Rate Limiting on ARP Miss Messages
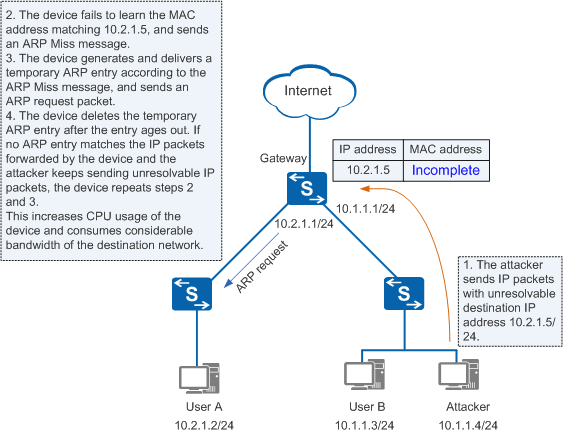
If a network device is flooded with IP packets that contain unresolvable destination IP addresses, the device generates a large number of ARP Miss messages. This is because the device has no ARP entry that matches the next hop of the route. IP packets (ARP Miss packets), which trigger ARP Miss messages, are sent to the control board for processing. The device generates and delivers many temporary ARP entries according to the ARP Miss messages, and sends a large number of ARP Request packets to the destination network. This increases CPU usage of the device and consumes considerable network bandwidth. As shown in Figure 1, the attacker sends IP packets with the unresolvable destination IP address 10.2.1.5/24 to the gateway.
To avoid the preceding problems, the device takes measures to limit the rate of ARP Miss messages.
Limiting the rate of ARP Miss messages based on source IP addresses
If the rate at which ARP Miss messages are sent from a source IP address exceeds the limit, the device considers that this address has initiated an attack.
If the ARP Miss message processing mode is set to block, the device discards excess ARP Miss packets and delivers an ACL to discard all subsequent packets sent from this source IP address. If the ARP Miss message processing mode is set to none-block, the device only discards excess ARP Miss packets.
If a source IP address is specified, the rate of ARP Miss messages triggered by IP packets from this source IP address is limited. If no source IP address is specified, the rate of ARP Miss messages triggered by IP packets from any source IP address is limited.
Limiting the rate of ARP Miss messages globally, in a VLAN, or on an interface
The maximum number of ARP Miss massages can be set globally, in a VLAN, or on an interface. The configurations on an interface, in a VLAN, and global configurations take effect in descending order of priority.
Limiting the rate of ARP Miss messages globally: limits the number of ARP Miss messages processed on the entire device.
Limiting the rate of ARP Miss messages in a VLAN: limits the number of ARP Miss messages processed on all interfaces in a VLAN. The configuration in a VLAN does not affect IP packet forwarding on interfaces in other VLANs.
Limiting the rate of ARP Miss messages on an interface: limits the number of ARP Miss messages processed on an interface. The configuration on an interface does not affect IP packet forwarding on other interfaces.
Limiting the rate of ARP Miss messages by setting the aging time of temporary ARP entries
When IP packets trigger ARP Miss messages, the device generates temporary ARP entries and sends ARP Request packets to the destination network.- In the aging time of temporary ARP entries:
- Before receiving an ARP reply packet, the device discards the IP packets matching the temporary ARP entry and does not generate ARP Miss messages.
- After receiving an ARP Reply packet, the device generates a correct ARP entry to replace the temporary entry.
- When temporary ARP entries age out, the device clears them. If no ARP entry matches the IP packets forwarded by the device, ARP Miss messages and temporary ARP entries are repeatedly generated.
When a device undergoes an ARP Miss attack, you can extend the aging time of temporary ARP entries and reduce the frequency of triggering ARP Miss messages to mitigate the impact on the device.
- In the aging time of temporary ARP entries: