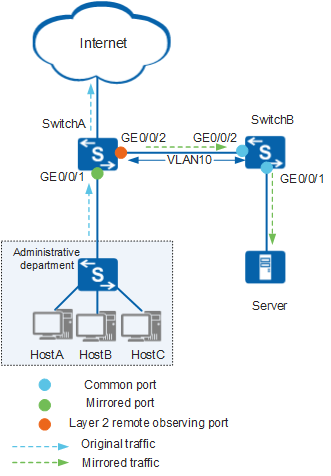
As shown in Figure 1, Layer 2 remote mirroring is configured on SwitchA. Mirrored packets are forwarded to intermediate device SwitchB through VLAN 10. SwitchB has no mirroring configuration and therefore forwards mirrored packets to the server in accordance with the common Layer 2 forwarding process. In addition, the mirrored packets cannot be forwarded according to the MAC address table because their destination MAC address is the same as that of the original packets, not the server's MAC address. To reach the server, the mirrored packets must be treated as unknown unicast packets and broadcast to all interfaces in VLAN 10. The mirrored packets can only be forwarded to the server in broadcast mode if the MAC address table of VLAN 10 contains no entry matching the destination MAC address of the mirrored packets.
In most Layer 2 remote mirroring scenarios, intermediate devices will not learn destination MAC addresses of mirrored packets in the corresponding VLANs. This means that mirrored packets can be forwarded to the monitoring devices in broadcast mode. In the following scenarios, however, Layer 2 remote port mirroring will fail because destination MAC addresses of mirrored packets can be learned in the corresponding VLANs.
The original service traffic and mirrored traffic are forwarded in the same VLAN.
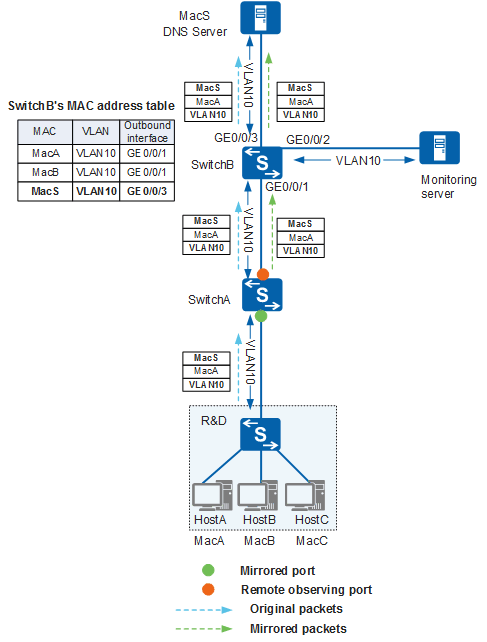
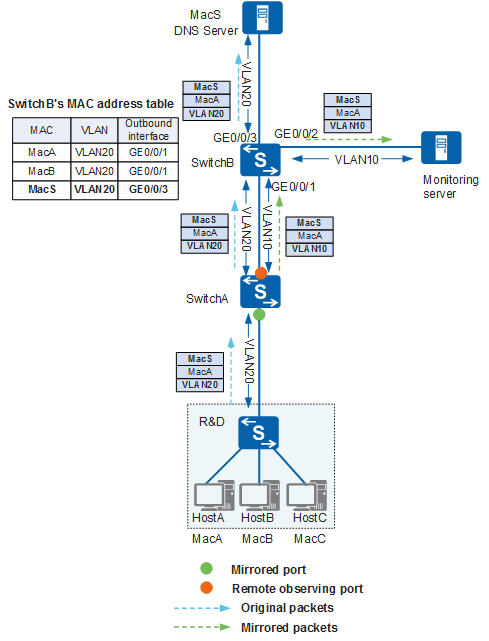
As shown in Figure 2, a company configures Layer 2 remote port mirroring on SwitchA to monitor the traffic sent from employees in the R&D department to the DNS server. The original traffic and mirrored traffic are both forwarded through VLAN 10. When SwitchA receives the packets sent from HostA to the DNS server, it copies the packets and forwards the mirrored packets in VLAN 10. The mirrored packets and original packets all use the MAC address of the DNS server as the destination MAC address. The devices between HostA and the DNS server all learn the MAC address entry matching the DNS server. Therefore, SwitchB forwards the mirrored packets that it receives in VLAN 10 according to the learned MAC address entry. The mirrored packets cannot reach the monitoring server, and Layer 2 remote port monitoring fails.
Solution:
Use different VLANs to forward the original service traffic and mirrored traffic, as shown in Figure 3. If the original service traffic and mirrored traffic need to be forwarded in the same VLAN, run the mac-address learning disable command to disable MAC address learning in this VLAN (VLAN 10 in this example). However, disabling MAC address learning will waste link bandwidth, especially when there are a large number of access users.
