Overview of Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling
Definition
Layer 2 protocol tunneling is a Layer 2 tunneling technology that transparently transmits BPDUs between private networks at different locations over a specified tunnel on a public Internet Service Provider (ISP) network.
Purpose
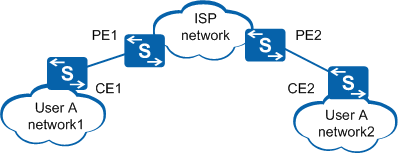
Leased lines of ISPs are often used to establish Layer 2 networks. As a result, private user networks can be located at two sides of ISP networks. In Figure 1, User A has two networks: network1 and network2. The two networks are connected through the ISP network. When network1 and network2 run the same Layer 2 protocol (such as MSTP), Layer 2 protocol packets from network1 and network2 must be transmitted through the ISP network to perform Layer 2 protocol calculation (for example, calculating a spanning tree). Generally, the destination MAC addresses in Layer 2 protocol packets of the same Layer 2 protocol are the same. For example, the MSTP PDUs are BPDUs with the destination MAC address 0180-C200-0000. Therefore, when a Layer 2 protocol packet reaches an edge device on the ISP network, the edge device cannot identify whether the Layer 2 protocol packet comes from a user network or the ISP network and sends the Layer 2 protocol packets to the CPU to calculate a spanning tree.
In Figure 1, devices on user network1 build a spanning tree together with PE1 but not with devices on user network2. As a result, the Layer 2 protocol packets on user network1 cannot traverse the ISP network to reach user network2.
- After receiving Layer 2 protocol packets sent from CE1, PE1 replaces the destination MAC address with a specified multicast MAC address. Then PE1 forwards the packets on the ISP network.
- Layer 2 protocol packets are forwarded to PE2. PE2 restores the original destination MAC address of the packets and sends them to CE2.
- Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
- Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)
- Ethernet Operation, Administration, and Maintenance 802.3ah (EOAM3ah)
- Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP)
- GARP VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP)
- GARP Multicast Registration Protocol (GMRP)
- HUAWEI Group Management Protocol (HGMP)
- VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP)
- Unidirectional Link Detection (UDLD)
- Port Aggregation Protocol (PAGP)
- Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP)
- Per VLAN Spanning Tree Plus (PVST+)
- Shared Spanning Tree Protocol (SSTP)
- Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP)
- Device Link Detection Protocol (DLDP)
- Ethernet Synchronization Message Channel (ESMC)
- User-defined protocols