Example for Configuring MAC Address Authentication to Control User Access
MAC Address Authentication Overview
As one of NAC authentication modes, MAC address authentication controls a user's network access rights based on the user's interface and MAC address. The user does not need to install any client software. MAC address authentication ensures security of enterprise intranets.
In MAC address authentication, client software does not need to be installed on user terminals, but MAC addresses must be registered on servers, resulting in complex management. Another two NAC authentication methods have their advantages and disadvantages: 802.1X authentication ensures high security, but it requires that 802.1X client software be installed on user terminals, causing inflexible network deployment. Portal authentication also does not require client software installation and provides flexible deployment, but it has low security.
MAC address authentication is applied to access authentication scenarios of dumb terminals such as printers and fax machines.
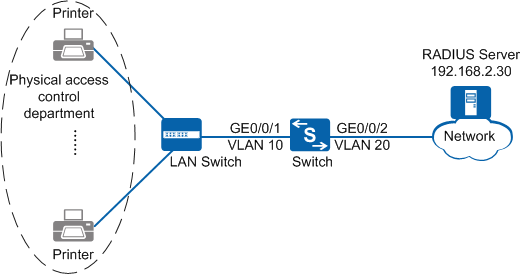
Networking Requirements
As shown in Figure 1, the terminals in the physical access control department are connected to the company's internal network through the Switch. Unauthorized access to the internal network can damage the company's service system and cause leakage of key information. Therefore, the administrator requires that the Switch should control the users' network access rights to ensure internal network security.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
- Create and configure a RADIUS server template, an AAA scheme, and an authentication domain. Bind the RADIUS server template and AAA scheme to the authentication domain so that the Switch can authenticate access users through the RADIUS server.
- Enable MAC address authentication so that the Switch can control network access rights of the dumb terminals in the physical access control department.

Before configuring this example, ensure that devices can communicate with each other on the network.
Procedure
- Create VLANs and configure the VLAN allowed by the interface to ensure network communication.
# Create VLAN 10 and VLAN 20.
<HUAWEI> system-view [HUAWEI] sysname Switch [Switch] vlan batch 10 20
# On the Switch, set GE0/0/1 connecting to users as an access interface, and add GE0/0/1 to VLAN 10.
[Switch] interface gigabitethernet0/0/1 [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port link-type access [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port default vlan 10 [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit

Configure the interface type and VLANs according to the actual situation. In this example, users are added to VLAN 10.
# On the Switch, set GE0/0/2 connecting to the RADIUS server as an access interface, and add GE0/0/2 to VLAN 20.
[Switch] interface gigabitethernet0/0/2 [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port link-type access [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port default vlan 20 [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit
- Create and configure a RADIUS server template, an AAA scheme, and an authentication domain.
# Create and configure the RADIUS server template rd1.
[Switch] radius-server template rd1 [Switch-radius-rd1] radius-server authentication 192.168.2.30 1812 [Switch-radius-rd1] radius-server shared-key cipher Huawei@2012 [Switch-radius-rd1] quit
# Create AAA scheme abc and set the authentication mode to RADIUS.
[Switch] aaa [Switch-aaa] authentication-scheme abc [Switch-aaa-authen-abc] authentication-mode radius [Switch-aaa-authen-abc] quit
# Create authentication domain isp1, and bind AAA scheme abc and RADIUS server template rd1 to authentication domain isp1.
[Switch-aaa] domain isp1 [Switch-aaa-domain-isp1] authentication-scheme abc [Switch-aaa-domain-isp1] radius-server rd1 [Switch-aaa-domain-isp1] quit [Switch-aaa] quit
# Configure the default domain isp1 in the system view. When a user enters the user name in the format of user@isp1, the user is authenticated in the authentication domain isp1. If the user name does not carry the domain name or carries a nonexistent domain name, the user is authenticated in the default domain.
[Switch] domain isp1 - Configure MAC address authentication.
# Switch the NAC mode to common mode. This step applies to only switches in V200R005C00 and later versions.
[Switch] undo authentication unified-mode Warning: Switching the authentication mode will take effect after system restart . Some configurations are invalid after the mode is switched. For the invalid co mmands, see the user manual. Save the configuration file and reboot now? [Y/N] y
- By default, the NAC unified mode is used.
- After the unified mode is switched to common mode, you must save the configuration and restart the device to make each function in the new configuration mode take effect. In versions earlier than V200R007C00, you need to manually run the commands for saving the configuration and restarting the device.
# Enable MAC address authentication globally and on the interface.
<Switch> system-view [Switch] mac-authen [Switch] interface gigabitethernet0/0/1 [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] mac-authen [Switch-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
- Verify the configuration.
- Run the display mac-authen command to check the MAC address authentication configuration. The command output (MAC address authentication is enabled) shows that MAC address authentication has been enabled on GE0/0/1.
- After the user starts the terminal, the device automatically obtains the terminal MAC address and uses it as the user name and password for authentication.
- The user can access the network after the authentication succeeds.
- After the user goes online, you can run the display access-user command on the device to check the online MAC address authentication user information.
Configuration Files
Configuration file of the Switch
# sysname Switch # vlan batch 10 20 # undo authentication unified-mode # domain isp1 # mac-authen # radius-server template rd1 radius-server shared-key cipher %^%#Q75cNQ6IF(e#L4WMxP~%^7'u17,]D87GO{"[o]`D%^%# radius-server authentication 192.168.2.30 1812 weight 80 # aaa authentication-scheme abc authentication-mode radius domain isp1 authentication-scheme abc radius-server rd1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type access port default vlan 10 mac-authen # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type access port default vlan 20 # return