IGMP Proxy
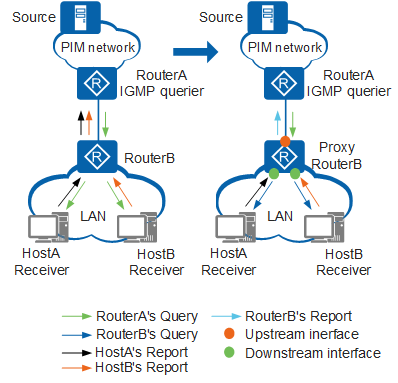
In a simple tree topology, as shown in the left half of Figure 1, RouterB directly connected to a user network segment does not need to run any complicated multicast routing protocol (such as PIM). However, RouterA has to manage many users because RouterB transparently transmit all IGMP messages from hosts to RouterA. When a large number of receiver hosts exist on the network or many hosts frequently join and leave groups, a lot of IGMP Report/Leave messages are sent to RouterA, greatly increasing loads on RouterA.
The preceding problem can be solved by configuring IGMP proxy on RouterB, as shown in the right half of Figure 1. IGMP proxy reduces loads on RouterA while ensuring normal forwarding of multicast messages.
IGMP proxy is deployed on a Layer 3 device (RouterB in Figure 1) between an access device (RouterA) and receiver hosts. On one hand, the IGMP proxy device collects and processes IGMP Report/Leave messages from downstream hosts before forwarding the messages to the upstream access device. On the other hand, the IGMP proxy device substitutes the IGMP querier to send Query messages to downstream hosts to maintain group memberships, and forwards multicast data to hosts based on the group memberships. In this example, RouterB is a host for RouterA and an IGMP querier for the hosts.
Upstream interface: an interface with IGMP proxy configured on the IGMP proxy device, which acts like a host. This interface is also called a host interface.
Downstream interface: an interface with IGMP configured on the IGMP proxy device, which acts like a multicast router. This interface is also called a router interface.
How IGMP Proxy Works
An IGMP proxy device performs two types of behaviors: host behaviors and router behaviors.
Host behavior
When an upstream interface of the IGMP proxy device receives a Query message, the IGMP proxy device responds with a Report message according to the multicast forwarding table. When the multicast forwarding table changes, the upstream interface sends Report/Leave messages to the access device. An IGMP proxy device performs host behaviors in the following ways:
- When an upstream interface of the IGMP proxy device receives a Query message, the IGMP proxy device responds with a Report message according to the multicast forwarding table.
- When the IGMP proxy device receives a Report message for a group,
it searches the multicast forwarding table for the group.
- If the group is not found in the multicast forwarding table, the IGMP proxy device sends a Report message for the group to the access device and adds the group to the multicast forwarding table.
- If the group is found in the multicast forwarding table, the IGMP proxy device does not send a Report message to the access device.
- When the IGMP proxy device receives a Leave message for a group,
it sends a Group-Specific Query message through the downstream interface
where the Leave message is received, to check whether this group has
other members attached to the interface.
- If there are no other members of this group attached to the interface, the IGMP proxy device deletes the interface from the forwarding entry of the group. The IGMP proxy device then checks whether the group has members on other interfaces. If so, the IGMP proxy device does not send a Leave message for this group to the access device. If not, the IGMP proxy device sends a Leave message for this group to the access device.
- If the group has other members attached to the interface, the IGMP proxy device continues forwarding multicast data to the interface.
Router behavior
An IGMP proxy device generates multicast forwarding entries according to Report/Leave messages received on downstream interfaces, receives multicast data from the upstream access device, and forwards multicast data to downstream interfaces specified in the matching multicast forwarding entries. An IGMP proxy device performs router behaviors in the same way as an IGMP router. For details, see IGMPv1 Fundamentals, Changes in IGMPv2, and Changes in IGMPv3.
Active/Standby and Active/Active Protection Mode
After enabling the IGMP proxy function on an upstream interface of an IGMP proxy device, you can configure an IGMP proxy interface protection mode to enhance link reliability. Two protection modes are supported:
- Active/standby mode: Enable IGMP proxy backup on another interface. This interface then acts as the backup IGMP proxy interface to protect the active IGMP proxy interface. If the active IGMP proxy interface fails, the upstream interface in multicast forwarding entries changes to the backup IGMP proxy interface to resume traffic forwarding quickly. When the active IGMP proxy interface recovers, the upstream interface in multicast forwarding entries restores to the active IGMP proxy interface.
- Active/active mode: Configure IGMP proxy on multiple interfaces so that these interfaces act as active IGMP proxy interfaces. Multicast forwarding entries are distributed on these interfaces based on the hash algorithm to implement multicast load splitting. The IGMP proxy device sends Join/Leave messages to all the active IGMP proxy interfaces. The interfaces back up one another. If one of them fails, the upstream interface in the matching entries changes to all the other active IGMP proxy interfaces to resume traffic forwarding quickly. When the faulty active IGMP proxy interface recovers, it becomes an upstream in multicast forwarding entries again and multiple interfaces share multicast traffic based on the hash algorithm. The switch supports a maximum of eight interfaces for multicast load splitting.
Automatic Switchback and Delayed Switchback
- Automatic switchback: Traffic is switched back immediately after the primary interface recovers.
- Delayed switchback: Traffic is not switched back immediately after the primary interface recovers. Instead, traffic switchback is performed after a delay, which prevents frequent traffic switchover and switchback in the case that the primary interface flaps. You can manually trigger traffic switchback before the delay expires.