Mirrored packets from different source MAC addresses are forwarded in the same VLAN.
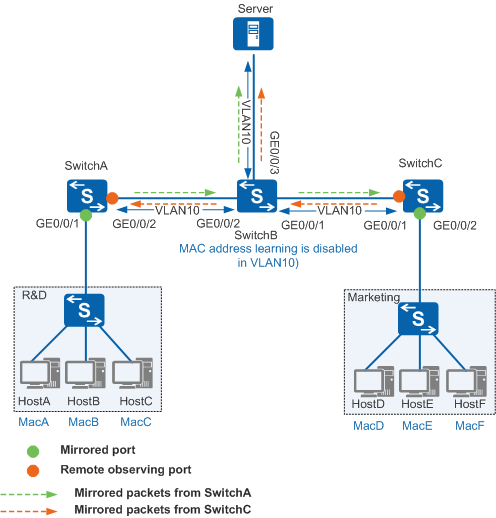
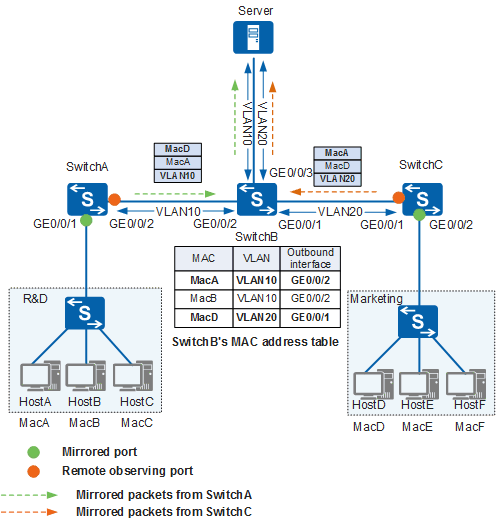
As shown in Figure 4, a company configures Layer 2 remote port mirroring on SwitchA and SwitchC to monitor communication traffic between the R&D and marketing departments. All mirrored packets are forwarded in VLAN 10, and the original communication traffic between the two departments is forwarded in another VLAN. When packets sent from downstream hosts arrive at the mirrored port on SwitchA and SwitchC, SwitchA and SwitchC copy the packets and forward the mirrored packets in VLAN 10. Source MAC addresses of the mirrored packets are MAC addresses of sender hosts, which can be learned in the MAC address table of SwitchB. Because destination MAC addresses of the mirrored packets are MAC addresses of destination hosts, SwitchB forwards the mirrored packets according to the matching entries found in its MAC address table. Layer 2 remote port mirroring fails.
Use any of the following methods to solve the preceding problem:
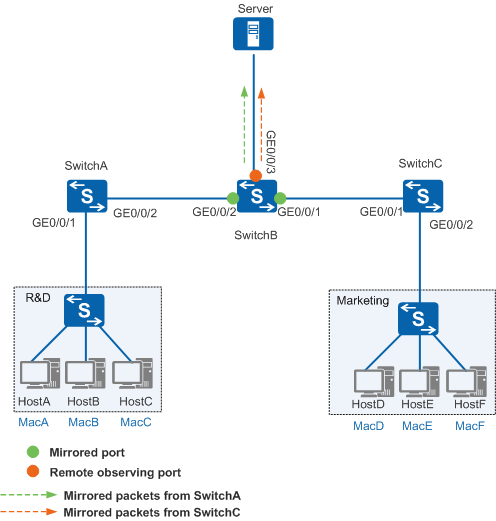
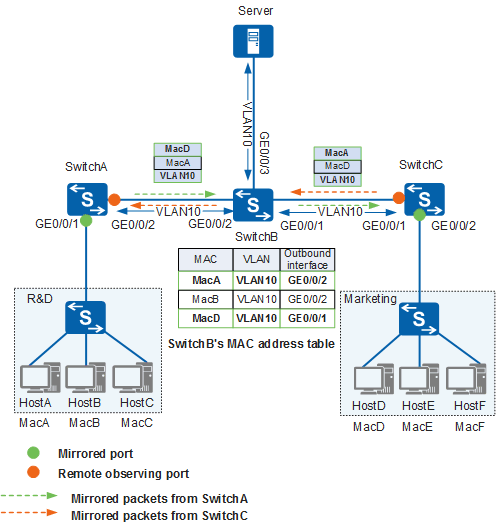
Run the mac-address learning disable command on SwitchB to disable MAC address learning in VLAN 10. Figure 5 shows the packet flows after MAC address learning is disabled in VLAN 10.
Configure port mirroring on SwitchB: configure the ports connected to SwitchA and SwitchC as mirrored ports, and configure the port connected to the monitoring server as a local observing port. Figure 6 shows the packet flow after port mirroring is configured on SwitchB.
Use different VLANs to forward the mirrored packets in different directions, as shown in Figure 7.