Overview of VLAN Aggregation
Definition
VLAN aggregation, also called super-VLAN, partitions a broadcast domain on a physical network into multiple VLANs (sub-VLANs) and aggregates them into a single logical VLAN (super-VLAN). The sub-VLANs are addressed from the same IP subnet and share a default gateway address, thereby reducing the number of IP addresses required on the network.
Purpose
VLAN technology is commonly used on packet-switched networks because it facilitates network design. For example, it can split a large broadcast domain into smaller ones, group hosts together regardless of their location, and separate hosts, resources, and traffic. However, communication between hosts in different broadcast domains typically requires a Layer 3 switch to be configured with a Layer 3 logical interface per VLAN. This wastes IP addresses because each VLAN requires a unique subnet ID, directed broadcast address, and subnet default gateway address, none of which can be assigned as a host's IP address. In addition, the IP address block allocated to a VLAN may contain more IP addresses than required. Unused IP addresses in one VLAN cannot be used in other VLANs.
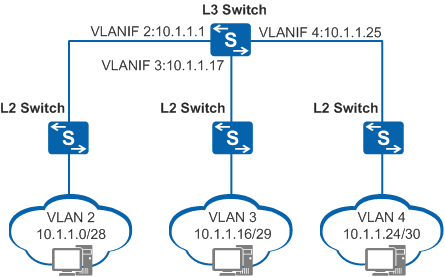
Consider the following example. In Figure 1, VLAN 2 contains 10 hosts. The VLAN is assigned the subnet 10.1.1.0/28, which provides 16 IP addresses. Of these addresses, 10.1.1.0 is the subnet ID, 10.1.1.15 is the directed broadcast address, and 10.1.1.1 is the default gateway address. The remaining 13 IP addresses are available for the 10 hosts, leaving three wasted IP addresses that cannot be used in other VLANs.
At least three IP addresses are wasted for VLAN 2, and at least nine IP addresses are wasted for three VLANs. Although VLAN 2 requires only 10 IP addresses, the remaining 3 IP addresses cannot be used by other VLANs and are wasted. If more VLANs are added, the problem is exacerbated.
To solve the preceding problem, VLAN aggregation can be used. VLAN aggregation maps each sub-VLAN to a broadcast domain, associates a super-VLAN with multiple sub-VLANs, and assigns only one IP subnet to the super-VLAN. Consequently, the gateway IP address of all sub-VLANs is the IP address of the associated super-VLAN.
By sharing the gateway address, the number of subnet IDs, subnet default gateway addresses, and directed broadcast IP addresses used is reduced. The switch assigns IP addresses to hosts in sub-VLANs according to the number of hosts. This ensures that each sub-VLAN acts as an independent broadcast domain, conserves IP addresses, and implements flexible addressing.