Example for Configuring Non-authentication for IP Phones and 802.1X Authentication for PCs Connected to IP Phones
Networking Requirements
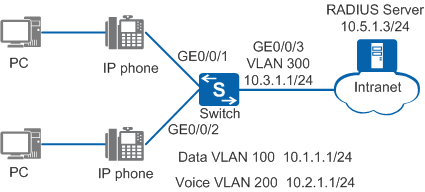
In Figure 1, to save investment costs, the customer requires that IP phones and PCs connect to the network through VoIP. IP phones support LLDP and can obtain the voice VLAN through LLDP. The network plan should meet the following requirements:
The priority of voice packets sent by IP phones is low and needs to be increased to ensure communication quality.
Voice and data packets are transmitted in VLAN 200 and VLAN 100, respectively.
IP phones and PCs obtain IP addresses from a DHCP server.
IP phones connect to switches without authentication and PCs connect to switches through 802.1X authentication.
Configuration Precautions
- This section describes only NAC configurations on Switch. The RADIUS server configurations are not provided here.
The RADIUS authentication and accounting keys configured on the RADIUS server must be the same as the shared key of the RADIUS server configured on the device.
- The default outbound interface IP address of the device is used as the source IP address for sending RADIUS packets to the RADIUS server. This IP address must be the same as the device IP address configured on the RADIUS server. You can change the source IP address as follows:
- Run the radius-server authentication ip-address port source command to configure a RADIUS authentication server and specify the source IP address used by the device to send RADIUS packets to the RADIUS authentication server.
- Run the radius-server accounting ip-address port source command to configure a RADIUS accounting server and specify the source IP address used by the device to send RADIUS packets to the RADIUS accounting server.
- Negotiating a voice VLAN through LLDP takes a period of time. To ensure that IP phones can quickly go online in the voice VLAN after going online in the data VLAN, enable MAC address migration.
- The IP phone interoperation solutions vary according to the attributes and models of IP phones. For details, see Interoperation Between Huawei Switches and IP Phones.
Configuration Roadmap
- Configure network connectivity on switches.
- Configure the DHCP function on Switch to assign IP addresses to PCs and IP phones.
- Configure AAA on Switch to implement RADIUS authentication, authorization, and accounting for users.
- Configure non-authentication for IP phones and 802.1X authentication for PCs connected to IP phones on Switch to implement access authentication.
Procedure
- Configure network connectivity.
# Create VLANs and enable the LLDP function.
<HUAWEI> system-view [HUAWEI] sysname Switch [Switch] vlan batch 100 200 300 [Switch] lldp enable
# Add interfaces to the data VLAN.
[Switch] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1 [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port link-type hybrid [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port hybrid pvid vlan 100 [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port hybrid untagged vlan 100 [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit [Switch] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/2 [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port link-type hybrid [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port hybrid pvid vlan 100 [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port hybrid untagged vlan 100 [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit [Switch] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/3 [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] port link-type access [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] port default vlan 300 [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] quit [Switch] interface vlanif 100 [Switch-Vlanif100] ip address 10.1.1.1 24 [Switch-Vlanif100] quit [Switch] interface vlanif 300 [Switch-Vlanif300] ip address 10.3.1.1 24 [Switch-Vlanif300] quit
# Add interfaces to the voice VLAN.
[Switch] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1 [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port hybrid tagged vlan 200 [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit [Switch] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/2 [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port hybrid tagged vlan 200 [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit [Switch] interface vlanif 200 [Switch-Vlanif200] ip address 10.2.1.1 24 [Switch-Vlanif200] quit
