Application Scenarios for VBST
To improve reliability of an enterprise network, access switches often connect to aggregation switches in dual-homing or multi-homing mode networking. In such networking, one link is the active link, and other links are standby links. When multiple links are used, loops may occur. As a result, broadcast storms occur and MAC address entries are damaged. In addition, one access switch often needs to transmit services from different VLANs.
Deploying MSTP can eliminate loops and load balance traffic from different VLANs, whereas it is difficult to configure and maintain MSTP multi-instance and multi-process.
You can deploy VBST. VBST constructs a spanning tree in each VLAN so that traffic from different VLANs is forwarded through different spanning trees. This eliminates loops and implements load balancing of traffic. In addition, VBST is easy to configure and maintain.
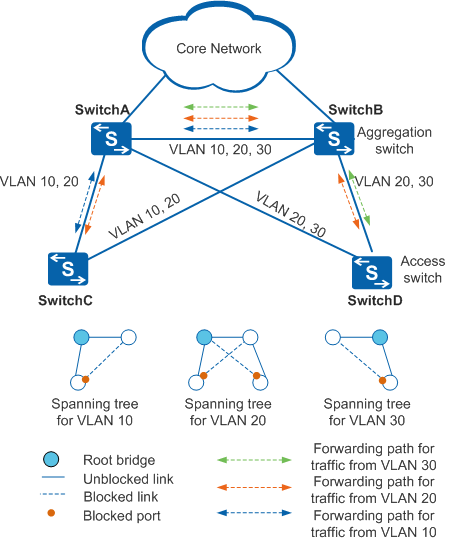
As shown in Figure 1, SwitchC and SwitchD are access switches; SwitchA and SwitchB are aggregation switches. SwitchC and SwitchD are dual-homed to SwitchA and SwitchB. To eliminate loops and load balance traffic from different VLANs, deploy VBST on SwitchA, SwitchB, SwitchC, and SwitchD. Configure SwitchA as the root bridge of VLAN 10 and VLAN 20 and SwitchB as the root bridge of VLAN 30.
Loops are eliminated based on VLANs. Figure 1 shows the formed spanning trees and forwarding paths. In Figure 1, traffic from VLAN 10, VLAN 20, and VLAN 30 is forwarded through their respective spanning trees. In this manner, traffic from VLAN 10, VLAN 20, and VLAN 30 is load balanced on paths SwitchC<->SwitchA, SwitchD<->SwitchA, and SwitchD<->SwitchB.