Example for Configuring a Single RRPP Ring with Multiple Instances
Networking Requirements
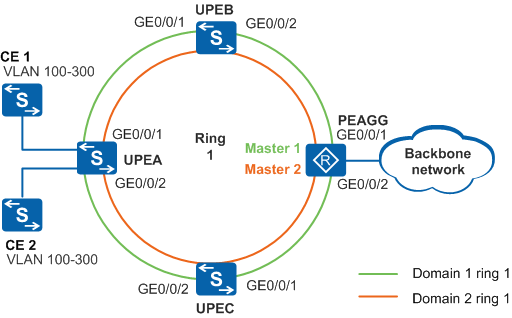
As shown in Figure 1, on a ring network, idle links are required to forward data. In this way, data in different VLANs are forwarded along different paths, improving network efficiency and implementing load balancing.
Data Plan
Table 1 shows the mapping between protected VLANs and instances in Domain 1 and Domain 2.
Domain ID |
Control VLAN ID |
Data VLAN ID |
Instance ID |
|---|---|---|---|
Domain 1 |
VLANs 5 and 6 |
VLANs 100 to 200 |
Instance 1 |
Domain 2 |
VLANs 10 and 11 |
VLANs 201 to 300 |
Instance 2 |
Table 2 shows the master node on each ring and the primary and secondary interfaces on each master node.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Create different RRPP domains and control VLANs.
Map the VLANs that need to pass through Ring 1 in Domain 1 to Instance 1, including data VLANs and control VLANs.
Map the VLANs that need to pass through Ring 1 in Domain 2 to Instance 2, including data VLANs and control VLANs.
Configure interfaces to be added to the RRPP domain on the devices so that data can pass through the interfaces. Disable protocols that conflict with RRPP, such as STP.
- Configure protected VLANs and create RRPP rings in RRPP domains.
Add UPEA, UPEB, UPEC, and PEAGG to Ring 1 in Domain 1. Configure PEAGG as the master node on Ring 1 in Domain 1 and configure UPEA, UPEB, and UPEC as transit nodes.
Add UPEA, UPEB, UPEC, and PEAGG to Ring 1 in Domain 2. Configure PEAGG as the master node on Ring 1 in Domain 2 and configure UPEA, UPEB, and UPEC as transit nodes.
Enable the RRPP ring and RRPP protocol on devices to make RRPP take effect.
Procedure
- Create an RRPP domain and its control VLAN.
# Configure UPEA. The configurations on UPEB, UPEC, and PEAGG are similar to that on UPEA and not mentioned here. For details, see the configuration files.
<HUAWEI> system-view [HUAWEI] sysname UPEA [UPEA] rrpp domain 1 [UPEA-rrpp-domain-region1] control-vlan 5 [UPEA-rrpp-domain-region1] quit [UPEA] rrpp domain 2 [UPEA-rrpp-domain-region2] control-vlan 10 [UPEA-rrpp-domain-region2] quit
- Configure instances, and map it to the data VLANs and control
VLANs allowed by the RRPP interface.
# Configure UPEA. The configurations on UPEB, UPEC, and PEAGG are the same as that of UPEA and not mentioned here. For details, see the configuration files.
[UPEA] vlan batch 100 to 300 [UPEA] stp region-configuration [UPEA-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 5 6 100 to 200 [UPEA-mst-region] instance 2 vlan 10 11 201 to 300 [UPEA-mst-region] active region-configuration [UPEA-mst-region] quit
- Configure the interfaces to be added into the RRPP rings.
# Configure UPEA. The configurations on UPEB, UPEC, and PEAGG are the same as that of UPEA and not mentioned here. For details, see the configuration files.
[UPEA] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1 [UPEA-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port link-type trunk [UPEA-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] undo port trunk allow-pass vlan 1 [UPEA-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port trunk allow-pass vlan 100 to 300 [UPEA-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] stp disable [UPEA-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit [UPEA] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/2 [UPEA-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port link-type trunk [UPEA-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] undo port trunk allow-pass vlan 1 [UPEA-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port trunk allow-pass vlan 100 to 300 [UPEA-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] stp disable [UPEA-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
- Specify a protected VLAN, and create and enable an RRPP
ring.
