Example for Configuring MSTP
Overview
Generally, redundant links are used on an Ethernet switching network to provide link backup and enhance network reliability. The use of redundant links, however, may produce loops, causing broadcast storms and rendering the MAC address table unstable. As a result, the communication quality deteriorates, and communication services may be interrupted. The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is used to solve these problems. STP prevents loops. Devices running STP discover loops on the network by exchanging information with each other, and block some ports to eliminate loops.
STP refers to STP defined in IEEE 802.1D, the Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) defined in IEEE 802.1w, and the Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) defined in IEEE 802.1s.
Spanning Tree Protocol |
Characteristics |
Application Scenario |
|---|---|---|
STP |
User or service traffic does not need to be differentiated, and all VLANs share a spanning tree. |
|
RSTP |
|
|
MSTP |
|
User or service traffic needs to be differentiated and load balanced. Traffic from different VLANs is forwarded through different spanning trees that are independent of each other. |
Configuration Notes
- This example applies to all versions of all S series switches.
- The ports connected to terminals do not participate in MSTP calculation. Therefore, configure the ports as edge ports or disable STP on the ports.
Networking Requirements
To implement redundancy on a complex network, network designers tend to deploy multiple physical links between two devices, one of which is the primary link and the others are backup links. Loops may occur, causing broadcast storms or rendering the MAC address table unstable. MSTP can be used to prevent loops. MSTP blocks redundant links and prunes a network into a tree topology free from loops.
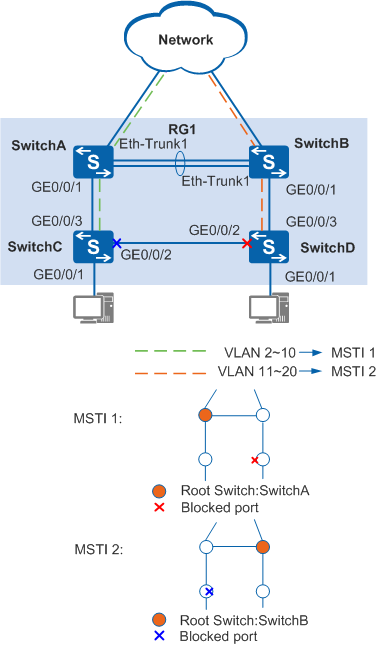
In Figure 1, SwitchA, SwitchB, SwitchC, and SwitchD run MSTP. MSTP uses multiple instances to implement load balancing of traffic in VLANs 2 to 10 and VLANs 11 to 20. The VLAN mapping table that defines the mapping between VLANs and MSTIs can be used.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure basic MSTP functions on switching devices of the ring network.
Enable protection functions to protect devices or links. For example, enable root protection on the designed port of the root bridge in each MSTI.

When the link between the root bridge and secondary root bridge goes Down, the port enabled with root protection becomes Discarding because root protection takes effect.
To improve reliability, you are advised to bind the link between the root bridge and secondary root bridge to an Eth-Trunk.
Configure Layer 2 forwarding on devices.
Procedure
- Configure basic MSTP functions.
Configure SwitchA, SwitchB, SwitchC, and SwitchD (access switches) in the MST region RG1 and create MSTI 1 and MSTI 2.
 Two switches belong to the same MST region when they have the same:
Two switches belong to the same MST region when they have the same:Name of the MST region
Mapping between VLANs and MSTIs
Revision level of the MST region
# Configure an MST region of root bridge SwitchA in MSTI 1.
<HUAWEI> system-view [HUAWEI] sysname SwitchA [SwitchA] stp region-configuration [SwitchA-mst-region] region-name RG1 //Configure the region name as RG1. [SwitchA-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 2 to 10 //Map VLANs 2 to 10 to MSTI 1. [SwitchA-mst-region] instance 2 vlan 11 to 20 //Map VLANs 11 to 20 to MSTI 2. [SwitchA-mst-region] active region-configuration //Activate the MST region configuration. [SwitchA-mst-region] quit
# Configure an MST region of root bridge SwitchB in MSTI 1.
<HUAWEI> system-view [HUAWEI] sysname SwitchB [SwitchB] stp region-configuration [SwitchB-mst-region] region-name RG1 //Configure the region name as RG1. [SwitchB-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 2 to 10 //Map VLANs 2 to 10 to MSTI 1. [SwitchB-mst-region] instance 2 vlan 11 to 20 //Map VLANs 11 to 20 to MSTI 2. [SwitchB-mst-region] active region-configuration //Activate the MST region configuration. [SwitchB-mst-region] quit
