(Optional) Configuring the MAC Address Migration Function
Context
The access locations of enterprise users' terminals always change. For example, employees move to other offices for working or presentation using laptops. By default, a user cannot immediately initiate authentication and access the network after being switched to a new interface. The user can initiate authentication on the current interface only after the user offline detection interval expires or the authentication interface is manually enabled and shut down to clear user online entries. To improve user experience, MAC address migration is enabled so that the user can immediately initiate authentication and access the network after be switched to another access interface.
MAC address migration allows online NAC authentication users to immediately initiate authentication and access the network after they are switched to other access interfaces. If the user is authenticated successfully on the new interface, the online user entry on the original interface is deleted immediately to ensure that only one interface records the online user entry.
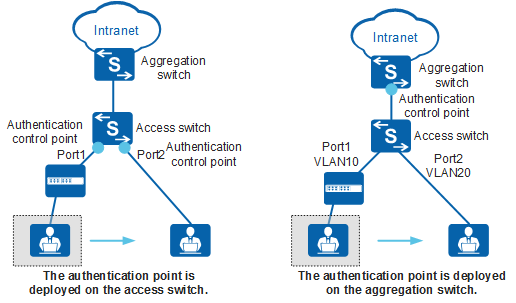
There are two typical MAC address migration scenarios, as shown in Figure 1. Scenario one: The authentication point is deployed on an access switch, and the user terminal is migrated from one authentication control point to another on the same switch. Scenario two: The authentication point is deployed on an aggregation switch. The authentication control point of the user terminal remains unchanged, and the user terminal is migrated between different interfaces on the same access switch or different access switches connected to the aggregation switch.

In normal case, enabling MAC address migration is not recommended. It should be enabled only when users have migration requirements during roaming. This prevents unauthorized users from forging MAC addresses of online users and sending ARP, 802.1X, or DHCP packets on other authentication control interfaces to trigger the MAC address migration function and force authorized user offline.
- Cascading migration through intermediate devices is not supported, because ARP and DHCP packets are not sent after the cascading migration.
- MAC address migration is not supported for Layer 3 Portal authentication users.
- In the Layer 2 BNG scenario, the device does not support MAC address migration.
- A user is switched from an interface configured with NAC authentication to another interface not configured with NAC authentication. In this case, the user can access the network only after the original online entry is aged because the new interface cannot send authentication packets to trigger MAC migration.
- In common mode, Portal authentication is triggered only after users who go online through a VLANIF interface send ARP packets and go offline; otherwise, the users can go online again only after the original user online entries age out. Portal authentication cannot be triggered after users who go online through physical interfaces migrate. The users can go online again only after the original user online entries age out.
- After a user who goes online from a VLANIF interface is quieted because of multiple MAC address migrations, MAC address migration can be performed for the quieted user only after the quiet period expires and the ARP entry is aged out.
- When an authorized VLAN is specified in the authentication mac-move enable vlan command, you are advised to enable the function of detecting the user status before user MAC address migration.
Procedure
- Run system-view
The system view is displayed.
- Run authentication mac-move enable vlan { all | { vlan-id1 [ to vlan-id2 ] } & <1–10> }
The MAC address migration function is enabled.
By default, MAC address migration is disabled.
VLANs need to be specified for users in MAC address migration. The VLANs before and after the migration can be specified for the users, and they can be the same or different.
- (Optional) Configure the MAC address migration quiet function.
When users frequently switch access interfaces (especially frequent switching due to loops), the device needs to process a large number of authentication packets and entries, which results in high CPU usage. To solve this problem, configure the MAC address migration quiet function. If the number of MAC address migration times for a user within 60 seconds exceeds the upper limit after the MAC address migration quiet function is enabled, the device quiets the user for a certain period. During the quiet period, the device does not allow users to perform MAC address migration.
In addition, the device can send logs and alarms about MAC address migration to improve maintainability of the MAC address migration quiet function.
Run authentication mac-move { quiet-times times | quiet-period quiet-value } *
The quiet period and the maximum number of MAC address migration times within 60 seconds before users enter the quiet state are configured.
The default quiet period is 0 seconds and the maximum number of MAC address migration times within 60 seconds before users enter the quiet state is 3.
Run authentication mac-move quiet-log enable
The device is enabled to record logs about MAC address migration quiet.
By default, the device is enabled to record logs about MAC address migration quiet.
After this function is enabled, the device records logs when adding or deleting MAC address migration quiet entries.
Run authentication mac-move quiet-user-alarm percentage lower-threshold upper-threshold
The upper and lower alarm thresholds for the percentage of MAC address migration users in quiet state are configured.
By default, the lower alarm threshold is 50 and upper alarm threshold is 100.
Run authentication mac-move quiet-user-alarm enable
The device is enabled to send alarms about MAC address migration quiet.
By default, the device is disabled from sending alarms about MAC address migration quiet.
After this function is enabled, the device sends alarms when the percentage of the actual user amount in the MAC address migration quiet table against the maximum number of users exceeds the upper alarm threshold configured. If the percentage decreases to be equal to or smaller than the lower alarm threshold, the device sends a clear alarm.
- (Optional) Enable a device to detect users' online status before user MAC address migration.
To prevent unauthorized users from spoofing online users to attack a device, run the authentication mac-move detect enable command to enable the device to detect users' online status before user MAC address migration. If no users are online, the device permits MAC address migration and allows users to go online from a new access interface. If a user is online, the device terminates MAC address migration and does not allow the user to go online from a new access interface.
Run authentication mac-move detect enable
A device is enabled to detect users' online status before user MAC address migration.
By default, a device is disabled from detecting users' online status before user MAC address migration.
Run authentication mac-move detect { retry-interval interval | retry-time times } *
The detection interval and maximum number of detections are set.
By default, a device detects users' online status once. The detection interval is 3 seconds.
Verifying the Configuration
- Run the display authentication mac-move configuration command to view configurations about the MAC address migration function.
- Run the display authentication mac-move quiet-user { all | mac-address mac-address } command to view information about MAC address migration users in quiet state.