# Configure UPEA as a transit node on Ring 1 in Domain 1 and specify primary and secondary interfaces on UPEA.
[UPEA] rrpp domain 1 [UPEA-rrpp-domain-region1] protected-vlan reference-instance 1 [UPEA-rrpp-domain-region1] ring 1 node-mode transit primary-port gigabitethernet 0/0/1 secondary-port gigabitethernet 0/0/2 level 0 [UPEA-rrpp-domain-region1] ring 1 enable [UPEA-rrpp-domain-region1] quit
# Configure UPEA as a transit node on Ring 1 in Domain 2 and specify primary and secondary interfaces on UPEA.
[UPEA] rrpp domain 2 [UPEA-rrpp-domain-region2] protected-vlan reference-instance 2 [UPEA-rrpp-domain-region2] ring 1 node-mode transit primary-port gigabitethernet 0/0/1 secondary-port gigabitethernet 0/0/2 level 0 [UPEA-rrpp-domain-region2] ring 1 enable [UPEA-rrpp-domain-region2] quit
# Configure UPEB as a transit node on Ring 1 in Domain 1 and specify primary and secondary interfaces on UPEB.
[UPEB] rrpp domain 1 [UPEB-rrpp-domain-region1] protected-vlan reference-instance 1 [UPEB-rrpp-domain-region1] ring 1 node-mode transit primary-port gigabitethernet 0/0/1 secondary-port gigabitethernet 0/0/2 level 0 [UPEB-rrpp-domain-region1] ring 1 enable [UPEB-rrpp-domain-region1] quit
# Configure UPEB as a transit node on Ring 1 in Domain 2 and specify primary and secondary interfaces on UPEB.
[UPEB] rrpp domain 2 [UPEB-rrpp-domain-region2] protected-vlan reference-instance 2 [UPEB-rrpp-domain-region2] ring 1 node-mode transit primary-port gigabitethernet 0/0/1 secondary-port gigabitethernet 0/0/2 level 0 [UPEB-rrpp-domain-region2] ring 1 enable [UPEB-rrpp-domain-region2] quit
# Configure UPEC as a transit node on Ring 1 in Domain 1 and specify primary and secondary interfaces on UPEC.
[UPEC] rrpp domain 1 [UPEC-rrpp-domain-region1] protected-vlan reference-instance 1 [UPEC-rrpp-domain-region1] ring 1 node-mode transit primary-port gigabitethernet 0/0/1 secondary-port gigabitethernet 0/0/2 level 0 [UPEC-rrpp-domain-region1] ring 1 enable [UPEC-rrpp-domain-region1] quit
# Configure UPEC as a transit node on Ring 1 in Domain 2 and specify primary and secondary interfaces on UPEC.
[UPEC] rrpp domain 2 [UPEC-rrpp-domain-region2] protected-vlan reference-instance 2 [UPEC-rrpp-domain-region2] ring 1 node-mode transit primary-port gigabitethernet 0/0/1 secondary-port gigabitethernet 0/0/2 level 0 [UPEC-rrpp-domain-region2] ring 1 enable [UPEC-rrpp-domain-region2] quit
# Configure PEAGG as the master node on Ring 1 in Domain 1, with GE0/0/1 as the primary interface and GE0/0/2 as the secondary interface.
[PEAGG] rrpp domain 1 [PEAGG-rrpp-domain-region1] protected-vlan reference-instance 1 [PEAGG-rrpp-domain-region1] ring 1 node-mode master primary-port gigabitethernet 0/0/1 secondary-port gigabitethernet 0/0/2 level 0 [PEAGG-rrpp-domain-region1] ring 1 enable [PEAGG-rrpp-domain-region1] quit
# Configure PEAGG as the master node on Ring 1 in Domain 2, with GE0/0/2 as the primary interface and GE0/0/1 as the secondary interface.
