Multicast Deployment on an IPv6 Network
This section describes typical multicast service scenarios on an IPv6 network and applications of multicast protocols. Configure multicast services based on the actual situations and service requirements on your network. This section provides only deployment of basic multicast services.
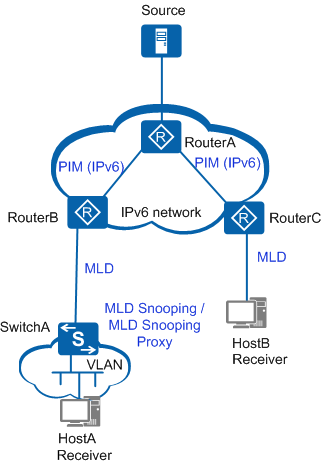
Before deploying IPv6 multicast services on a network, ensure that IPv6 unicast routes on the network are reachable.
Protocol |
Application Position |
Purpose |
|---|---|---|
IPv6 PIM (mandatory) |
IPv6 PIM must be configured on all interfaces of Layer 3 multicast devices, including all interfaces of RouterA, RouterB, and RouterC. For the configuration procedure, see IPv6 PIM Configuration. |
IPv6 PIM sends multicast data from the multicast source to RouterB and RouterC, which are connected to multicast receivers. |
MLD (mandatory) |
MLD must be configured on user-side interfaces of Layer 3 multicast devices RouterB and RouterC. For the configuration procedure, see MLD Configuration. |
MLD allows receiver hosts to join or leave multicast groups, and allows RouterB and RouterC to maintain and manage group memberships. |
MLD snooping and MLD snooping proxy (optional) |
MLD snooping and MLD snooping proxy must be configured on SwitchA, a Layer 2 device located between a Layer 3 multicast device and Host A. For the configuration procedure, see MLD Snooping Configuration. |
MLD snooping listens to MLD packets exchanged between RouterB and hosts to create and maintain a Layer 2 multicast forwarding table. In this manner, SwitchA can control forwarding of multicast data packets on the Layer 2 network. With the MLD snooping proxy function, SwitchA can act in place of RouterB to send MLD Query messages to Host A, and in place of Host A to send MLD Report/Done messages to SwitchB. |