VLAN Assignment
VLAN Assignment Modes
VLANs can be assigned based on interfaces, MAC addresses, policies, IP subnets, and protocols. Table 1 compares different VLAN assignment modes.
VLAN Assignment Mode |
Implementation |
Advantage and Disadvantage |
Usage Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|
Interface-based VLAN assignment |
VLANs are assigned based on interfaces. A network administrator preconfigures a PVID for each interface on a switch. When an untagged frame arrives at an interface, the switch adds the PVID of the interface to the frame. The frame is then transmitted in the VLAN specified by the PVID. |
Advantage: It is simple to define VLAN members. Disadvantage: The network administrator needs to reconfigure VLANs when VLAN members change. |
Networks of any scale and with devices at fixed locations |
MAC address-based assignment |
VLANs are assigned based on source MAC addresses of frames. A network administrator preconfigures mappings between MAC addresses and VLAN IDs. When receiving an untagged frame, the switch adds the VLAN tag mapping the MAC address of the frame to the frame. Then the frame is transmitted in the specified VLAN. |
Advantage: When physical locations of users change, the network administrator does not need to reconfigure VLANs for the users. This improves security and access flexibility on a network. Disadvantage: The network administrator must predefine VLANs for all members on a network. |
Small-scale networks where user terminals often change physical locations but their NICs seldom change, for example, mobile computers |
IP subnet-based VLAN assignment |
VLANs are assigned based on source IP addresses and subnet masks. A network administrator preconfigures mappings between IP addresses and VLAN IDs. When receiving an untagged frame, the switch adds the VLAN tag to the frame according to the preconfigured mappings. Then the frame is transmitted in the specified VLAN. |
Advantage:
Disadvantage: Users must be distributed regularly and multiple users are on the same network segment. |
Scenarios where there are high requirements for mobility and simplified management and low requirements for security. For example, this mode can be used if a PC with multiple IP addresses needs to access servers on different network segments or a PC needs to join a new VLAN automatically after the PC's IP address changes. |
Protocol-based VLAN assignment |
VLANs are assigned based on protocol (suite) types and encapsulation formats of frames. A network administrator preconfigures mappings between protocol types and VLAN IDs. When receiving an untagged frame, the switch adds the VLAN tag to the frame according to the preconfigured mappings. The frame is then transmitted in the specified VLAN. |
Advantage: This mode binds service types to VLANs, facilitating management and maintenance. Disadvantage:
|
Networks using multiple protocols |
Policy-based VLAN assignment (MAC addresses, IP addresses, and interfaces) |
VLANs are assigned based on policies such as combinations of interfaces, MAC addresses, and IP addresses. A network administrator preconfigures policies. When receiving an untagged frame that matches a configured policy, the switch adds a specified VLAN tag to the frame. The frame is then transmitted in the specified VLAN. |
Advantage:
Disadvantage: Each policy needs to be manually configured. |
Complex networks |
Priorities of VLAN Assignment Modes
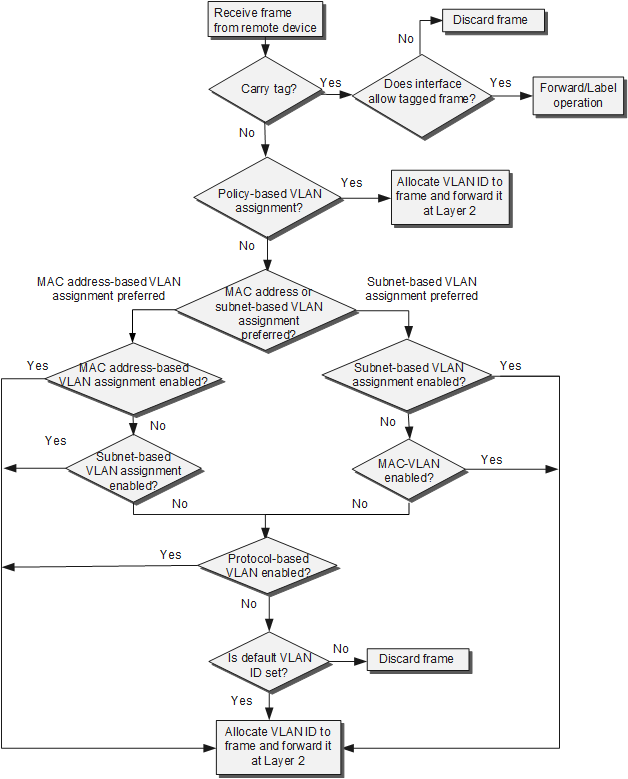
If incoming untagged frames match multiple VLAN assignment modes, the VLAN assignment modes are selected in the following order of priority (from high to low): policy-based VLAN assignment > MAC address-based or IP subnet-based VLAN assignment > protocol-based VLAN assignment > interface-based VLAN assignment.
If frames match both MAC address-based and IP subnet-based VLAN assignment modes, MAC address-based VLAN assignment is used by default. You can change priorities of the two VLAN assignment modes to select a preferred VLAN assignment mode for packets.
Interface-based VLAN assignment has the lowest priority but is the most commonly used.
Figure 1 illustrates the matching sequence of VLAN assignment modes.