[PEAGG] rrpp domain 2 [PEAGG-rrpp-domain-region2] protected-vlan reference-instance 2 [PEAGG-rrpp-domain-region2] ring 1 node-mode master primary-port gigabitethernet 0/0/2 secondary-port gigabitethernet 0/0/1 level 0 [PEAGG-rrpp-domain-region2] ring 1 enable [PEAGG-rrpp-domain-region2] quit
- Enable RRPP.
# Configure UPEA. The configurations on UPEB, UPEC, and PEAGG are the same as that of UPEA and not mentioned here. For details, see the configuration files.
[UPEA] rrpp enable
- Verify the configuration.
After the preceding configurations are complete and the network becomes stable, run the following commands to verify the configuration. UPEA and PEAGG are used as examples.
# Run the display rrpp brief command on UPEA. The command output is as follows:
[UPEA] display rrpp brief Abbreviations for Switch Node Mode : M - Master , T - Transit , E - Edge , A - Assistant-Edge RRPP Protocol Status: Enable RRPP Working Mode: HW RRPP Linkup Delay Timer: 0 sec (0 sec default) Number of RRPP Domains: 2 Domain Index : 1 Control VLAN : major 5 sub 6 Protected VLAN : Reference Instance 1 Hello Timer : 1 sec(default is 1 sec) Fail Timer : 6 sec(default is 6 sec) Ring Ring Node Primary/Common Secondary/Edge Is ID Level Mode Port Port Enabled ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 0 T GigabitEthernet0/0/1 GigabitEthernet0/0/2 Yes Domain Index : 2 Control VLAN : major 10 sub 11 Protected VLAN : Reference Instance 2 Hello Timer : 1 sec(default is 1 sec) Fail Timer : 6 sec(default is 6 sec) Ring Ring Node Primary/Common Secondary/Edge Is ID Level Mode Port Port Enabled ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 0 T GigabitEthernet0/0/1 GigabitEthernet0/0/2 Yes
The command output shows that RRPP is enabled on UPEA.
In Domain 1, the major control VLAN is VLAN 5 and the protected VLANs are VLANs mapping Instance 1. UPEA is a transit node on Ring 1. GigabitEthernet0/0/1 is the primary interface and GigabitEthernet0/0/2 is the secondary interface.
In Domain 2, the major control VLAN is VLAN 10 and the protected VLANs are VLANs mapping Instance 2. UPEA is a transit node on Ring 1. GigabitEthernet0/0/1 is the primary interface and GigabitEthernet0/0/2 is the secondary interface.
# Run the display rrpp brief command on PEAGG. The command output is as follows:
[PEAGG] display rrpp brief Abbreviations for Switch Node Mode : M - Master , T - Transit , E - Edge , A - Assistant-Edge RRPP Protocol Status: Enable RRPP Working Mode: HW RRPP Linkup Delay Timer: 0 sec (0 sec default) Number of RRPP Domains: 2 Domain Index : 1 Control VLAN : major 5 sub 6 Protected VLAN : Reference Instance 1 Hello Timer : 1 sec(default is 1 sec) Fail Timer : 6 sec(default is 6 sec) Ring Ring Node Primary/Common Secondary/Edge Is ID Level Mode Port Port Enabled ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 0 M GigabitEthernet0/0/1 GigabitEthernet0/0/2 Yes Domain Index : 2 Control VLAN : major 10 sub 11 Protected VLAN : Reference Instance 2 Hello Timer : 1 sec(default is 1 sec) Fail Timer : 6 sec(default is 6 sec) Ring Ring Node Primary/Common Secondary/Edge Is ID Level Mode Port Port Enabled ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 0 M GigabitEthernet0/0/2 GigabitEthernet0/0/1 Yes
The command output shows that RRPP is enabled on PEAGG.
