Example for Configuring Band Steering
Configuration Process
You need to configure and maintain WLAN features and functions in different profiles. These WLAN profiles include regulatory domain profile, radio profile, VAP profile, AP system profile, AP wired port profile, WIDS profile, WDS profile, and Mesh profile. When configuring WLAN services, you need to set related parameters in the WLAN profiles and bind the profiles to the AP group or APs. Then the configuration is automatically delivered to and takes effect on the APs. WLAN profiles can reference one another; therefore, you need to know the relationships among the profiles before configuring them. For details about the profile relationships and their basic configuration procedure, see WLAN Service Configuration Procedure.
Networking Requirements
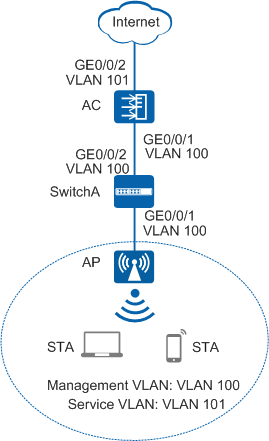
As shown in Figure 1, 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz wireless networks are deployed in the conference hall. An AP works on dual frequency bands and directly connects to an AC. STAs connected to the AP support both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands.
To improve user experience and reduce burden on the 2.4 GHz frequency band, the customer requires that STAs preferentially connect to the 5 GHz frequency band.
Configuration Roadmap
- Configure the AP, AC, switch, and upper-layer devices to communicate at Layer 2.
- Configure the AC as a DHCP server to assign IP addresses to the STAs and AP.
- Configure the AP to go online.
- Create an AP group for unified configuration. The APs that require the same configuration can be added to the group.
- Configure AC system parameters, including the country code and source interface used by the AC to communicate with the AP.
- Configure the AP authentication mode and import the AP offline so that the AP can go online properly.
- Configure WLAN service parameters for STAs to access the WLAN.
- Configure the band steering function and proper band steering parameters so that STAs can preferentially access the 5 GHz frequency band.
Item |
Data |
|---|---|
DHCP server |
The AC functions as a DHCP server to assign IP addresses to the STAs and AP. |
IP address pool for the AP |
10.23.100.2-10.23.100.254/24 |
IP address pool for the STAs |
10.23.101.2-10.23.101.254/24 |
AC's source interface address |
VLANIF 100: 10.23.100.1/24 |
AP group |
|
Regulatory domain profile |
|
SSID profile |
|
Security profile |
|
VAP profile |
|
2G radio profile |
|
RRM profile |
Name: band-steer |
Configuration Notes
- No ACK mechanism is provided for multicast packet transmission on air interfaces. In addition, wireless links are unstable. To ensure stable transmission of multicast packets, they are usually sent at low rates. If a large number of such multicast packets are sent from the network side, the air interfaces may be congested. You are advised to configure multicast packet suppression to reduce impact of a large number of low-rate multicast packets on the wireless network. Exercise caution when configuring the rate limit; otherwise, the multicast services may be affected.
- In direct forwarding mode, you are advised to configure multicast packet suppression on switch interfaces connected to APs.
- In tunnel forwarding mode, you are advised to configure multicast packet suppression in traffic profiles of the AC.
Configure port isolation on the interfaces of the device directly connected to APs. If port isolation is not configured and direct forwarding is used, a large number of unnecessary broadcast packets may be generated in the VLAN, blocking the network and degrading user experience.
In tunnel forwarding mode, the management VLAN and service VLAN cannot be the same. Only packets from the management VLAN are transmitted between the AC and APs. Packets from the service VLAN are not allowed between the AC and APs.
Procedure
- Set the NAC mode to unified on the AC so that users can connect to the network properly.
<HUAWEI> system-view [HUAWEI] authentication unified-mode

If the NAC mode is changed from traditional to unified, the unified mode takes effect after you save the configuration and restart the device.
- Configure SwitchA and the AC so that the AP and AC can transmit CAPWAP packets.
# Add GE0/0/1 that connects SwitchA to the AP to management VLAN 100 and add GE0/0/2 that connects SwitchA to the AC to the same VLAN.
<HUAWEI> system-view [HUAWEI] sysname SwitchA [SwitchA] vlan batch 100 [SwitchA] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1 [SwitchA-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port link-type trunk [SwitchA-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port trunk pvid vlan 100 [SwitchA-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port trunk allow-pass vlan 100 [SwitchA-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit [SwitchA] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/2 [SwitchA-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port link-type trunk [SwitchA-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port trunk allow-pass vlan 100 [SwitchA-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
# Add GE0/0/1 that connects the AC to SwitchA to VLAN 100.
[HUAWEI] sysname AC [AC] vlan batch 100 101 [AC] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1 [AC-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port link-type trunk [AC-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port trunk allow-pass vlan 100 [AC-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
- Configure the AC to communicate with the upstream device.

