802.1X Authentication Process
Triggering of 802.1X Authentication
- A client sends an EAPoL-Start packet.
- A client sends a DHCP, ARP, DHCPv6, ND, or any packet.
- The device sends an EAP-Request/Identity packet.
Authentication Processes in EAP Relay and EAP Termination Modes
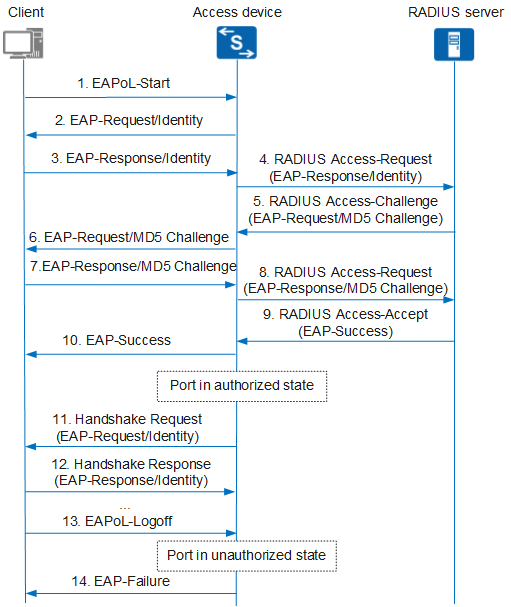
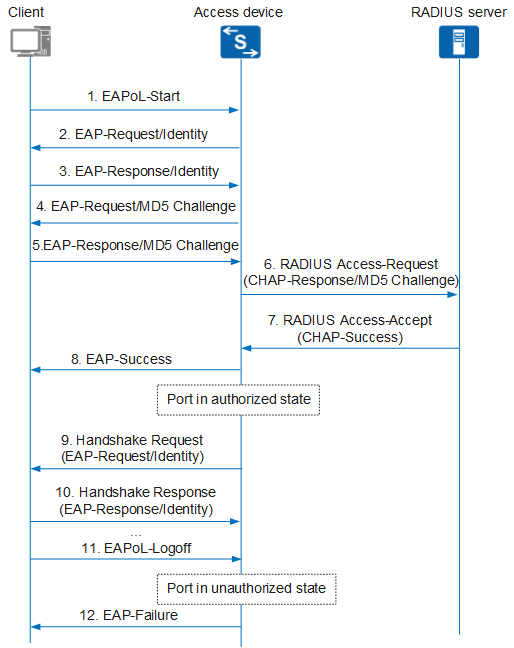
In the 802.1X authentication system, the access device exchanges information with the RADIUS server in EAP relay or EAP termination mode. Figure 1 and Figure 2 respectively show the 802.1X authentication processes in EAP relay and EAP termination modes. In both processes, authentication is initiated by the client.
To access an extranet, a user starts the 802.1X client program, enters the applied and registered user name and password, and initiates a connection request. At this time, the client sends an EAPoL-Start packet to the access device to start the authentication process.
After receiving the EAPoL-Start packet, the access device returns an EAP-Request/Identity packet to the client for its identity.
Upon receipt of the EAP-Request/Identity packet, the client sends an EAP-Response/Identity packet that contains the user name to the access device.
The access device encapsulates the EAP-Response/Identity packet into a RADIUS Access-Request packet and sends the RADIUS packet to the authentication server.
After receiving the user name forwarded by the access device, the RADIUS server searches the user name table in the database for the corresponding password, encrypts the password with a randomly generated MD5 challenge, and sends a RADIUS Access-Challenge packet containing the MD5 challenge to the access device.
The access device forwards the MD5 challenge sent by the RADIUS server to the client.
Upon receipt of the MD5 challenge, the client encrypts the password with the MD5 challenge, generates an EAP-Response/MD5-Challenge packet, and sends the packet to the access device.
- The access device encapsulates the EAP-Response/MD5-Challenge packet into a RADIUS Access-Request packet and sends the RADIUS packet to the RADIUS server.
- The RADIUS server compares the received encrypted password with the locally encrypted password. If the two passwords match, the user is considered to be valid and the RADIUS server sends a RADIUS Access-Accept packet (authentication is successful) to the access device.
- After receiving the RADIUS Access-Accept packet, the access device sends an EAP-Success packet to the client, changes the port state to authorized, and allows the user to access the network through the port.
- When the user is online, the access device periodically sends a handshake packet to the client to monitor the user.
- After receiving a handshake packet, the client sends a response packet to the access device, indicating that the user is still online. By default, the access device disconnects the user if it does not receive any response from the client after sending two consecutive handshake packets. The handshake mechanism allows the access device to detect unexpected user disconnections.
- To go offline, the client sends an EAPoL-Logoff packet to the access device.
- The access device changes the port state from authorized to unauthorized and sends an EAP-Failure packet to the client.
In EAP termination mode, the MD5 challenge for encrypting the user password is randomly generated by the access device, instead of the authentication server in EAP relay mode. Besides, in EAP termination mode, the access device uses the CHAP protocol to encapsulate the user name, challenge, and password encrypted by the client into standard RADIUS packets and sends them to the authentication server for authentication. In EAP relay mode, in contrast, the access device is only responsible for encapsulating EAP packets into RADIUS packets and transparently transmitting them to the authentication server.