Optimized ARP Reply
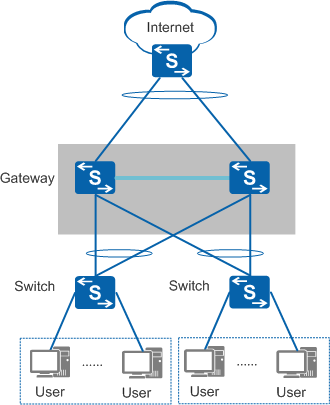
In Figure 1, when a stack of multiple switches functions as an access gateway, the stack can receive a large number of ARP packets requesting for the stack's interface MAC address. If all these ARP Request packets are sent to the master switch, the CPU usage of the master switch increases, and other services are affected.
To address the preceding problem, enable optimized ARP reply, which
improves the switch's capability of defending against ARP flood attack.
After this function is enabled, the stack performs the following operations:
- When receiving an ARP Request packet of which the destination IP address is the local interface address, the switch where the interface is located directly returns an ARP Reply packet.
- When a stack system receives an ARP Request packet of which the destination IP address is not the local interface address and intra-VLAN proxy ARP is enabled on the master switch, the switch where the interface is located checks whether the ARP Request packet meets the proxy condition. If so, the switch returns an ARP Reply packet. If not, the switch discards the packet.

The optimized ARP reply function can be configured
on a stand-alone fixed switch, but does not take effect.
By default, the optimized ARP reply function
is enabled. After a device receives an ARP Request packet, the device
checks whether an ARP entry corresponding to the source IP address
of the ARP Request packet exists.
- If there is a corresponding ARP entry, the stack performs optimized ARP reply to this ARP Request packet.
- If there is no corresponding ARP entry, the stack does not perform optimized ARP reply to this ARP Request packet.