Configure AC uplink interfaces to transparently transmit packets of service VLANs as required and communicate with the upstream device.
# Add AC uplink interface GE0/0/2 to service VLAN 101.
[AC] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/2 [AC-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port link-type trunk [AC-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port trunk allow-pass vlan 101 [AC-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
- Configure the AC as a DHCP server to allocate IP addresses to STAs and the AP.
# Configure the AC as the DHCP server to allocate an IP address to the AP from the IP address pool on VLANIF 100, and allocate IP addresses to STAs from the IP address pool on VLANIF 101.
 Configure the DNS server as required. The common methods are as follows:
Configure the DNS server as required. The common methods are as follows:- In interface address pool scenarios, run the dhcp server dns-list ip-address &<1-8> command in the VLANIF interface view.
- In global address pool scenarios, run the dns-list ip-address &<1-8> command in the IP address pool view.
[AC] dhcp enable [AC] interface vlanif 100 [AC-Vlanif100] ip address 10.23.100.1 24 [AC-Vlanif100] dhcp select interface [AC-Vlanif100] quit [AC] interface vlanif 101 [AC-Vlanif101] ip address 10.23.101.1 24 [AC-Vlanif101] dhcp select interface [AC-Vlanif101] quit
- Configure the AP to go online.
# Create an AP group and add the AP to the AP group.
[AC] wlan [AC-wlan-view] ap-group name ap-group1 [AC-wlan-ap-group-ap-group1] quit
# Create a regulatory domain profile, configure the AC country code in the profile, and apply the profile to the AP group.
[AC-wlan-view] regulatory-domain-profile name domain1 [AC-wlan-regulate-domain-domain1] country-code cn [AC-wlan-regulate-domain-domain1] quit [AC-wlan-view] ap-group name ap-group1 [AC-wlan-ap-group-ap-group1] regulatory-domain-profile domain1 Warning: Modifying the country code will clear channel, power and antenna gain configurations of the radio and reset the AP. Continue?[Y/N]:y [AC-wlan-ap-group-ap-group1] quit [AC-wlan-view] quit
# Configure the AC's source interface.
[AC] capwap source interface vlanif 100
# Import the AP offline on the AC and add the AP to AP group ap-group1. Assume that the AP's MAC address is 60de-4476-e360. Configure a name for the AP based on the AP's deployment location, so that you can know where the AP is deployed from its name. For example, name the AP area_1 if it is deployed in Area 1.
The default AP authentication mode is MAC address authentication. If the default settings are retained, you do not need to run the ap auth-mode mac-auth command.
In this example, the AP5030DN is used and has two radios: radio 0 (2.4 GHz radio) and radio 1 (5 GHz radio).
[AC] wlan [AC-wlan-view] ap auth-mode mac-auth [AC-wlan-view] ap-id 0 ap-mac 60de-4476-e360 [AC-wlan-ap-0] ap-name area_1 Warning: This operation may cause AP reset. Continue? [Y/N]:y [AC-wlan-ap-0] ap-group ap-group1 Warning: This operation may cause AP reset. If the country code changes, it will clear channel, power and antenna gain configuration s of the radio, Whether to continue? [Y/N]:y [AC-wlan-ap-0] quit
# After the AP is powered on, run the display ap all command to check the AP state. If the State field is displayed as nor, the AP goes online normally.
[AC-wlan-view] display ap all
Total AP information: nor : normal [1] Extrainfo : Extra information P : insufficient power supply -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ID MAC Name Group IP Type State STA Uptime ExtraInfo -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0 60de-4476-e360 area_1 ap-group1 10.23.100.254 AP5030DN nor 0 10S - -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Total: 1
- Configure WLAN service parameters.# Create security profile wlan-security and set the security policy in the profile.

In this example, the security policy is set to WPA2+PSK+AES and password to a1234567. In actual situations, the security policy must be configured according to service requirements.
[AC-wlan-view] security-profile name wlan-security [AC-wlan-sec-prof-wlan-security] security wpa2 psk pass-phrase a1234567 aes [AC-wlan-sec-prof-wlan-security] quit
# Create SSID profile wlan-ssid and set the SSID name to wlan-net.
[AC-wlan-view] ssid-profile name wlan-ssid [AC-wlan-ssid-prof-wlan-ssid] ssid wlan-net [AC-wlan-ssid-prof-wlan-ssid] quit
# Create VAP profile wlan-vap, set the data forwarding mode and service VLAN, and apply the security profile and SSID profile to the VAP profile.