# Configure an MST region of SwitchC.
<HUAWEI> system-view [HUAWEI] sysname SwitchC [SwitchC] stp region-configuration [SwitchC-mst-region] region-name RG1 //Configure the region name as RG1. [SwitchC-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 2 to 10 //Map VLANs 2 to 10 to MSTI 1. [SwitchC-mst-region] instance 2 vlan 11 to 20 //Map VLANs 11 to 20 to MSTI 2. [SwitchC-mst-region] active region-configuration //Activate the MST region configuration. [SwitchC-mst-region] quit
# Configure an MST region of SwitchD.
<HUAWEI> system-view [HUAWEI] sysname SwitchD [SwitchD] stp region-configuration [SwitchD-mst-region] region-name RG1 //Configure the region name as RG1. [SwitchD-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 2 to 10 //Map VLANs 2 to 10 to MSTI 1. [SwitchD-mst-region] instance 2 vlan 11 to 20 //Map VLANs 11 to 20 to MSTI 2. [SwitchD-mst-region] active region-configuration //Activate the MST region configuration. [SwitchD-mst-region] quit
Configure root bridges and secondary root bridges of MSTI 1 and MSTI 2 in the MST region RG1.
Configure the root bridge and secondary root bridge in MSTI 1.
# Configure SwitchA as the root bridge in MSTI 1.
[SwitchA] stp instance 1 root primary
# Configure SwitchB as the secondary root bridge in MSTI 1.
[SwitchB] stp instance 1 root secondary
Configure the root bridge and secondary root bridge in MSTI 2.
# Configure SwitchB as the root bridge in MSTI 2.
[SwitchB] stp instance 2 root primary
# Configure SwitchA as the secondary root bridge in MSTI 2.
[SwitchA] stp instance 2 root secondary
Set the path costs of the ports to be blocked in MSTI 1 and MSTI 2 to be larger than the default values.

The path cost range depends on the algorithm. Huawei's proprietary algorithm is used as an example. Set the path costs of the ports to be blocked in MSTI 1 and MSTI 2 to 20000.
Switching devices on the same network must use the same algorithm to calculate the path cost of ports.
Configure SwitchA to use Huawei's proprietary algorithm to calculate the path cost.
[SwitchA] stp pathcost-standard legacy
# Configure SwitchB to use Huawei's proprietary algorithm to calculate the path cost.
[SwitchB] stp pathcost-standard legacy
# Configure SwitchC to use Huawei's proprietary algorithm to calculate the path cost and set the path cost of GE0/0/2 to 20000 in MSTI 2.
[SwitchC] stp pathcost-standard legacy [SwitchC] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/2 [SwitchC-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] stp instance 2 cost 20000 [SwitchC-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
# Configure SwitchD to use Huawei's proprietary algorithm to calculate the path cost and set the path cost of GE0/0/2 to 20000 in MSTI 1.
[SwitchD] stp pathcost-standard legacy [SwitchD] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/2 [SwitchD-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] stp instance 1 cost 20000 [SwitchD-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
Enable MSTP to eliminate loops.
Enable MSTP globally on devices.
[SwitchA] stp enable
# Enable MSTP on SwitchB.
[SwitchB] stp enable
# Enable MSTP on SwitchC.
[SwitchC] stp enable
# Enable MSTP on SwitchD.
[SwitchD] stp enable
Configure the ports connected to the terminal as edge ports.
# Configure GE0/0/1 of SwitchC as an edge port.
[SwitchC] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1 [SwitchC-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] stp edged-port enable [SwitchC-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
(Optional) Configure BPDU protection on SwitchC.
[SwitchC] stp bpdu-protection
# Configure GE0/0/1 of SwitchC as an edge port.
[SwitchD] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1 [SwitchD-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] stp edged-port enable [SwitchD-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
(Optional) Configure BPDU protection on SwitchD.
[SwitchD] stp bpdu-protection
 If edge ports are connected to network devices that have STP enabled and BPDU protection is enabled, the edge ports will be shut down and their attributes remain unchanged after they receive BPDUs.
If edge ports are connected to network devices that have STP enabled and BPDU protection is enabled, the edge ports will be shut down and their attributes remain unchanged after they receive BPDUs.