In Domain 1, the major control VLAN is VLAN 5, the protected VLAN is the VLAN mapped to Instance 1, and the master node on Ring 1 is PEAGG. GigabitEthernet0/0/1 is the primary interface and GigabitEthernet0/0/2 is the secondary interface.
In Domain 2, the major control VLAN is VLAN 10, the protected VLAN is the VLAN mapped to Instance 2, and the master node on Ring 1 is PEAGG. GigabitEthernet0/0/2 is the primary interface and GigabitEthernet0/0/1 is the secondary interface.
# Check detailed information about UPEA in Domain 1. Run the display rrpp verbose domain command on UPEA. The command output is as follows:
[UPEA] display rrpp verbose domain 1 Domain Index : 1 Control VLAN : major 5 sub 6 Protected VLAN : Reference Instance 1 Hello Timer : 1 sec(default is 1 sec) Fail Timer : 6 sec(default is 6 sec) RRPP Ring : 1 Ring Level : 0 Node Mode : Transit Ring State : LinkUp Is Enabled : Enable Is Active: Yes Primary port : GigabitEthernet0/0/1 Port status: UP Secondary port : GigabitEthernet0/0/2 Port status: UP
The command output shows that the control VLAN in Domain 1 is VLAN 5, and the protected VLANs are the VLANs mapping Instance 1. UPEA is a transit node in Domain 1 and is in LinkUp state.
# Check detailed information about UPEA in Domain 2.
[UPEA] display rrpp verbose domain 2 Domain Index : 2 Control VLAN : major 10 sub 11 Protected VLAN : Reference Instance 2 Hello Timer : 1 sec(default is 1 sec) Fail Timer : 6 sec(default is 6 sec) RRPP Ring : 1 Ring Level : 0 Node Mode : Transit Ring State : LinkUp Is Enabled : Enable Is Active: Yes Primary port : GigabitEthernet0/0/1 Port status: UP Secondary port : GigabitEthernet0/0/2 Port status: UP
The command output shows that, in Domain 2, the control VLAN is VLAN 10 and the protected VLAN is the VLAN mapped to Instance 2. UPEA is a transit node in Domain 2 and is in LinkUp state.
Run the display rrpp verbose domain command on PEAGG. The command output is as follows:
# Check detailed information about PEAGG in Domain 1.
[PEAGG] display rrpp verbose domain 1 Domain Index : 1 Control VLAN : major 5 sub 6 Protected VLAN : Reference Instance 1 Hello Timer : 1 sec(default is 1 sec) Fail Timer : 6 sec(default is 6 sec) RRPP Ring : 1 Ring Level : 0 Node Mode : Master Ring State : Complete Is Enabled : Enable Is Active: Yes Primary port : GigabitEthernet0/0/1 Port status: UP Secondary port : GigabitEthernet0/0/2 Port status: BLOCKED
The command output shows that the control VLAN in Domain 1 is VLAN 5, and the protected VLANs are the VLANs mapping Instance 1.
PEAGG is the master node in Domain 1 and is in Complete state.
The primary interface is GigabitEthernet0/0/1 and the secondary interface is GigabitEthernet0/0/2.
# Check detailed information about PEAGG in Domain 2.
[PEAGG] display rrpp verbose domain 2 Domain Index : 2 Control VLAN : major 10 sub 11 Protected VLAN : Reference Instance 2 Hello Timer : 1 sec(default is 1 sec) Fail Timer : 6 sec(default is 6 sec) RRPP Ring : 1 Ring Level : 0 Node Mode : Master Ring State : Complete Is Enabled : Enable Is Active: Yes Primary port : GigabitEthernet0/0/2 Port status: UP Secondary port : GigabitEthernet0/0/1 Port status: BLOCKED
The command output shows that, in Domain 2, the control VLAN is VLAN 10, and the protected VLAN is the VLAN mapped to Instance 2.
PEAGG is the master node in Domain 2 and is in Complete state.
The primary interface is GigabitEthernet0/0/2 and the secondary interface is GigabitEthernet0/0/1.