# Enable the voice VLAN on interfaces and configure the interfaces to authorize the voice VLAN in TLV mode.
[Switch] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1 [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] voice-vlan 200 enable //Configure VLAN 200 as the voice VLAN. [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] stp edged-port enable //Configure the interface as an edge port. [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] poe legacy enable //Enable Switch (a PoE switch) to check the compatibility of PDs to ensure that it can provide power for non-standard PDs. [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] lldp tlv-enable med-tlv network-policy voice-vlan vlan 200 cos 6 dscp 60 //Configure the interface to advertise Network Policy TLV that encapsulates a voice VLAN and configure priorities. [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] lldp compliance cdp txrx //Enable the interface to exchange information with CDP-capable voice devices. [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] lldp compliance cdp receive //Enable CDP-compatible LLDP on the interface. [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit [Switch] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/2 [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] voice-vlan 200 enable [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] stp edged-port enable [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] poe legacy enable [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] lldp tlv-enable med-tlv network-policy voice-vlan vlan 200 cos 6 dscp 60 [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] lldp compliance cdp txrx [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] lldp compliance cdp receive [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
# Configure a static route destined for the server area. In this example, the next hop is 10.3.1.2.
[Switch] ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.3.1.2
- Configure the DHCP function.
[Switch] dhcp enable [Switch] interface vlanif 100 [Switch-Vlanif100] dhcp select interface [Switch-Vlanif100] quit [Switch] interface vlanif 200 [Switch-Vlanif200] dhcp select interface [Switch-Vlanif200] quit
- Configure AAA.# Create and configure a RADIUS server template named rd1.
[Switch] radius-server template rd1 [Switch-radius-rd1] radius-server authentication 10.5.1.3 1812 [Switch-radius-rd1] radius-server accounting 10.5.1.3 1813 [Switch-radius-rd1] radius-server shared-key cipher Huawei@2014 [Switch-radius-rd1] quit
# Create an AAA authentication scheme named abc and set the authentication mode to RADIUS.[Switch] aaa [Switch-aaa] authentication-scheme abc [Switch-aaa-authen-abc] authentication-mode radius [Switch-aaa-authen-abc] quit
# Configure an accounting scheme named acco1.[Switch-aaa] accounting-scheme acco1 [Switch-aaa-accounting-acco1] accounting-mode radius [Switch-aaa-accounting-acco1] accounting realtime 15 [Switch-aaa-accounting-acco1] quit
# Create an authentication domain named isp, and bind the AAA authentication scheme abc, accounting scheme acco1, and RADIUS server template rd1 to the domain.[Switch-aaa] domain isp [Switch-aaa-domain-isp] authentication-scheme abc [Switch-aaa-domain-isp] accounting-scheme acco1 [Switch-aaa-domain-isp] radius-server rd1 [Switch-aaa-domain-isp] quit [Switch-aaa] quit
- Configure non-authentication for IP phones and 802.1X authentication for PCs.# Change the NAC mode to unified.
[Switch] authentication unified-mode

By default, the unified mode is enabled. After you change the NAT mode between common and unified, the device automatically restarts.
# Configure an 802.1X access profile and set the client authentication timeout interval to 30 seconds.[Switch] dot1x-access-profile name d1 [Switch-dot1x-access-profile-d1] dot1x authentication-method eap [Switch-dot1x-access-profile-d1] dot1x timer client-timeout 30 [Switch-dot1x-access-profile-d1] quit
# Enable MAC address migration and pre-migration detection.[Switch] authentication mac-move enable vlan all [Switch] authentication mac-move detect enable
# Bind the 802.1X access profile to the authentication profile p1.[Switch] authentication-profile name p1 [Switch-authen-profile-p1] dot1x-access-profile d1
# Configure a forcible authentication domain. If user names carry domain names, you do not need to configure a forcible authentication domain for 802.1X users.
[Switch-authen-profile-p1] access-domain isp dot1x force
# Enable IP phones to go online without authentication.
[Switch-authen-profile-p1] authentication device-type voice authorize [Switch-authen-profile-p1] quit
# Bind the authentication profile to interfaces.
[Switch] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1 [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] authentication-profile p1 [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit [Switch] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/2 [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] authentication-profile p1 [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
- Verify the configuration.
After an IP phone starts, it automatically obtains an IP address and connects to the network without authentication.
A user starts a PC and enters the user name and password, triggering 802.1X authentication. After the authentication is successful, the user can access the network.
- After the user goes online, run the display access-user mac-address command to check information about the online user.