- Enable protection functions. For example, enable root protection
on the designed port of the root bridge in each MSTI.
# Enable root protection on GE0/0/1 of SwitchA.
[SwitchA] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1 [SwitchA-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] stp root-protection [SwitchA-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Enable root protection on GE0/0/1 of SwitchB.
[SwitchB] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1 [SwitchB-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] stp root-protection [SwitchB-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
- Configure Layer 2 forwarding on switches of the ring network.
Create VLANs 2 to 20 on SwitchA, SwitchB, SwitchC, and SwitchD.
# Create VLANs 2 to 20 on SwitchA.
[SwitchA] vlan batch 2 to 20
# Create VLANs 2 to 20 on SwitchB.
[SwitchB] vlan batch 2 to 20
# Create VLANs 2 to 20 on SwitchC.
[SwitchC] vlan batch 2 to 20
# Create VLANs 2 to 20 on SwitchD.
[SwitchD] vlan batch 2 to 20
Add ports connected to the ring to VLANs.
# Add GE0/0/1 on SwitchA to VLANs.
[SwitchA] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1 [SwitchA-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port link-type trunk [SwitchA-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 to 20 [SwitchA-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Add Eth-Trunk1 on SwitchA to VLANs.
[SwitchA] interface Eth-Trunk 1 [SwitchA-Eth-Trunk1] trunkport gigabitethernet 0/0/2 [SwitchA-Eth-Trunk1] trunkport gigabitethernet 0/0/3 [SwitchA-Eth-Trunk1] port link-type trunk [SwitchA-Eth-Trunk1] port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 to 20 [SwitchA-Eth-Trunk1] quit
# Add GE0/0/1 on SwitchB to VLANs.
[SwitchB] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1 [SwitchB-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port link-type trunk [SwitchB-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 to 20 [SwitchB-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Add Eth-Trunk1 on SwitchB to VLANs.
[SwitchB] interface Eth-Trunk 1 [SwitchB-Eth-Trunk1] trunkport gigabitethernet 0/0/2 [SwitchB-Eth-Trunk1] trunkport gigabitethernet 0/0/3 [SwitchB-Eth-Trunk1] port link-type trunk [SwitchB-Eth-Trunk1] port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 to 20 [SwitchB-Eth-Trunk1] quit
# Add GE0/0/1 on SwitchC to VLANs.
[SwitchC] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1 [SwitchC-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port link-type access [SwitchC-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port default vlan 2 [SwitchC-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Add GE0/0/2 on SwitchC to VLANs.
[SwitchC] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/2 [SwitchC-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port link-type trunk [SwitchC-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 to 20 [SwitchC-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
# Add GE0/0/3 on SwitchC to VLANs.
[SwitchC] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/3 [SwitchC-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] port link-type trunk [SwitchC-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 to 20 [SwitchC-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] quit
# Add GE0/0/1 on SwitchD to VLANs.
[SwitchD] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1 [SwitchD-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port link-type access [SwitchD-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port default vlan 11 [SwitchD-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Add GE0/0/2 on SwitchD to VLANs.
[SwitchD] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/2 [SwitchD-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port link-type trunk [SwitchD-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 to 20 [SwitchD-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
# Add GE0/0/3 on SwitchD to VLANs.
[SwitchD] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/3 [SwitchD-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] port link-type trunk [SwitchD-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 to 20 [SwitchD-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] quit
- Verify the configuration.
After the configuration is complete and the network topology becomes stable, perform the following operations to verify the configuration.

MSTI 1 and MSTI 2 are used as examples, so you do not need to check the port status in MSTI 0.
# Run the display stp brief command on SwitchA to view the port status and protection type. The displayed information is as follows:
[SwitchA] display stp brief MSTID Port Role STP State Protection 0 GigabitEthernet0/0/1 DESI FORWARDING ROOT 0 Eth-Trunk1 DESI FORWARDING NONE 1 GigabitEthernet0/0/1 DESI FORWARDING ROOT 1 Eth-Trunk1 DESI FORWARDING NONE 2 GigabitEthernet0/0/1 DESI FORWARDING ROOT 2 Eth-Trunk1 ROOT FORWARDING NONE
In MSTI 1, Eth-Trunk1 and GE0/0/1 on SwitchA are designed ports because SwitchA is the root bridge. In MSTI 2, GE0/0/1 on SwitchA is the designed port and Eth-Trunk1 is the root port.