Configuration Files
UPEA configuration file
# sysname UPEA # vlan batch 5 to 6 10 to 11 100 to 300 # rrpp enable # stp region-configuration instance 1 vlan 5 to 6 100 to 200 instance 2 vlan 10 to 11 201 to 300 active region-configuration # rrpp domain 1 control-vlan 5 protected-vlan reference-instance 1 ring 1 node-mode transit primary-port GigabitEthernet0/0/1 secondary-port GigabitEthernet0/0/2 level 0 ring 1 enable rrpp domain 2 control-vlan 10 protected-vlan reference-instance 2 ring 1 node-mode transit primary-port GigabitEthernet0/0/1 secondary-port GigabitEthernet0/0/2 level 0 ring 1 enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk undo port trunk allow-pass vlan 1 port trunk allow-pass vlan 5 to 6 10 to 11 100 to 300 stp disable # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type trunk undo port trunk allow-pass vlan 1 port trunk allow-pass vlan 5 to 6 10 to 11 100 to 300 stp disable # return
UPEB configuration file
# sysname UPEB # vlan batch 5 to 6 10 to 11 100 to 300 # rrpp enable # stp region-configuration instance 1 vlan 5 to 6 100 to 200 instance 2 vlan 10 to 11 201 to 300 active region-configuration # rrpp domain 1 control-vlan 5 protected-vlan reference-instance 1 ring 1 node-mode transit primary-port GigabitEthernet0/0/1 secondary-port GigabitEthernet0/0/2 level 0 ring 1 enable rrpp domain 2 control-vlan 10 protected-vlan reference-instance 2 ring 1 node-mode transit primary-port GigabitEthernet0/0/1 secondary-port GigabitEthernet0/0/2 level 0 ring 1 enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk undo port trunk allow-pass vlan 1 port trunk allow-pass vlan 5 to 6 10 to 11 100 to 300 stp disable # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type trunk undo port trunk allow-pass vlan 1 port trunk allow-pass vlan 5 to 6 10 to 11 100 to 300 stp disable # return
UPEC configuration file
# sysname UPEC # vlan batch 5 to 6 10 to 11 100 to 300 # rrpp enable # stp region-configuration instance 1 vlan 5 to 6 100 to 200 instance 2 vlan 10 to 11 201 to 300 active region-configuration # rrpp domain 1 control-vlan 5 protected-vlan reference-instance 1 ring 1 node-mode transit primary-port GigabitEthernet0/0/1 secondary-port GigabitEthernet0/0/2 level 0 ring 1 enable rrpp domain 2 control-vlan 10 protected-vlan reference-instance 2 ring 1 node-mode transit primary-port GigabitEthernet0/0/1 secondary-port GigabitEthernet0/0/2 level 0 ring 1 enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk undo port trunk allow-pass vlan 1 port trunk allow-pass vlan 5 to 6 10 to 11 100 to 300 stp disable # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type trunk undo port trunk allow-pass vlan 1 port trunk allow-pass vlan 5 to 6 10 to 11 100 to 300 stp disable # return
PEAGG configuration file
# sysname PEAGG # vlan batch 5 to 6 10 to 11 100 to 300 # rrpp enable # stp region-configuration instance 1 vlan 5 to 6 100 to 200 instance 2 vlan 10 to 11 201 to 300 active region-configuration # rrpp domain 1 control-vlan 5 protected-vlan reference-instance 1 ring 1 node-mode master primary-port GigabitEthernet0/0/1 secondary-port GigabitEthernet0/0/2 level 0 ring 1 enable rrpp domain 2 control-vlan 10 protected-vlan reference-instance 2 ring 1 node-mode master primary-port GigabitEthernet0/0/2 secondary-port GigabitEthernet0/0/1 level 0 ring 1 enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk undo port trunk allow-pass vlan 1 port trunk allow-pass vlan 5 to 6 10 to 11 100 to 300 stp disable # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type trunk undo port trunk allow-pass vlan 1 port trunk allow-pass vlan 5 to 6 10 to 11 100 to 300 stp disable # return