[AC-wlan-view] vap-profile name wlan-vap [AC-wlan-vap-prof-wlan-vap] forward-mode tunnel [AC-wlan-vap-prof-wlan-vap] service-vlan vlan-id 101 [AC-wlan-vap-prof-wlan-vap] security-profile wlan-security [AC-wlan-vap-prof-wlan-vap] ssid-profile wlan-ssid [AC-wlan-vap-prof-wlan-vap] quit
# Bind VAP profile wlan-vap to the AP group and apply the profile to radio 0 and radio 1 of the AP.
[AC-wlan-view] ap-group name ap-group1 [AC-wlan-ap-group-ap-group1] vap-profile wlan-vap wlan 1 radio all [AC-wlan-ap-group-ap-group1] quit
- Configure the band steering function.# Enable the band steering function in the VAP profile wlan-vap. By default, the band steering function is enabled.

When band steering is enabled on one radio of an AP, the function takes effect on the SSID of the AP. If different VAP profiles are applied to two radios of the AP, you only need to enable the band steering function in the VAP profile of one radio.
[AC-wlan-view] vap-profile name wlan-vap [AC-wlan-vap-prof-wlan-vap] undo band-steer disable [AC-wlan-vap-prof-wlan-vap] quit
# Create the RRM profile band-steer and configure load balancing between radios in the profile to prevent heavy load on a single radio. The start threshold for load balancing between radios is 15, and the load difference threshold is 25%.
[AC-wlan-view] rrm-profile name band-steer [AC-wlan-rrm-prof-band-steer] band-steer balance start-threshold 15 [AC-wlan-rrm-prof-band-steer] band-steer balance gap-threshold 25 [AC-wlan-rrm-prof-band-steer] quit
# Create the 2G radio profile radio2g and bind the RRM profile band-steer to the 2G radio profile.
If different RRM profiles are bound to the 2G and 5G radio profiles and configured with different band steering parameters, parameters in the 2G radio profile preferentially take effect.
[AC-wlan-view] radio-2g-profile name radio2g [AC-wlan-radio-2g-prof-radio2g] rrm-profile band-steer [AC-wlan-radio-2g-prof-radio2g] quit
# Bind the 2G radio profile radio2g to the AP group ap-group1.
[AC-wlan-view] ap-group name ap-group1 [AC-wlan-ap-group-ap-group1] radio-2g-profile radio2g [AC-wlan-ap-group-ap-group1] quit
- Verify the configuration.
Connect STAs to the WLAN with SSID wlan-net and enter the password a1234567. Run the display station ssid wlan-net command on the AC. The command output shows that the STAs are connected to the WLAN wlan-net.
[AC-wlan-view] display station ssid wlan-net Rf/WLAN: Radio ID/WLAN ID Rx/Tx: link receive rate/link transmit rate(Mbps) --------------------------------------------------------------------------------- STA MAC AP ID Ap name Rf/WLAN Band Type Rx/Tx RSSI VLAN IP address --------------------------------------------------------------------------------- e019-1dc7-1e08 0 area_1 1/1 5G 11n 46/59 -68 101 10.23.101.254 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Total: 1 2.4G: 0 5G: 1
Run the display vap-profile name wlan-vap command on the AC. The command output shows that the band steering function is enabled in the VAP profile.
[AC-wlan-view] display vap-profile name wlan-vap -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ... Band steer : enable ... --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Run the display rrm-profile name band-steer command on the AC to check the band steering configuration.
[AC-wlan-view] display rrm-profile name band-steer ------------------------------------------------------------ ... Band balance start threshold : 15 Band balance gap threshold(%) : 25 ... ------------------------------------------------------------
- In the conference hall, most STAs connect to the 5 GHz frequency band, and users enjoy good service experience.
Configuration Files
- SwitchA configuration file
# sysname SwitchA # vlan batch 100 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk pvid vlan 100 port trunk allow-pass vlan 100 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 100 # return
AC configuration file
# sysname AC # vlan batch 100 to 101 # dhcp enable # interface Vlanif100 ip address 10.23.100.1 255.255.255.0 dhcp select interface # interface Vlanif101 ip address 10.23.101.1 255.255.255.0 dhcp select interface # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 100 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 101 # capwap source interface vlanif100 # wlan security-profile name wlan-security security wpa2 psk pass-phrase %^%#m"tz0f>~7.[`^6RWdzwCy16hJj/Mc!,}s`X*B]}A%^%# aes ssid-profile name wlan-ssid ssid wlan-net vap-profile name wlan-vap forward-mode tunnel service-vlan vlan-id 101 ssid-profile wlan-ssid security-profile wlan-security regulatory-domain-profile name domain1 rrm-profile name band-steer band-steer balance start-threshold 15 band-steer balance gap-threshold 25 radio-2g-profile name radio2g rrm-profile band-steer ap whitelist mac 60de-4476-e360 auto ap-group name ap-group1 regulatory-domain-profile domain1 radio 0 radio-2g-profile radio2g vap-profile wlan-vap wlan 1 radio 1 vap-profile wlan-vap wlan 1 ap-id 0 type-id 19 ap-mac 60de-4476-e360 ap-sn 210235554710CB000042 ap-name area_1 ap-group ap-group1 # return