# Run the display stp brief command on SwitchB. The following information is displayed:
[SwitchB] display stp brief MSTID Port Role STP State Protection 0 GigabitEthernet0/0/1 DESI FORWARDING ROOT 0 Eth-Trunk1 ROOT FORWARDING NONE 1 GigabitEthernet0/0/1 DESI FORWARDING ROOT 1 Eth-Trunk1 ROOT FORWARDING NONE 2 GigabitEthernet0/0/1 DESI FORWARDING ROOT 2 Eth-Trunk1 DESI FORWARDING NONE
In MSTI 2, GE0/0/1 and Eth-Trunk1 on SwitchB are designed ports because SwitchB is the root bridge. In MSTI 1, GE0/0/1 on SwitchB is the designed port and Eth-Trunk1 is the root port.
# Run the display stp interface brief command on SwitchC. The following information is displayed:
[SwitchC] display stp interface gigabitethernet 0/0/3 brief MSTID Port Role STP State Protection 0 GigabitEthernet0/0/3 ROOT FORWARDING NONE 1 GigabitEthernet0/0/3 ROOT FORWARDING NONE 2 GigabitEthernet0/0/3 ROOT FORWARDING NONE
[SwitchC] display stp interface gigabitethernet 0/0/2 brief MSTID Port Role STP State Protection 0 GigabitEthernet0/0/2 DESI FORWARDING NONE 1 GigabitEthernet0/0/2 DESI FORWARDING NONE 2 GigabitEthernet0/0/2 ALTE DISCARDING NONE
GE0/0/3 on SwitchC is the root port in MSTI 1 and MSTI 2. GE0/0/2 on SwitchC is blocked in MSTI 2 and is the designated port in MSTI 1.
# Run the display stp interface brief command on SwitchD. The following information is displayed:
[SwitchD] display stp interface gigabitethernet 0/0/3 brief MSTID Port Role STP State Protection 0 GigabitEthernet0/0/3 ROOT FORWARDING NONE 1 GigabitEthernet0/0/3 ROOT FORWARDING NONE 2 GigabitEthernet0/0/3 ROOT FORWARDING NONE
[SwitchD] display stp interface gigabitethernet 0/0/2 brief MSTID Port Role STP State Protection 0 GigabitEthernet0/0/2 ALTE DISCARDING NONE 1 GigabitEthernet0/0/2 ALTE DISCARDING NONE 2 GigabitEthernet0/0/2 DESI FORWARDING NONE
GE0/0/3 on SwitchD is the root port in MSTI 1 and MSTI 2. GE0/0/2 on SwitchD is blocked in MSTI 1 and is the designated port in MSTI 2.
Configuration Files
SwitchA configuration file
# sysname SwitchA # vlan batch 2 to 20 # stp instance 1 root primary stp instance 2 root secondary stp pathcost-standard legacy # stp region-configuration region-name RG1 instance 1 vlan 2 to 10 instance 2 vlan 11 to 20 active region-configuration # interface Eth-Trunk1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 to 20 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 to 20 stp root-protection # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 eth-trunk 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/3 eth-trunk 1 # return
SwitchB configuration file
# sysname SwitchB # vlan batch 2 to 20 # stp instance 1 root secondary stp instance 2 root primary stp pathcost-standard legacy # stp region-configuration region-name RG1 instance 1 vlan 2 to 10 instance 2 vlan 11 to 20 active region-configuration # interface Eth-Trunk1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 to 20 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 to 20 stp root-protection # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 eth-trunk 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/3 eth-trunk 1 # return
SwitchC configuration file
# sysname SwitchC # vlan batch 2 to 20 # stp bpdu-protection stp pathcost-standard legacy # stp region-configuration region-name RG1 instance 1 vlan 2 to 10 instance 2 vlan 11 to 20 active region-configuration # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type access port default vlan 2 stp edged-port enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 to 20 stp instance 2 cost 20000 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/3 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 to 20 # return
SwitchD configuration file
# sysname SwitchD # vlan batch 2 to 20 # stp bpdu-protection stp pathcost-standard legacy # stp region-configuration region-name RG1 instance 1 vlan 2 to 10 instance 2 vlan 11 to 20 active region-configuration # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type access port default vlan 11 stp edged-port enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 to 20 stp instance 1 cost 20000 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/3 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 to 20 # return